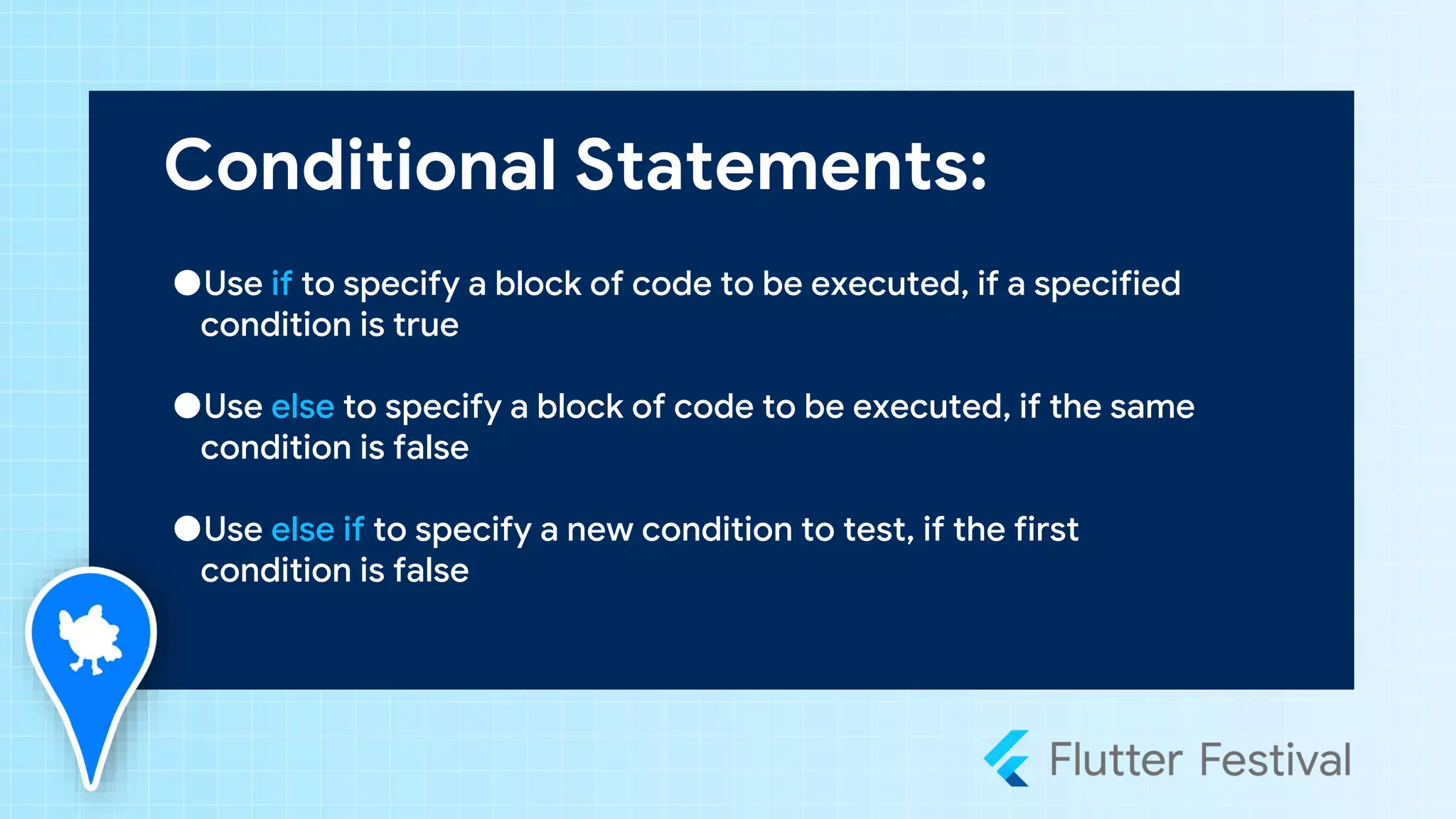
