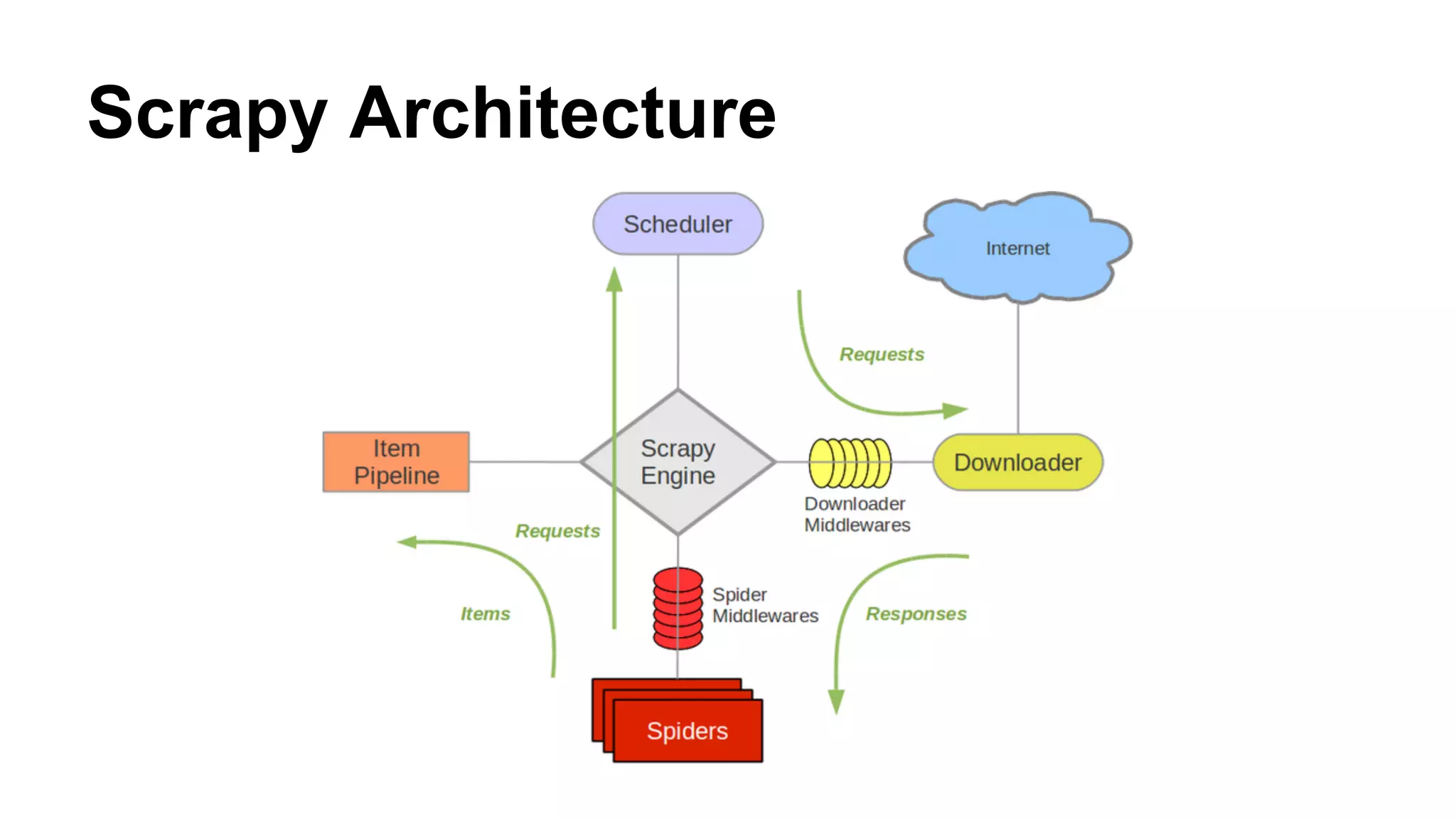
Scrapy is an open source and Python-based web crawling framework. It provides tools and components for writing web spiders to extract structured data from websites, including built-in selectors, item pipelines, link extractors, and request/response handling. Spiders define rules for crawling sites by following links and extracting items using selectors, which are then passed through the framework's asynchronous data flow and stored or processed using items pipelines.







