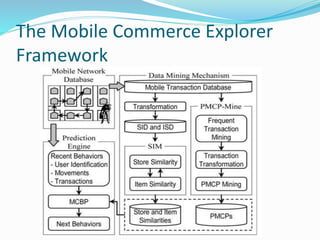
The paper presents a novel framework called Mobile Commerce Explorer (MCE) for mining and predicting mobile users' transaction behaviors and movement patterns within mobile commerce environments. It employs three key techniques: a similarity inference model, a personal mobile commerce pattern mining algorithm, and a behavior prediction model, aiming to enhance the efficiency of such analyses. The findings indicate that the MCE framework can uncover personal mobile commerce patterns and behaviors that may lead to new store and item recommendations for users.