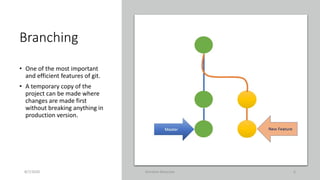
Git is a widely used version control system that allows tracking changes to files and code during software development. It provides features like branching, merging, and distributed collaboration. Data scientists can use Git and GitHub for version control, collaboration, and improving their personal branding by making their work public on GitHub. Key Git commands include git add to stage files, git commit to save changes locally, and git push to upload to a remote repository.