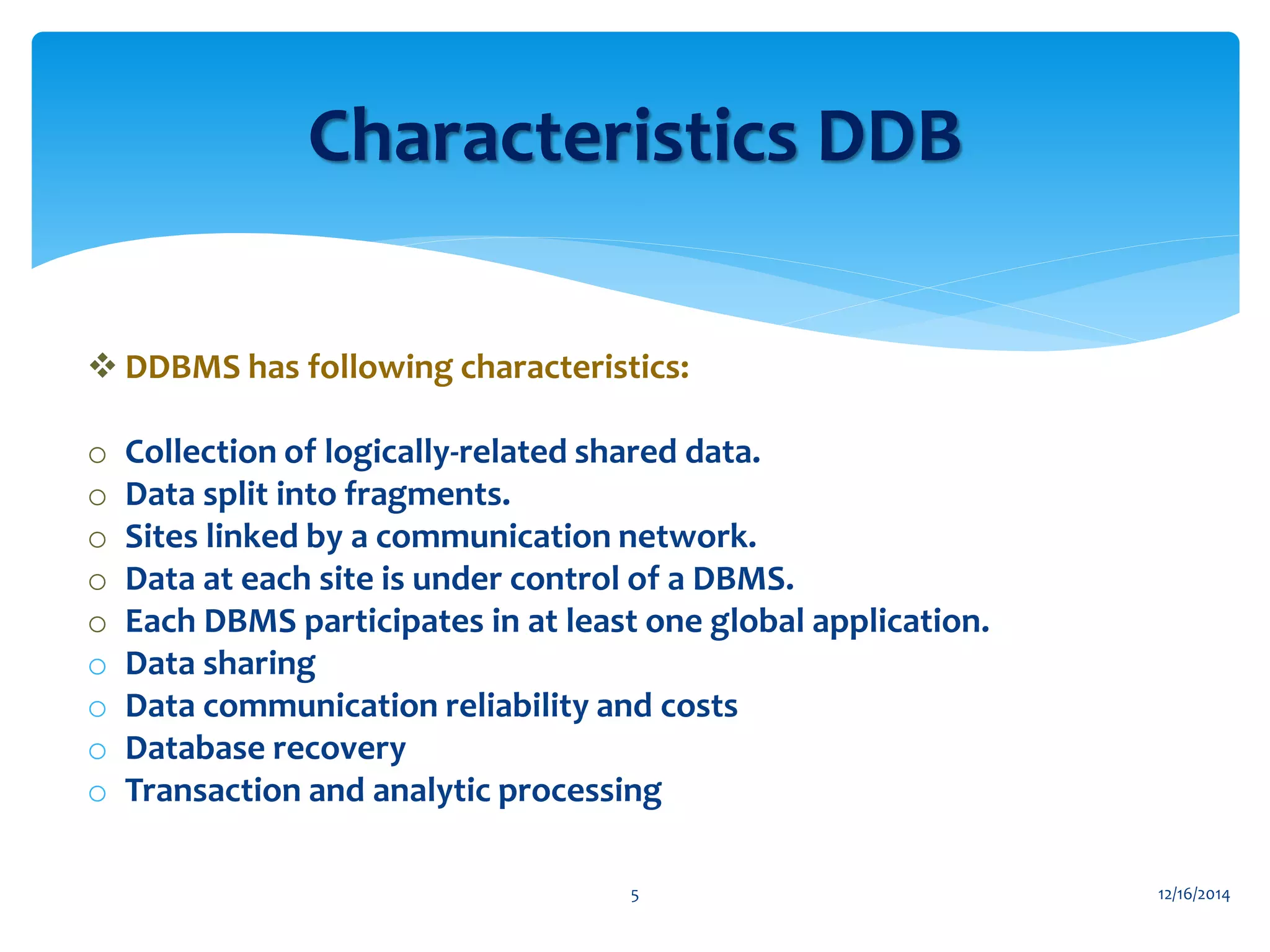
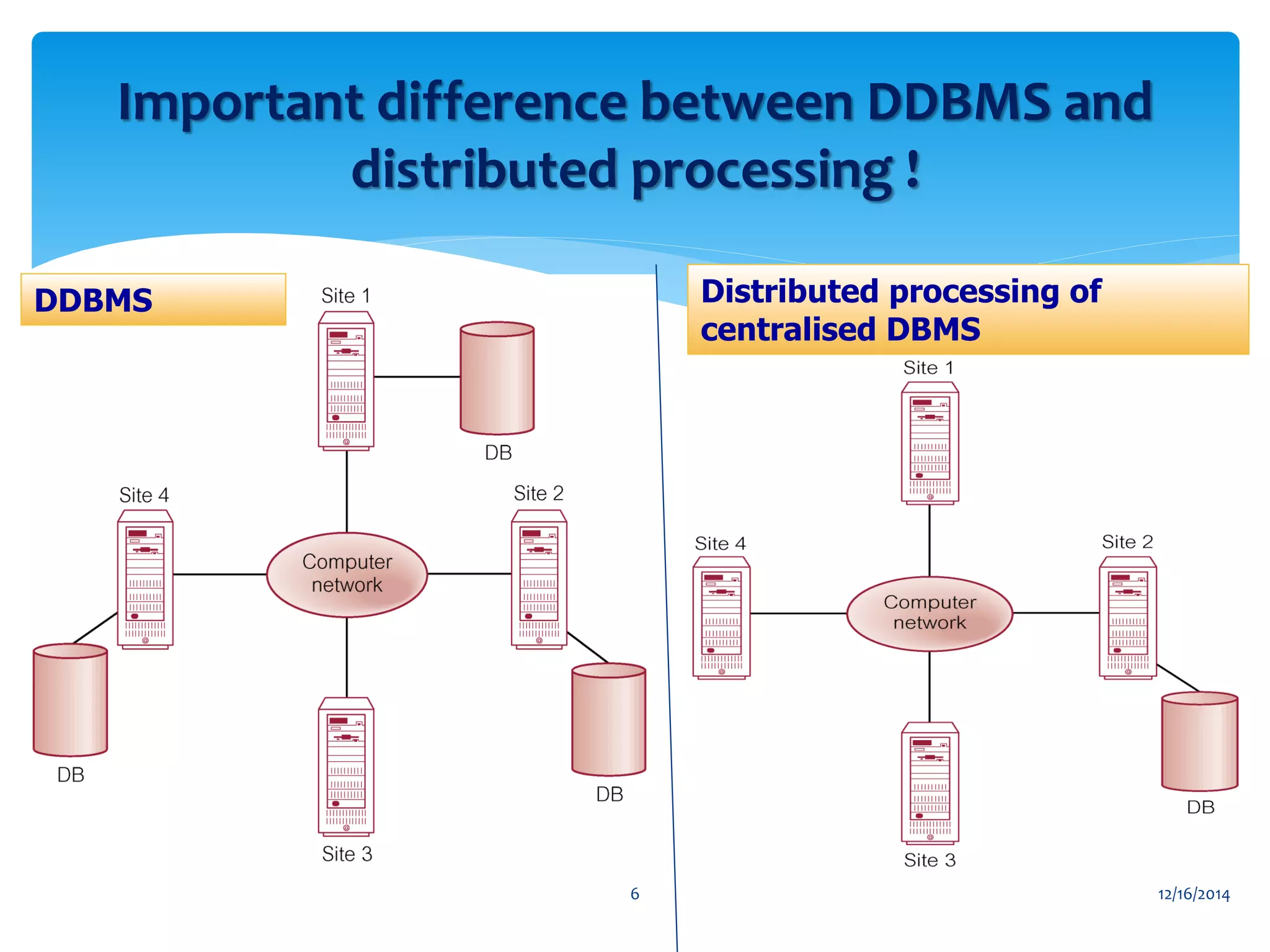
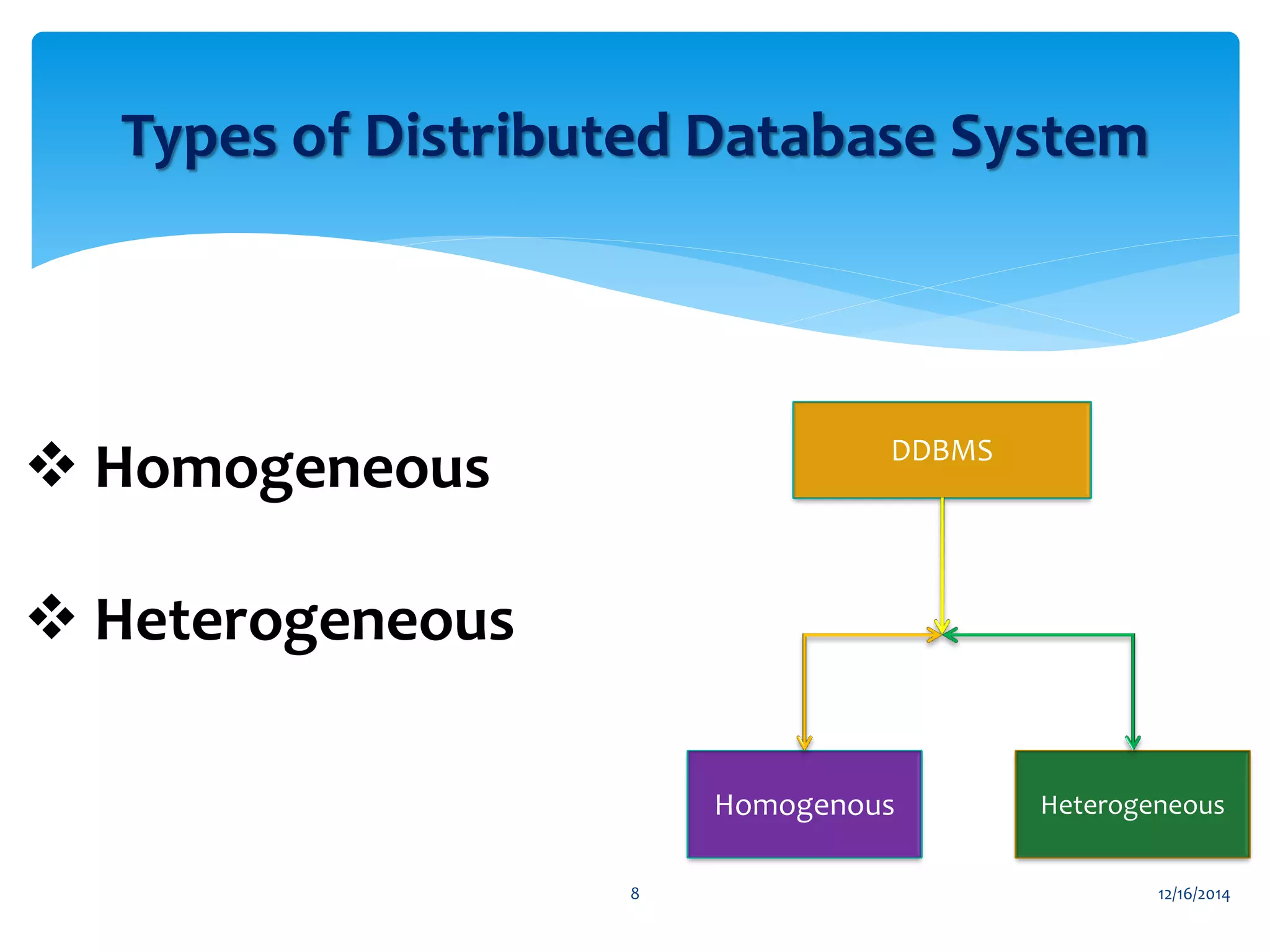
