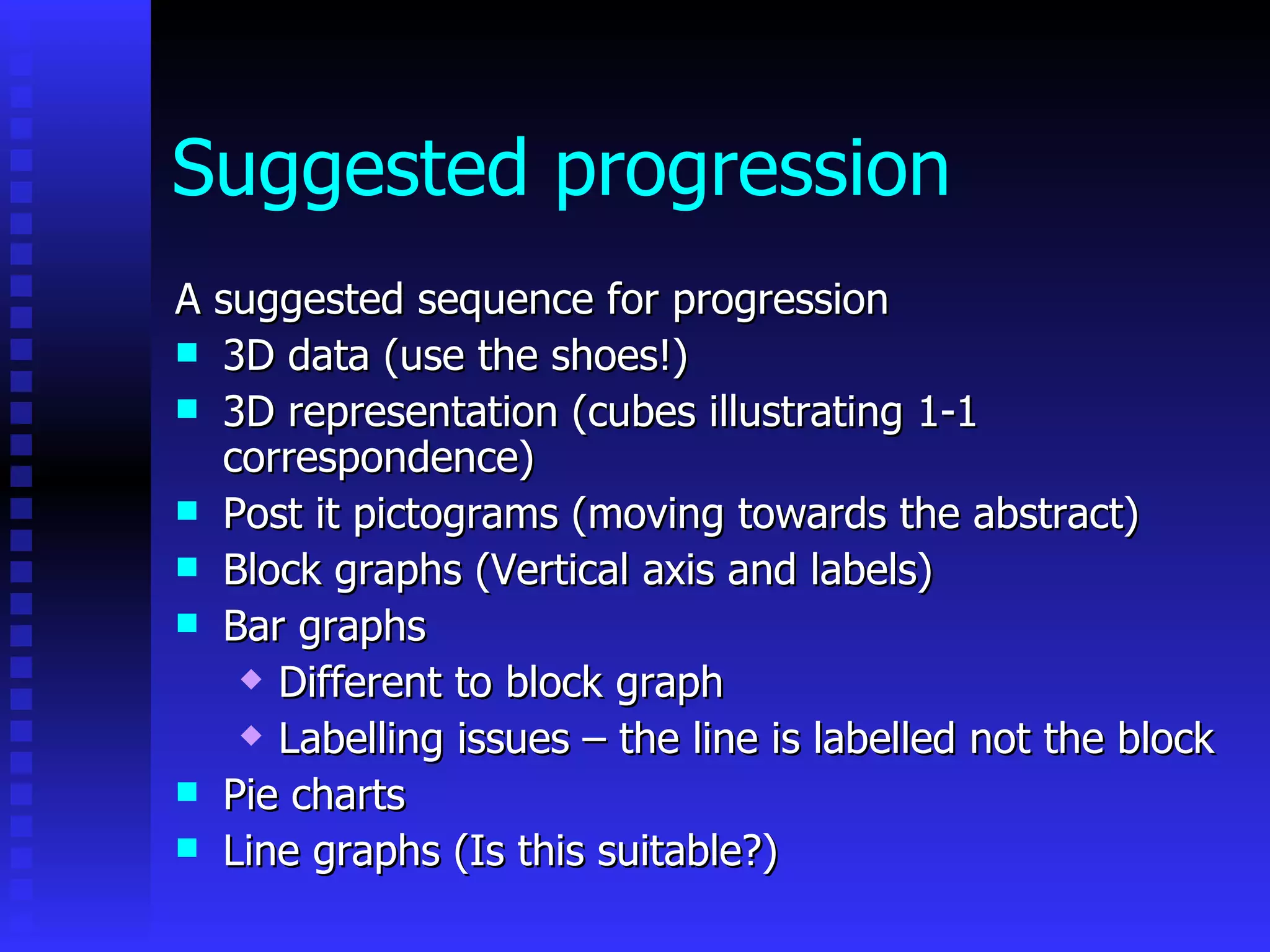
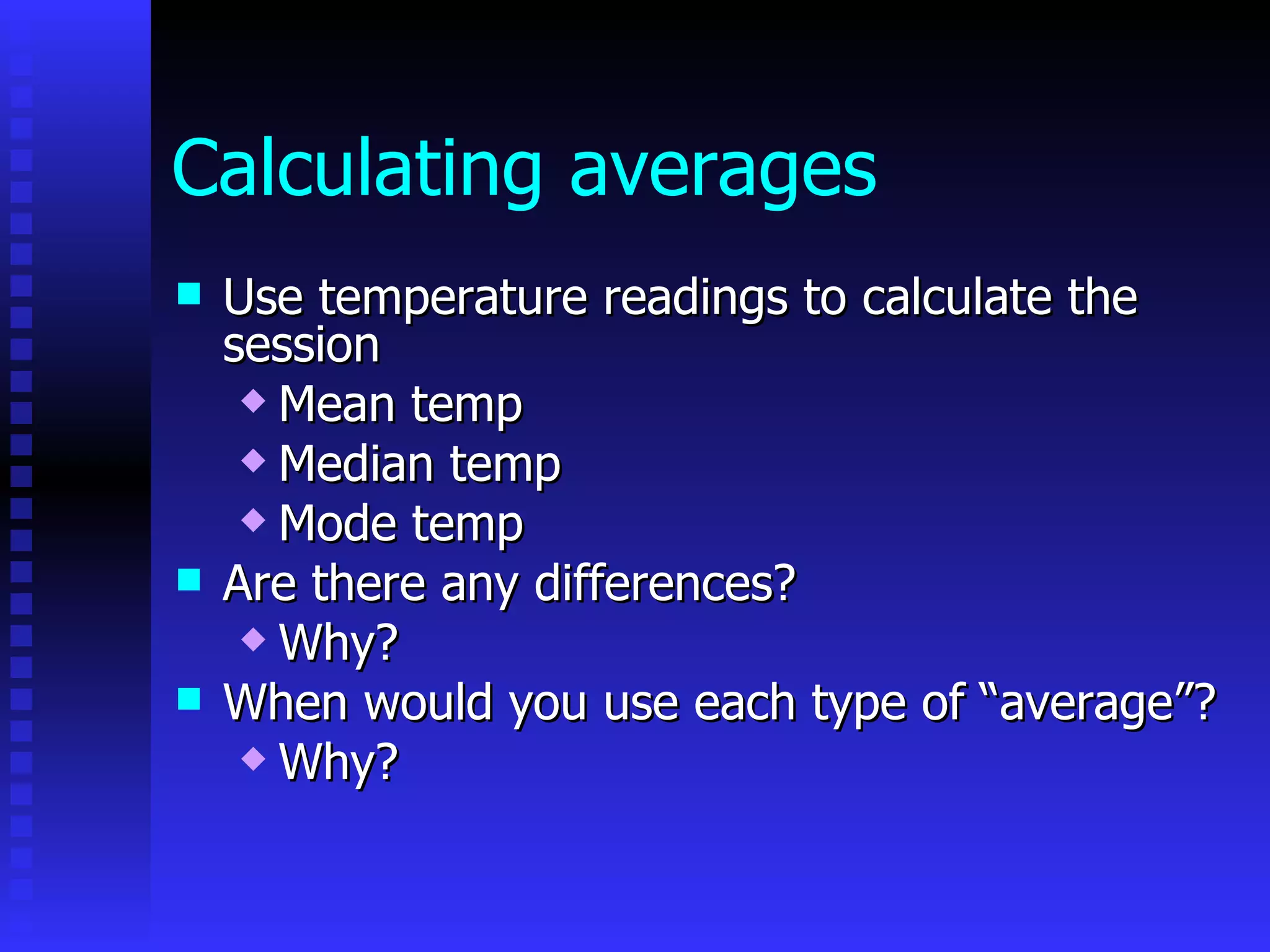
This document discusses teaching data handling and statistics to children. It covers 5 key stages of data handling: posing questions, collecting data, processing data, representing data, and interpreting data. Some example activities are described that involve sorting data in different ways. Progression in techniques for sorting data is outlined. The use of ICT tools like 2Simple software, Excel, and different types of graphs like bar graphs, pie charts and line graphs is also discussed. Interpreting data through calculating averages, means, medians and modes is covered. The document provides directed tasks to further develop subject knowledge around discrete and continuous data types.