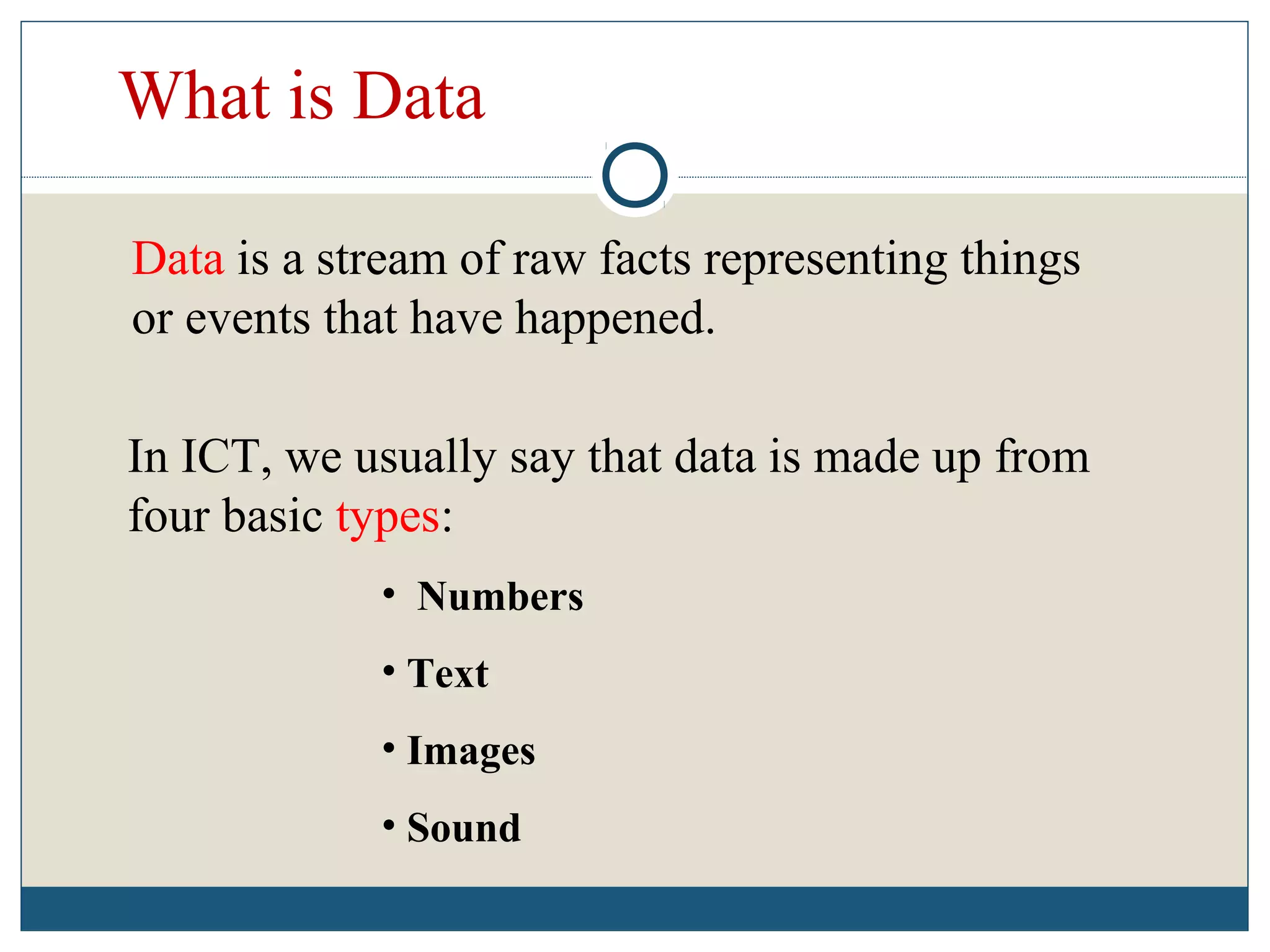
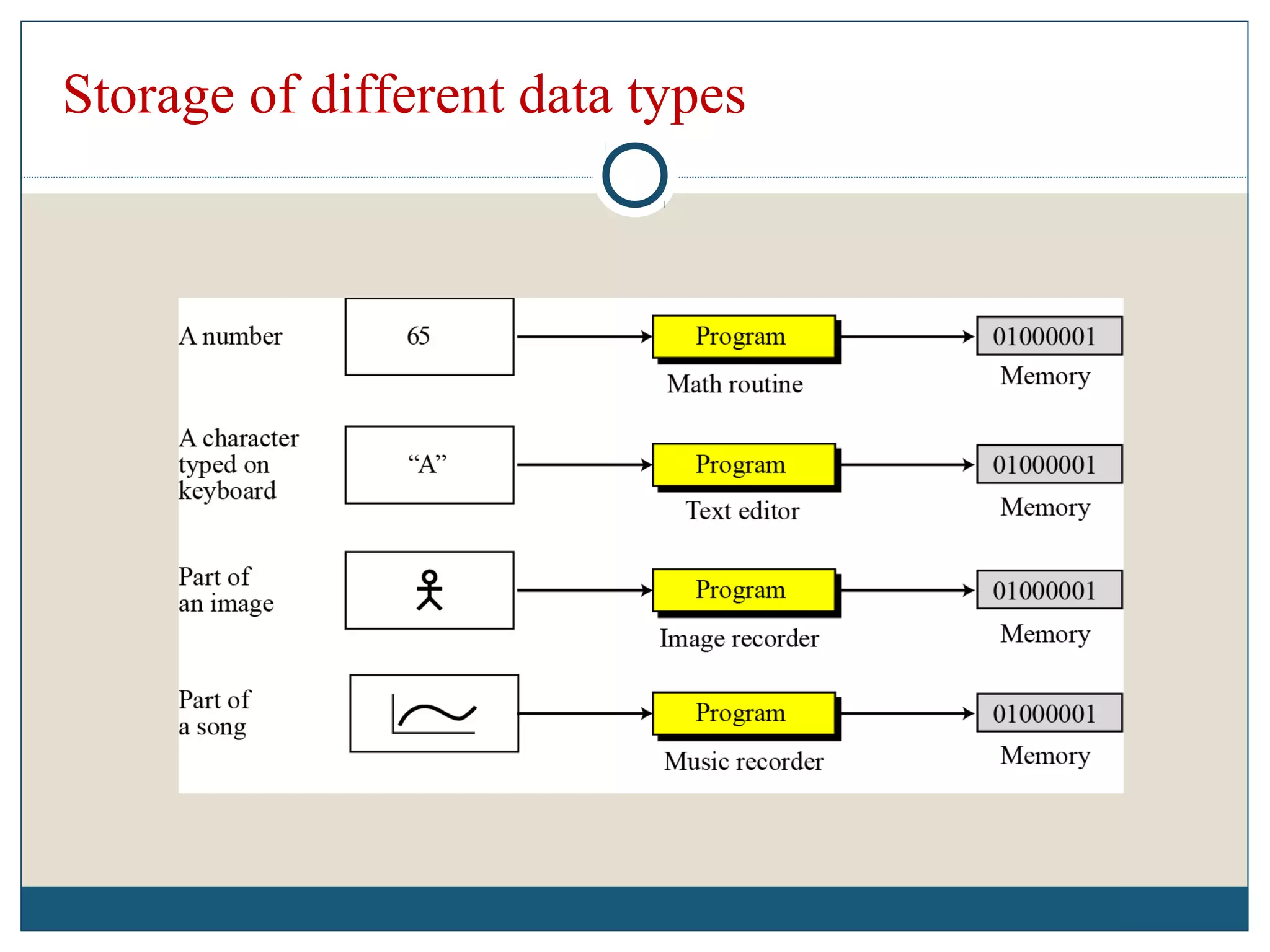
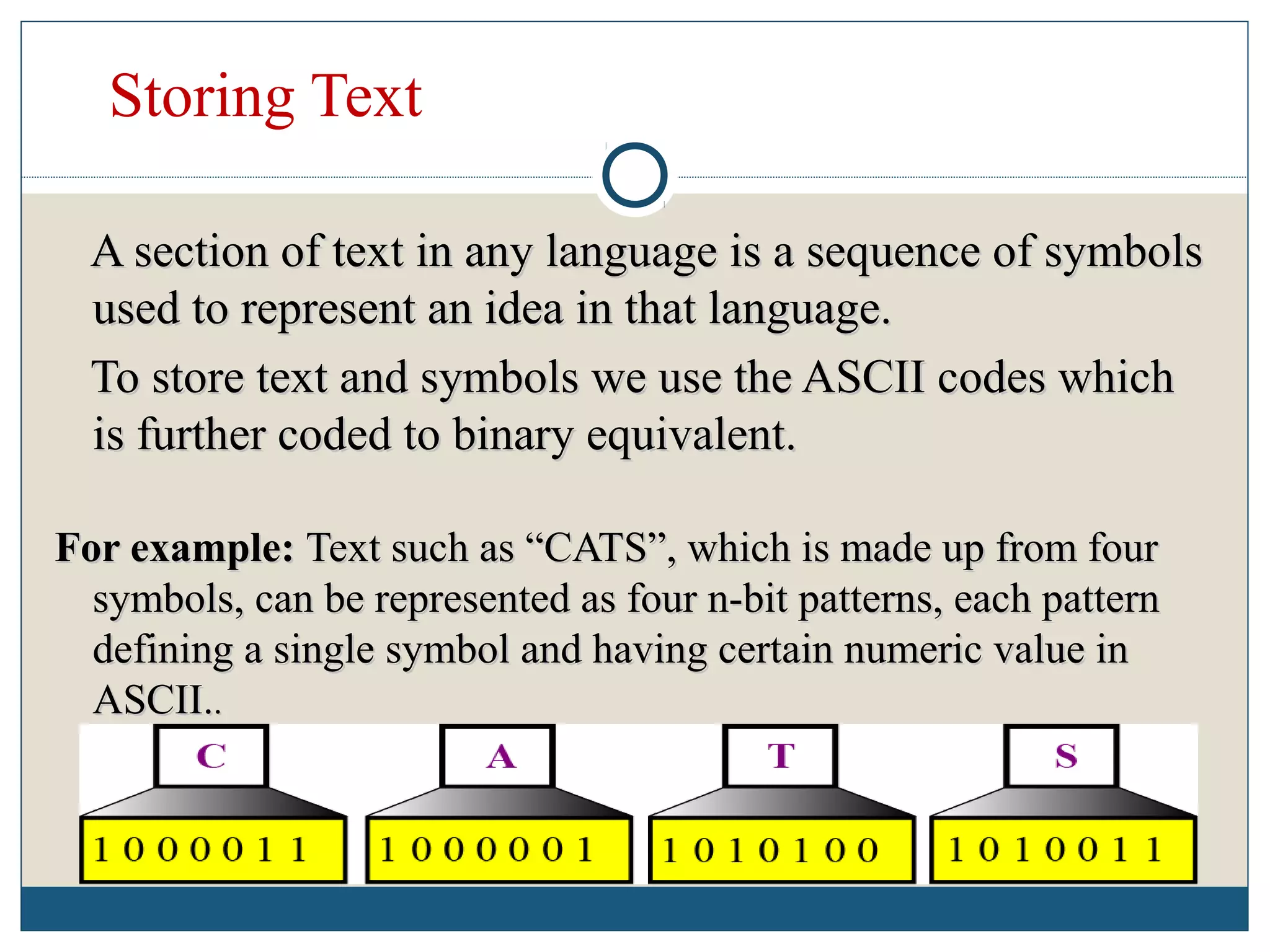
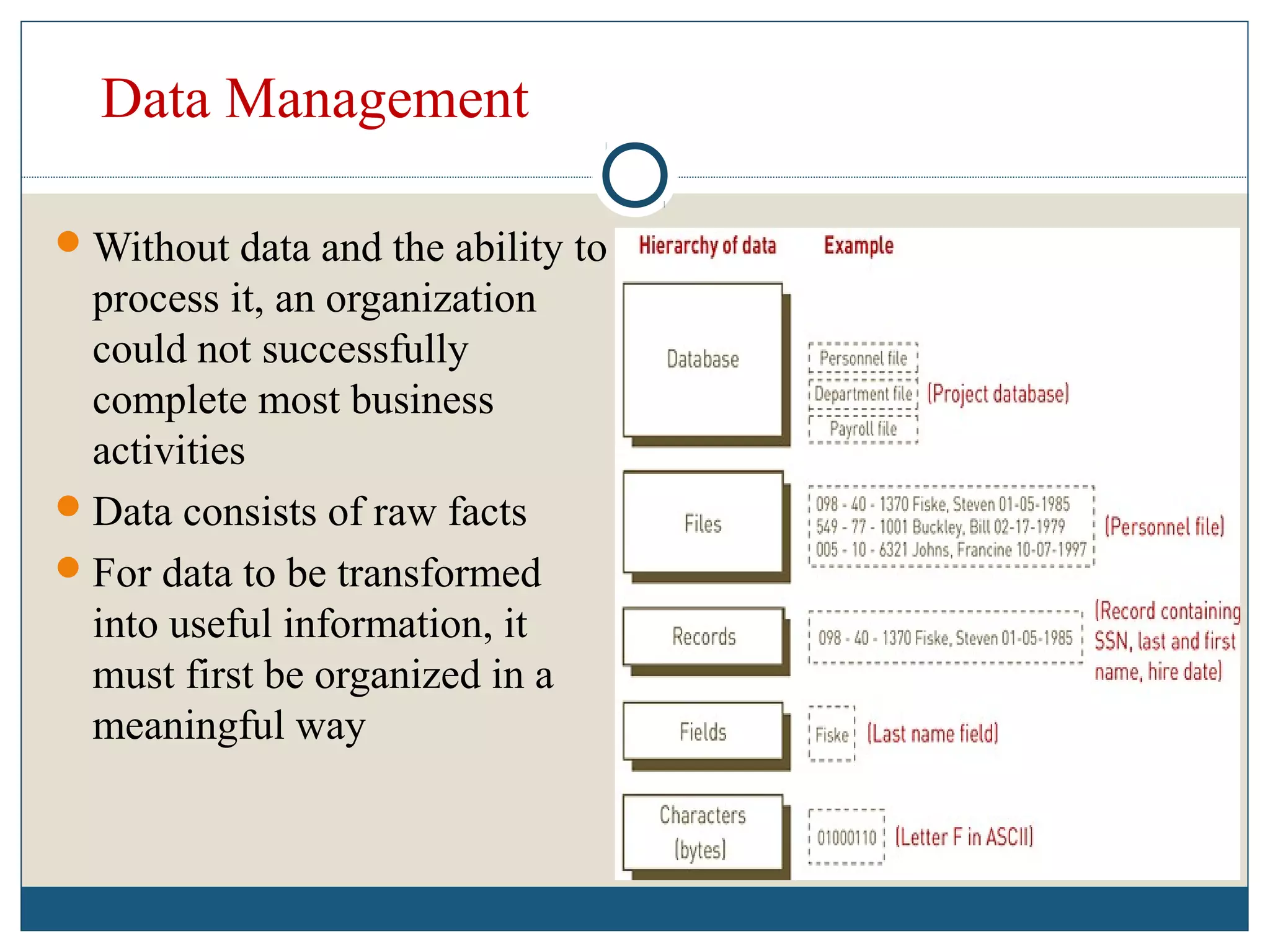