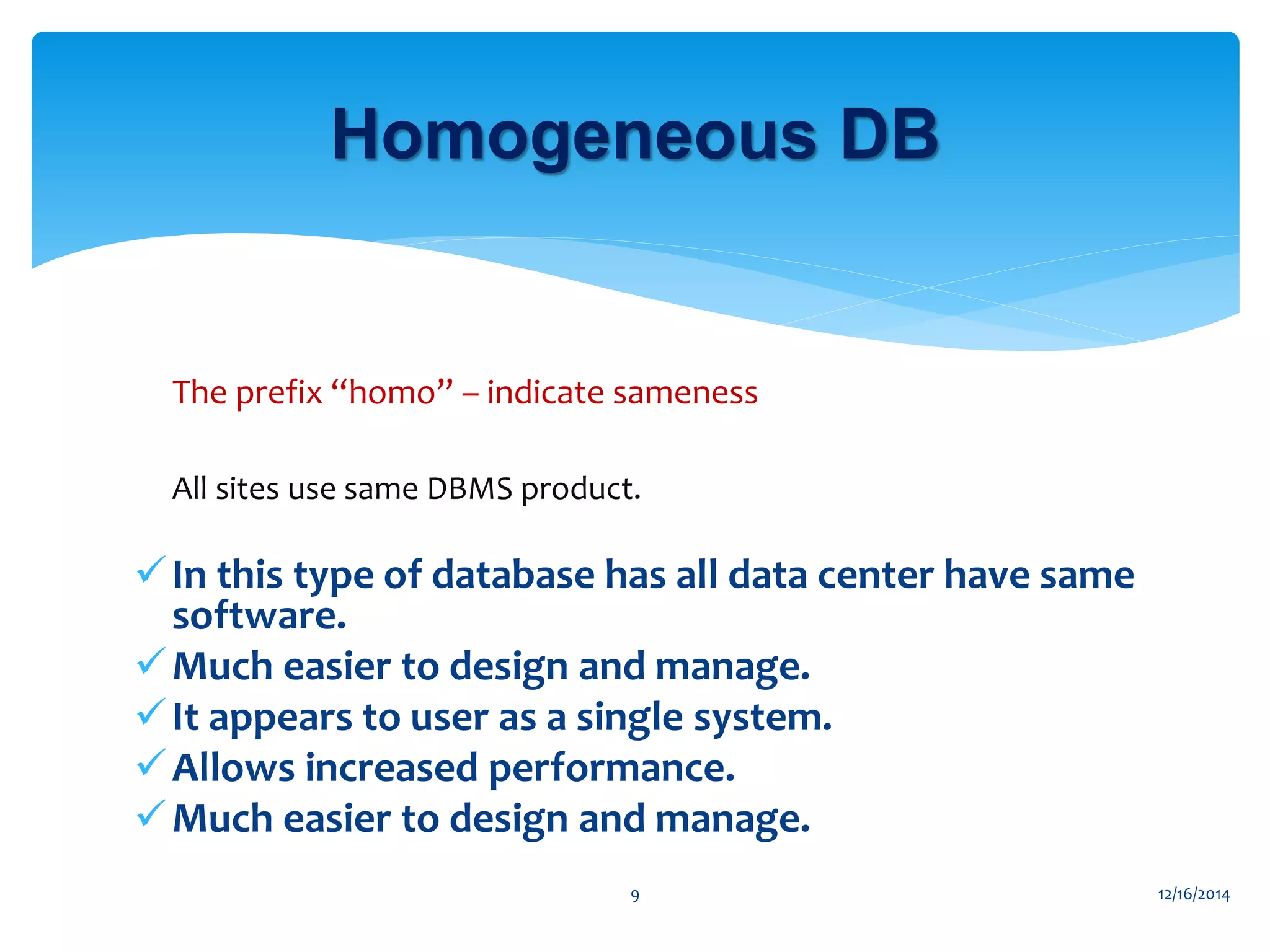
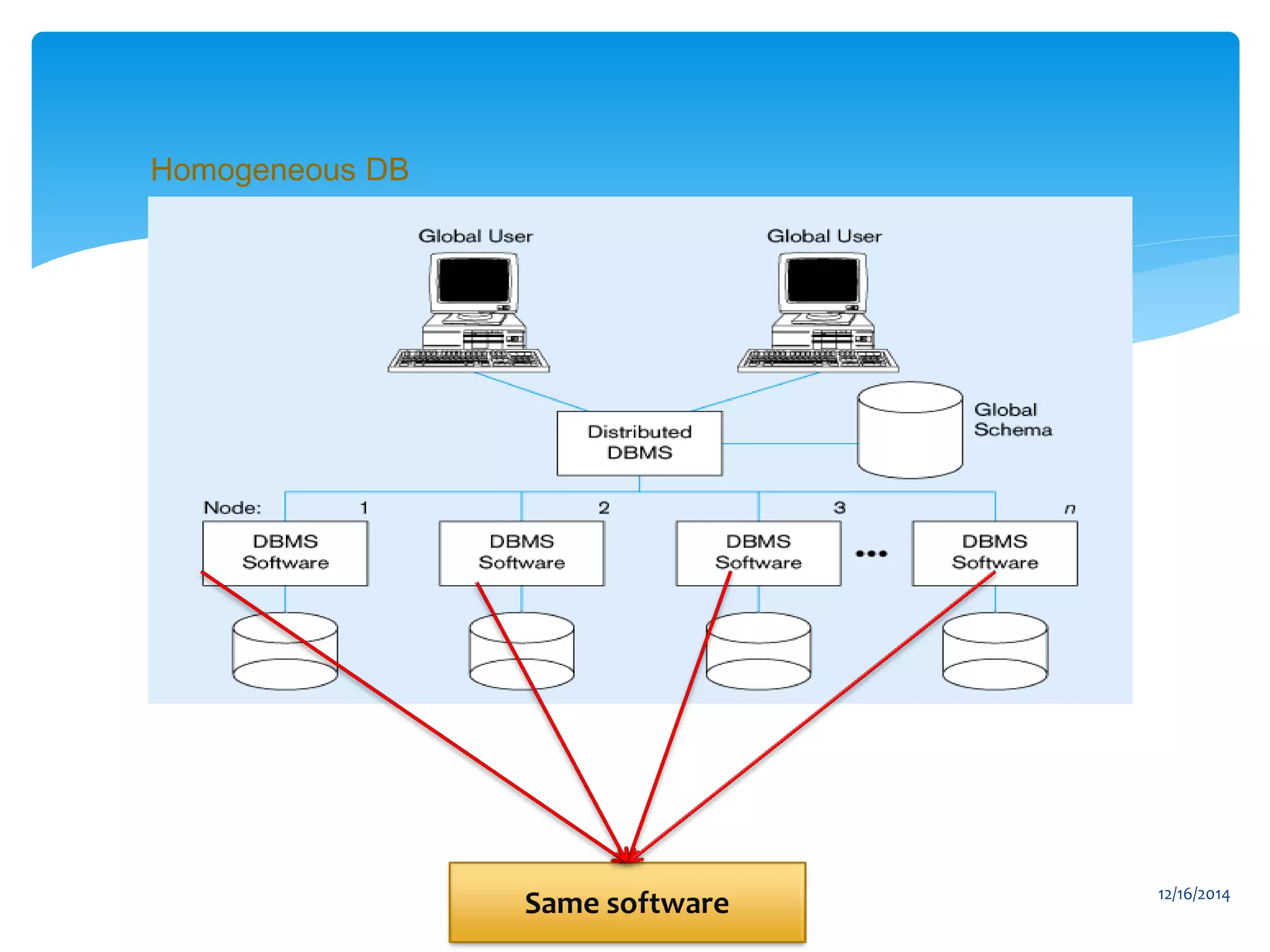
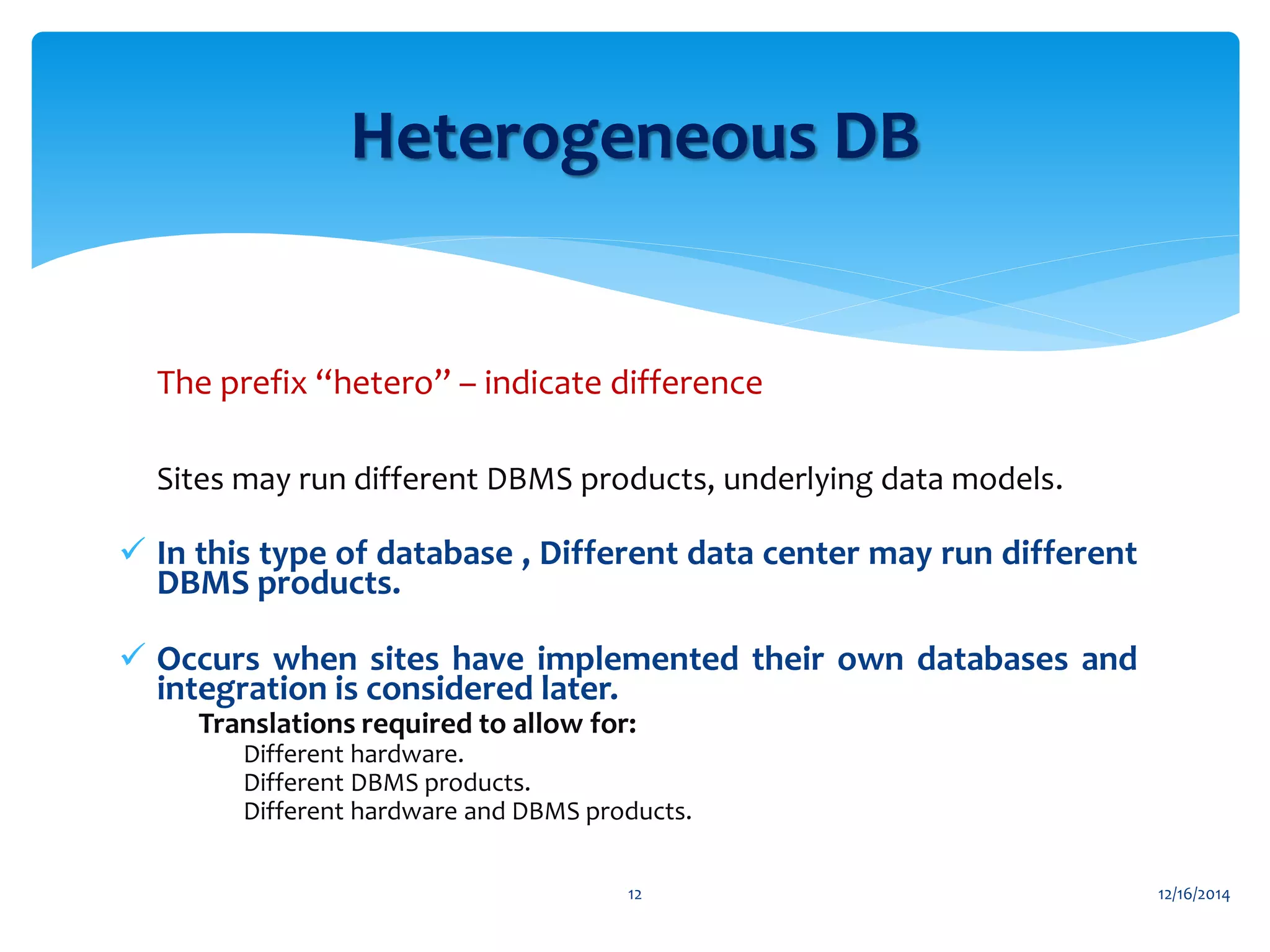
