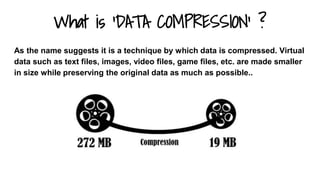
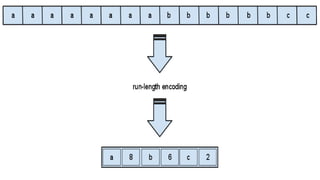
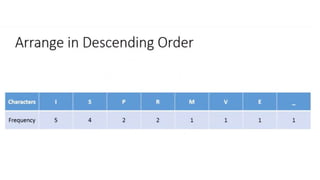
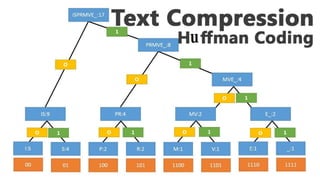
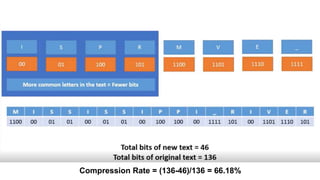
This document discusses different data compression algorithms. It defines data compression as a technique that makes files smaller in size while preserving the original data. There are two main reasons for data compression: to reduce the large amount of space used by files, and to speed up downloading of large files. It describes lossless compression, which allows perfect reconstruction of data, and lossy compression, which results in some loss of quality or information. Some common algorithms discussed are Run-Length Encoding, Huffman Coding, Lempel-Ziv-Welch Encoding, and Discrete Cosine Transform. Run-Length Encoding replaces repeated characters with codes to indicate repetition count. Huffman Coding assigns shorter codes to more common characters.