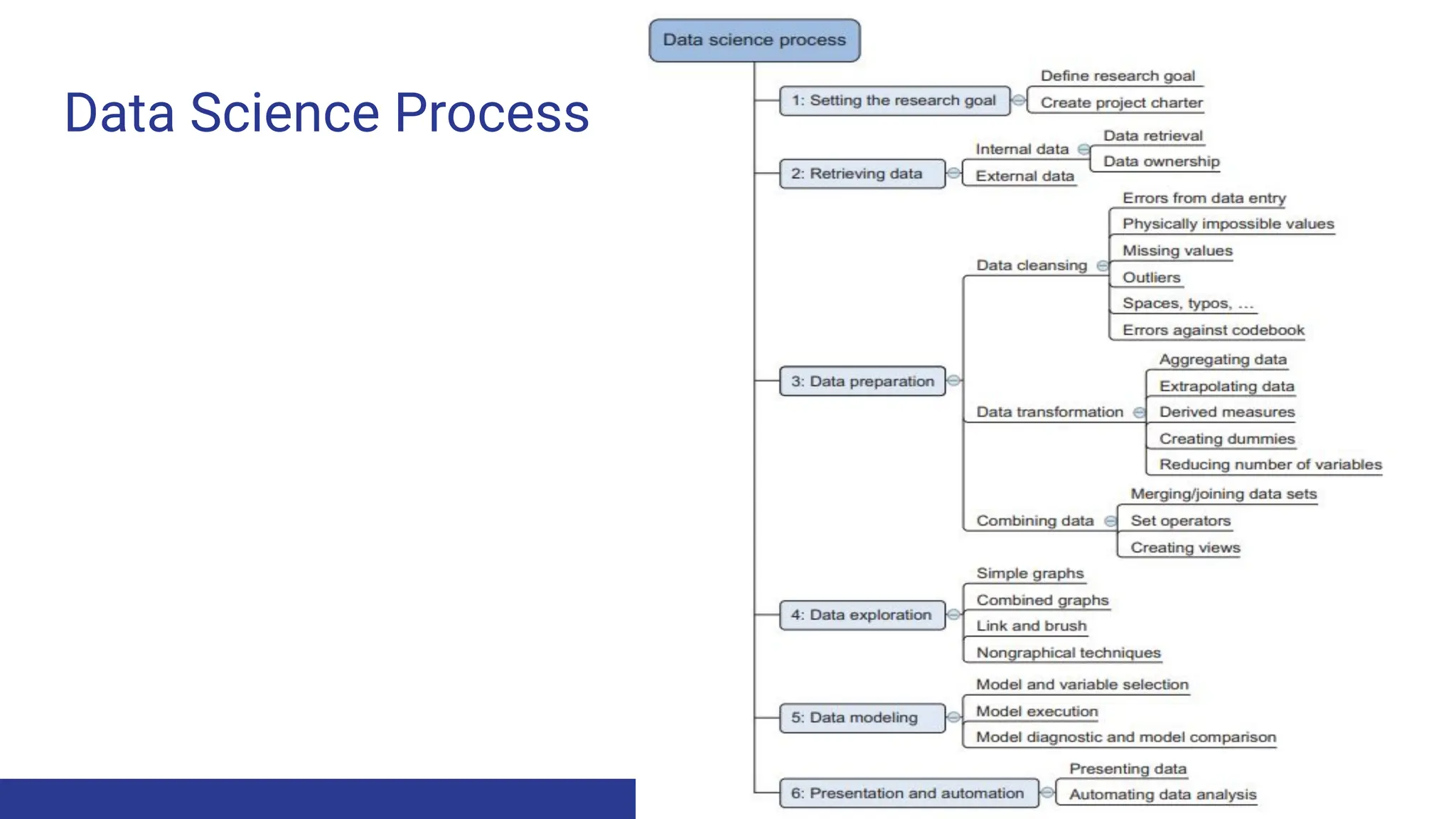
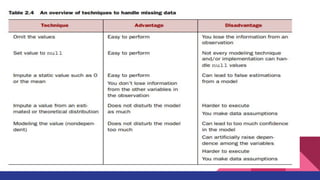
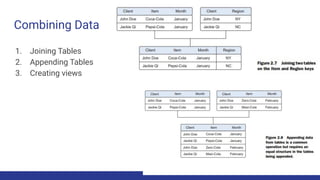
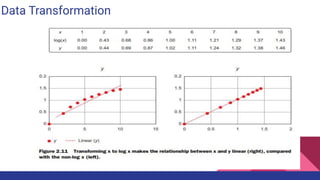
1. The data science process involves 6 steps: setting goals, retrieving data from internal and external sources, data preparation including cleansing, combining data through joins and appends, exploratory data analysis, building models through an iterative process of selecting techniques and variables, and presenting results for automation.
2. Data is stored internally in databases, data warehouses, data marts and data lakes, with databases for storage, warehouses for analysis, and marts serving specific business units. Data lakes contain raw data.
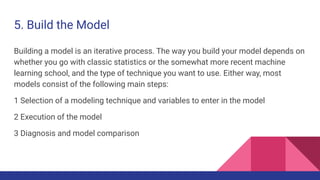
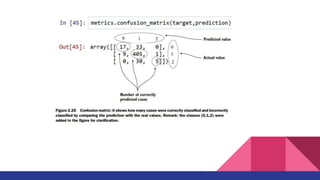
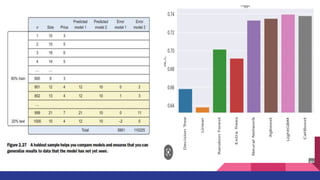
3. Building models is iterative, using either statistics or machine learning, to select variables and techniques and diagnose models for comparison.