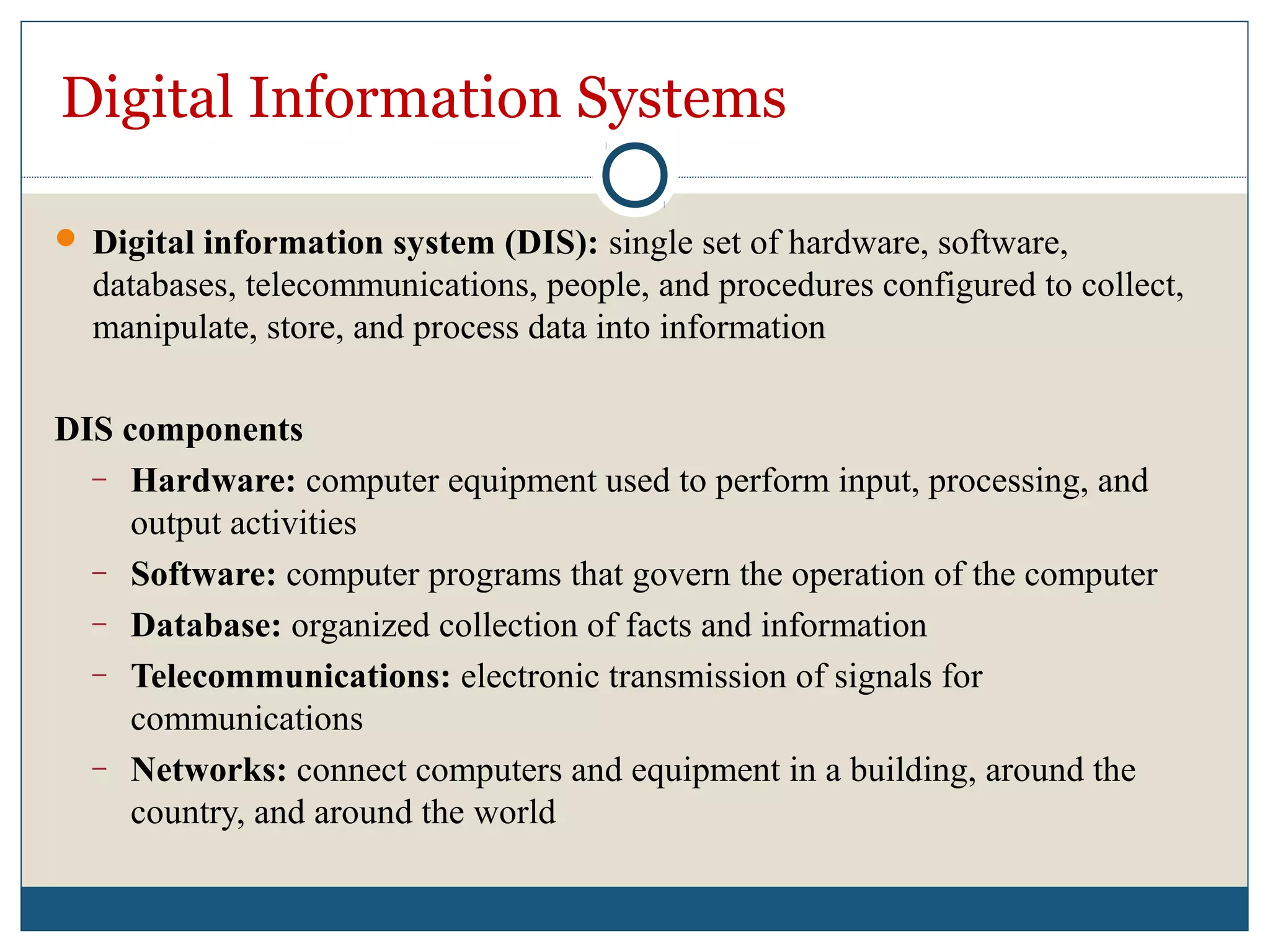
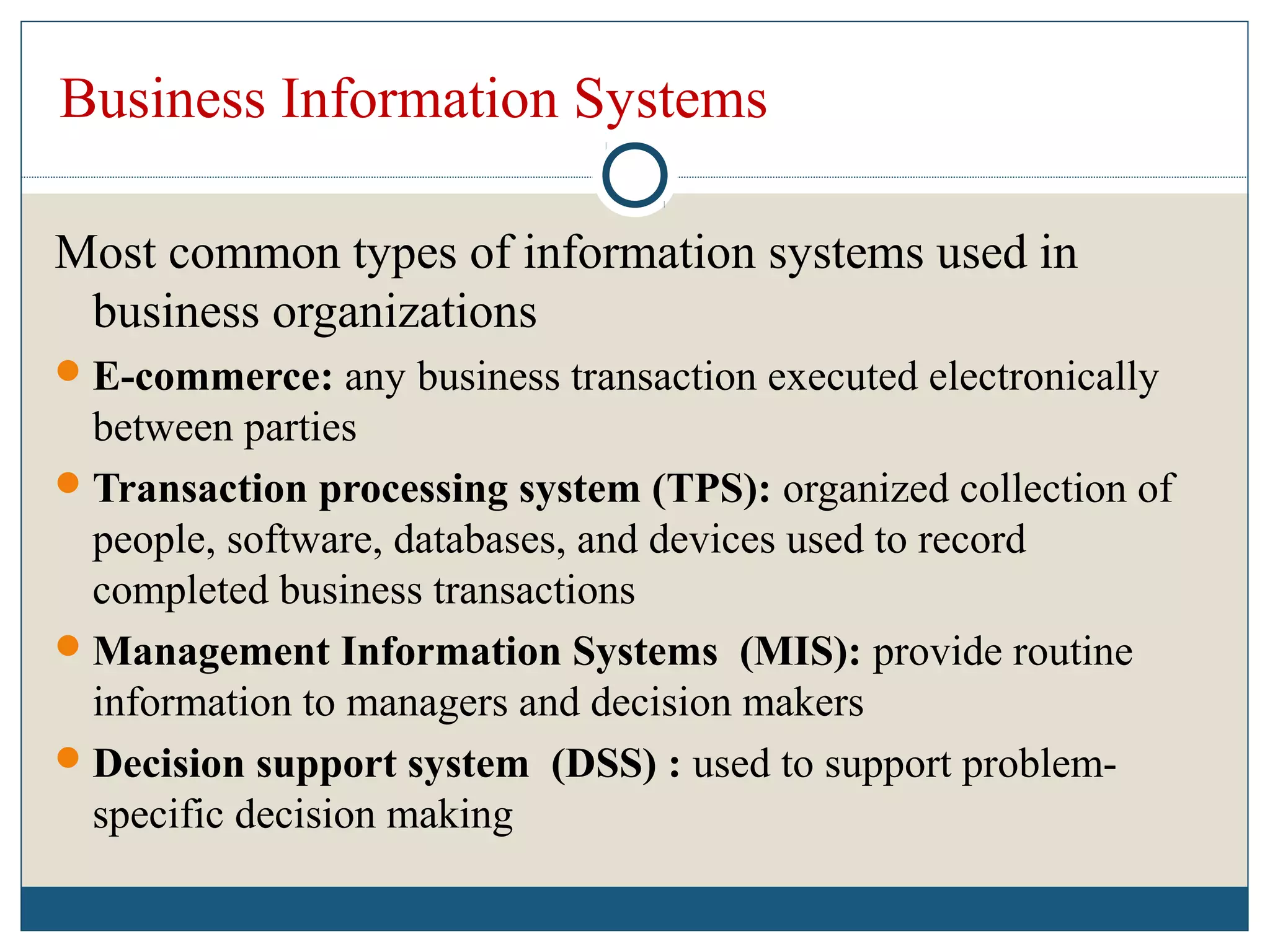
Data refers to raw facts that are stored in computers as numbers, text, images, or sound. All data types are converted to binary digits (bits) for storage and later reconstructed. Text is stored through ASCII codes, images use pixels mapped to bit patterns, and sound is represented by discrete samples encoded as bits. Information involves processing and organizing data to make it meaningful. Databases centrally store structured data that can be retrieved, added to, modified, or deleted when needed. Digital information systems encompass the hardware, software, networks, people, and processes used to collect, manipulate, store, and transform data into useful information for businesses and their management.