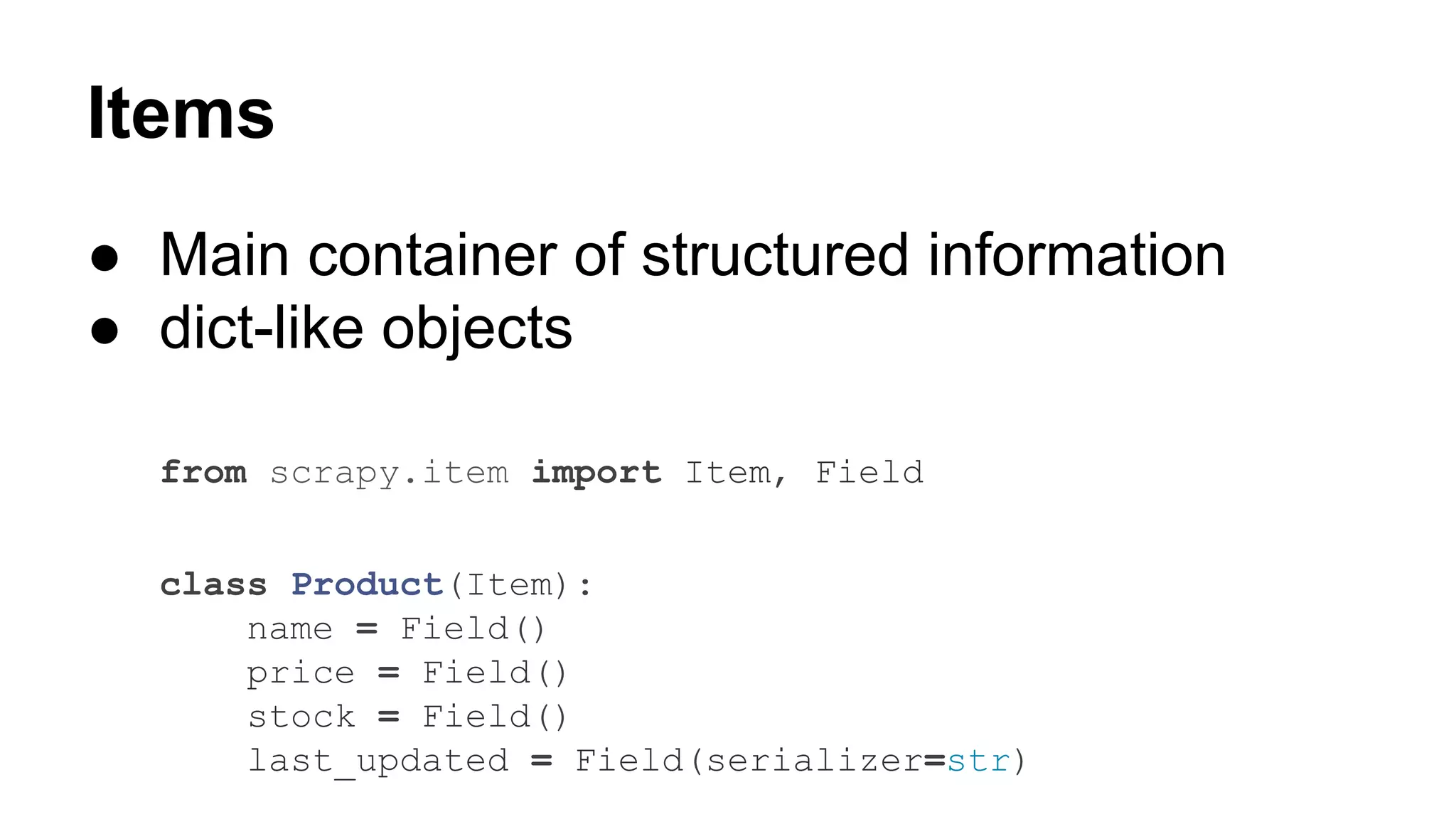
![Items
>>> product = Product(name='Desktop PC', price=1000)
>>> print product
Product(name='Desktop PC', price=1000)
>>> product['name']
Desktop PC
>>> product.get('name')
Desktop PC
>>> product.keys()
['price', 'name']
>>> product.items()
[('price', 1000), ('name', 'Desktop PC')]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataphillyscrapy-131118204940-phpapp01/75/Scrapy-talk-at-DataPhilly-10-2048.jpg)



![BaseSpider
...
class MySpider(BaseSpider):
name = 'example.com'
allowed_domains = ['example.com']
start_urls = [
● Send Requests example.
com/[1:3].html
'http://www.example.com/1.html',
'http://www.example.com/2.html',
'http://www.example.com/3.html',
]
● Yield title Item
def parse(self, response):
sel = Selector(response)
for h3 in sel.xpath('//h3').extract():
yield MyItem(title=h3)
for url in sel.xpath('//a/@href').extract():
yield Request(url, callback=self.parse)
● Yield new Request](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataphillyscrapy-131118204940-phpapp01/75/Scrapy-talk-at-DataPhilly-14-2048.jpg)


![Selectors
● Mechanisms for extracting data from HTML
● Built over the lxml library
● Two methods
○ XPath: sel.xpath('//a[contains(@href,
"image")]/@href' ).
extract()
○
CSS: sel.css('a[href*=image]::attr(href)' ).extract()
● Response object is called into Selector
○
sel = Selector(response)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataphillyscrapy-131118204940-phpapp01/75/Scrapy-talk-at-DataPhilly-17-2048.jpg)