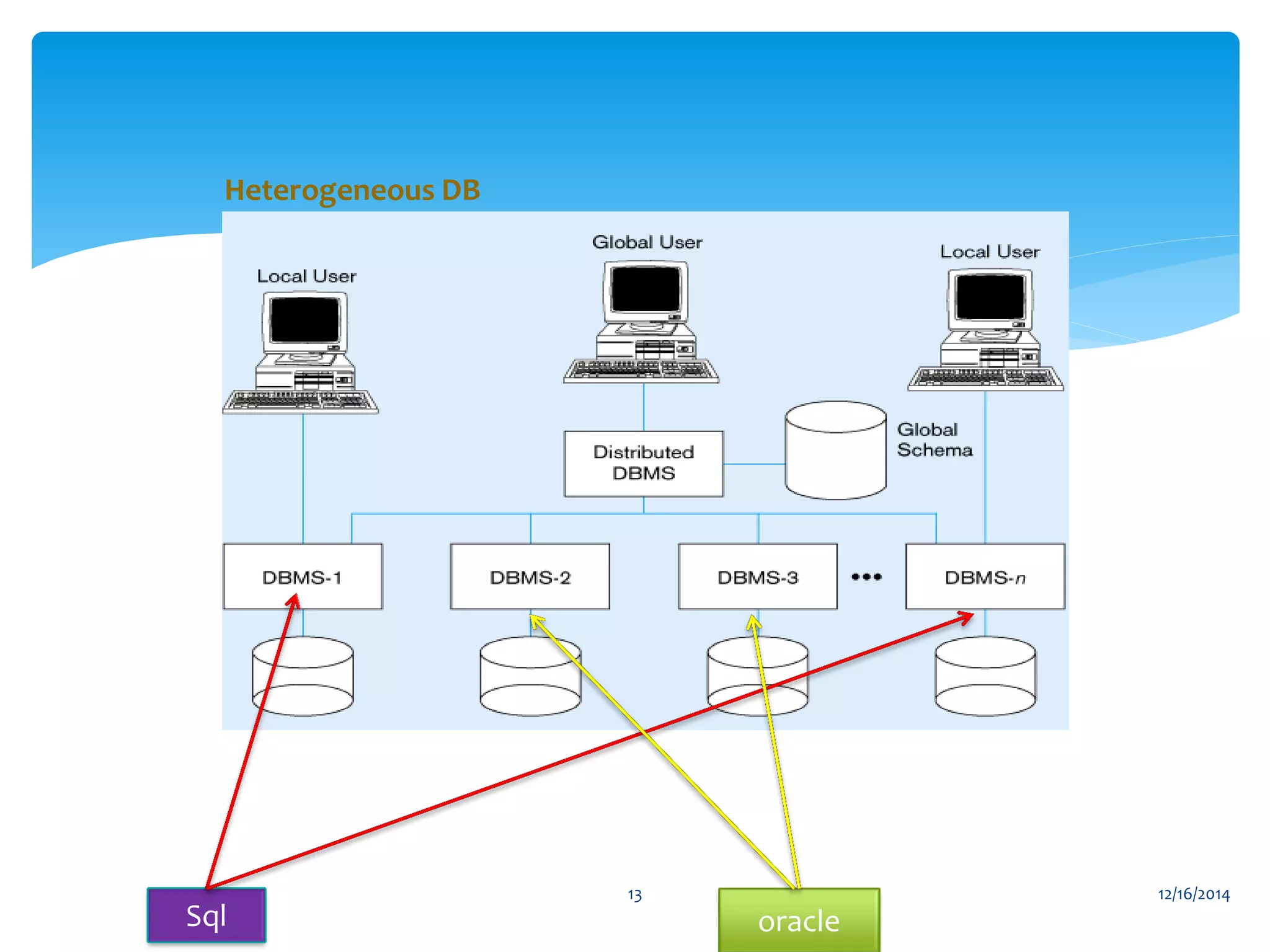
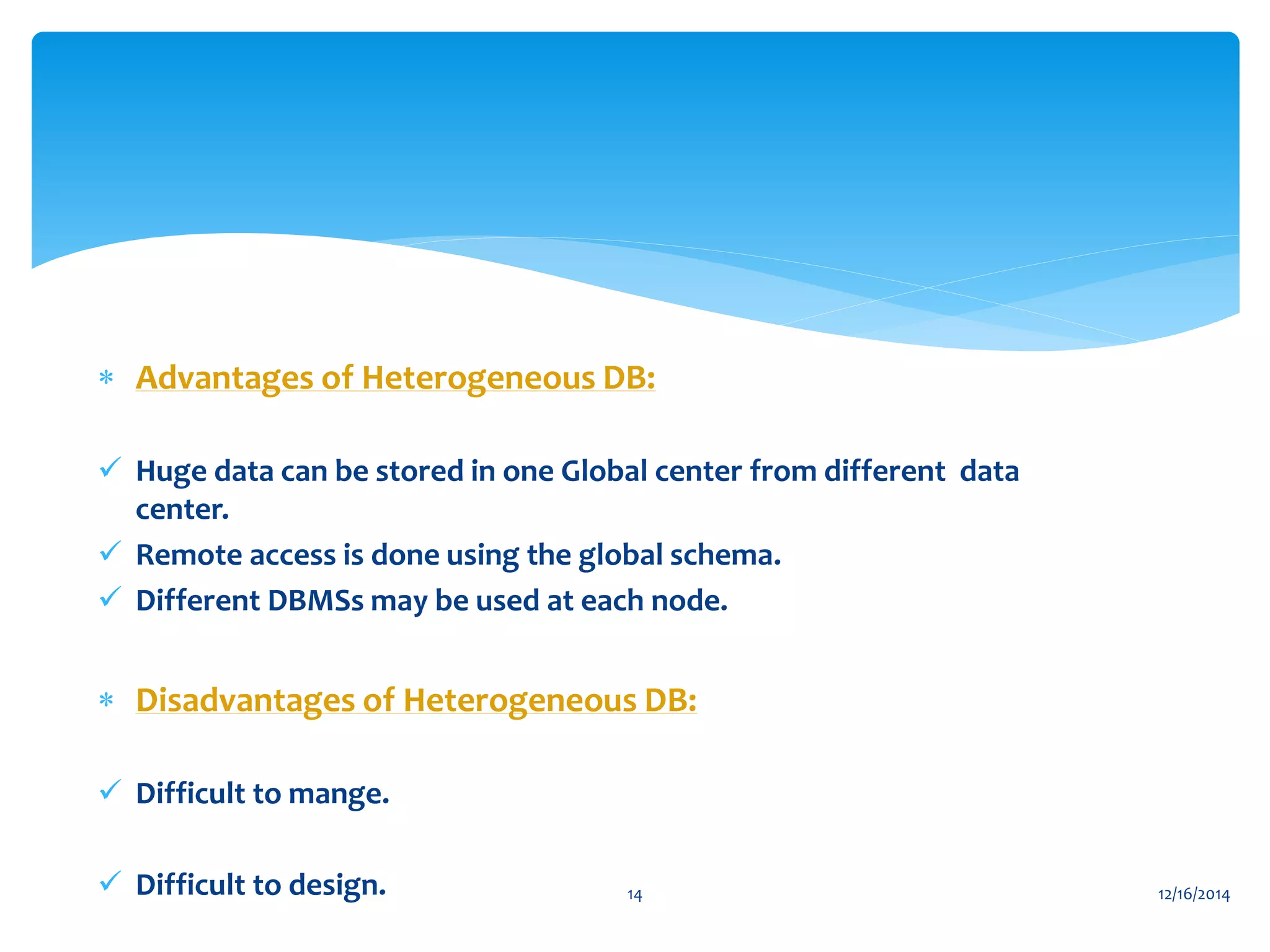
