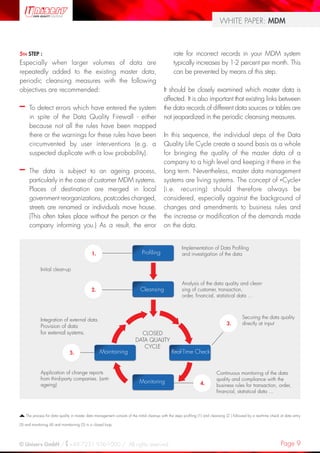
This white paper discusses the importance of data quality for successful Master Data Management (MDM) systems. It defines MDM as consolidating all relevant company data from different systems into a single version of truth. High quality meta data and content data are critical for MDM success. The paper describes how data profiling can analyze meta data quality issues across sources. It also discusses challenges in keeping data quality high as MDM systems operate continuously with live data updates and entries. The paper proposes a Data Quality Life Cycle approach including identifying data sources, initial data cleansing, real-time data validation, and ongoing monitoring to help maintain high quality master data.


![Page 3© Uniserv GmbH / +49 7231 936-1000 / All rights reserved.
WHITE PAPER: MDM
Master Data Management:
what exactly does it mean?
One of the great challenges in the corporate
environment nowadays is effective master data
management (MDM). The precise meaning of this
term can be explained best of all by the following
definition of David Loshin (2009):
The aim is to obtain the so-called «single version
of truth», i.e. that only one system has to be con-
sulted to display all the relevant data of the entire
company for the respective aspect. Searching for
information across different systems is not neces-
sary. Working with the data is more efficient.
From this consideration, it can be recognized
that MDM is not just a software solution but more
importantly a question of the internal organization
and definition of company data. In a final step,
This data is synchronized in various ways and
made available to the end user. Depending on the
complexity of the existing systems and data of a
company, the successful implementation of a MDM
system can take several months or even years.
THE IMPLEMENTATION IS TYPICALLY DIVIDED INTO DIFFER-
ENT PHASES:
–– first of all, the actual master data must be identi-
fied and a list drawn up of the systems in which
it is stored.
–– The next step is to agree on a Master Data
Object Model and ensure that the meta data
is consistent.
Once these fundamental aspects have been clari-
fied, the various requirements for the data are
decided on. Firstly, the requirements of the data
users in the operative area must be considered.
However, these specific demands also have to be
considered in the implementation if MDM is to be
basis of a Data Warehouse or Business Intelligence
analyses.
Further important points are issues such as data
protection or compliance with anti-terrorism regula-
tions. In short, all the legal, operative and analyti-
cal requirements for the data must be considered.
Moreover, the data should be available in an
appropriate quality, so that the content require-
ments for the data can be satisfied.
Setting up a master data management system always
means implementing a company-wide project.
Projects of this size demand a great deal of brain-
work from all concerned, especially if they involve
the creation of the Master Data Object Model or the
standardization of the meta data. The current trend is
to call in external consultants who can liaise between
the various stakeholders and departments and the
personnel responsible for the various data sources
with a degree of detachment in these phases.
« [MDM IS…] ENVISIONING HOW TO
ORGANIZE AN ENTERPRISE VIEW OF THE
ORGANIZATION’S KEY BUSINESS
INFORMATION OBJECTS AND TO
GOVERN THEIR QUALITY, USE, AND
SYNCHRONIZATION TO OPTIMIZE THE
USE OF INFORMATION TO ACHIEVE
THE ORGANIZATION’S OPERATIONAL
AND STRATEGIC BUSINESS OBJECTS ».](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/data-quality-mdm-en-101027022105-phpapp01/85/Data-Quality-MDM-3-320.jpg)