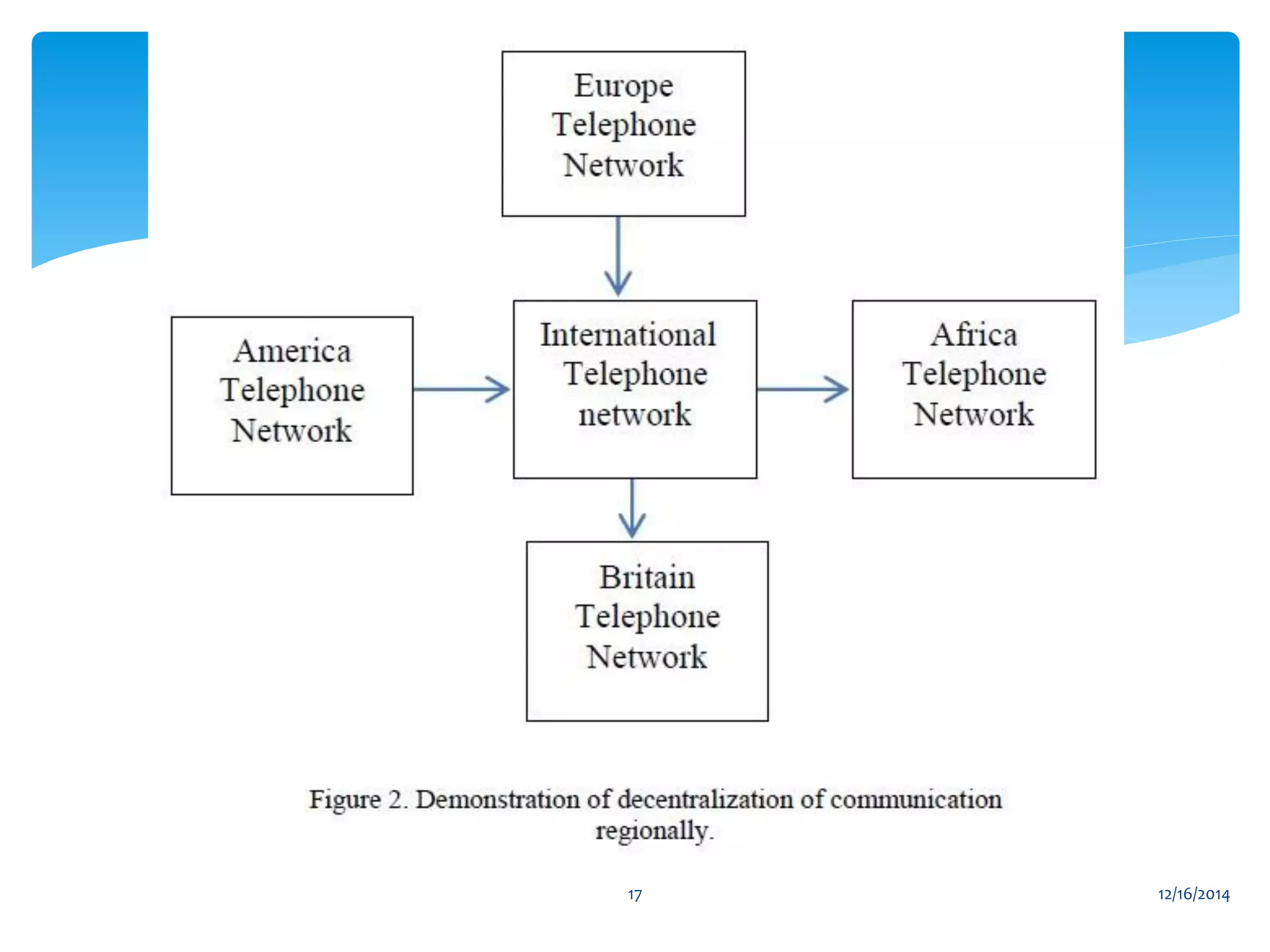
The document presents an overview of distributed databases and their management systems, highlighting characteristics, types (homogeneous and heterogeneous), and challenges such as resource distribution and data updating. It discusses advantages and disadvantages of using distributed database management systems, as well as problems encountered, solutions proposed, and future research directions in updating strategies. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity for ongoing assessments of challenges in distributed databases.