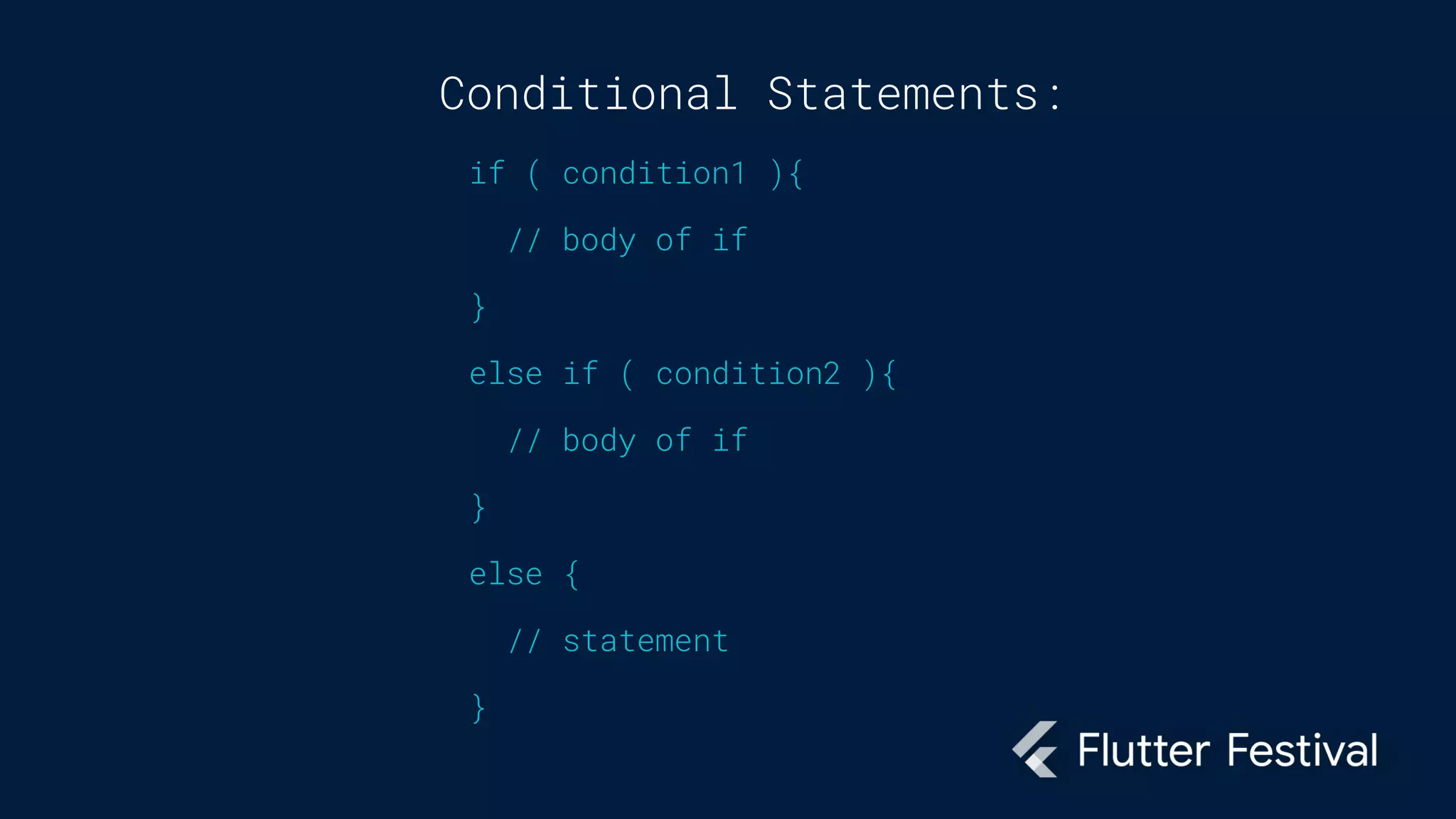
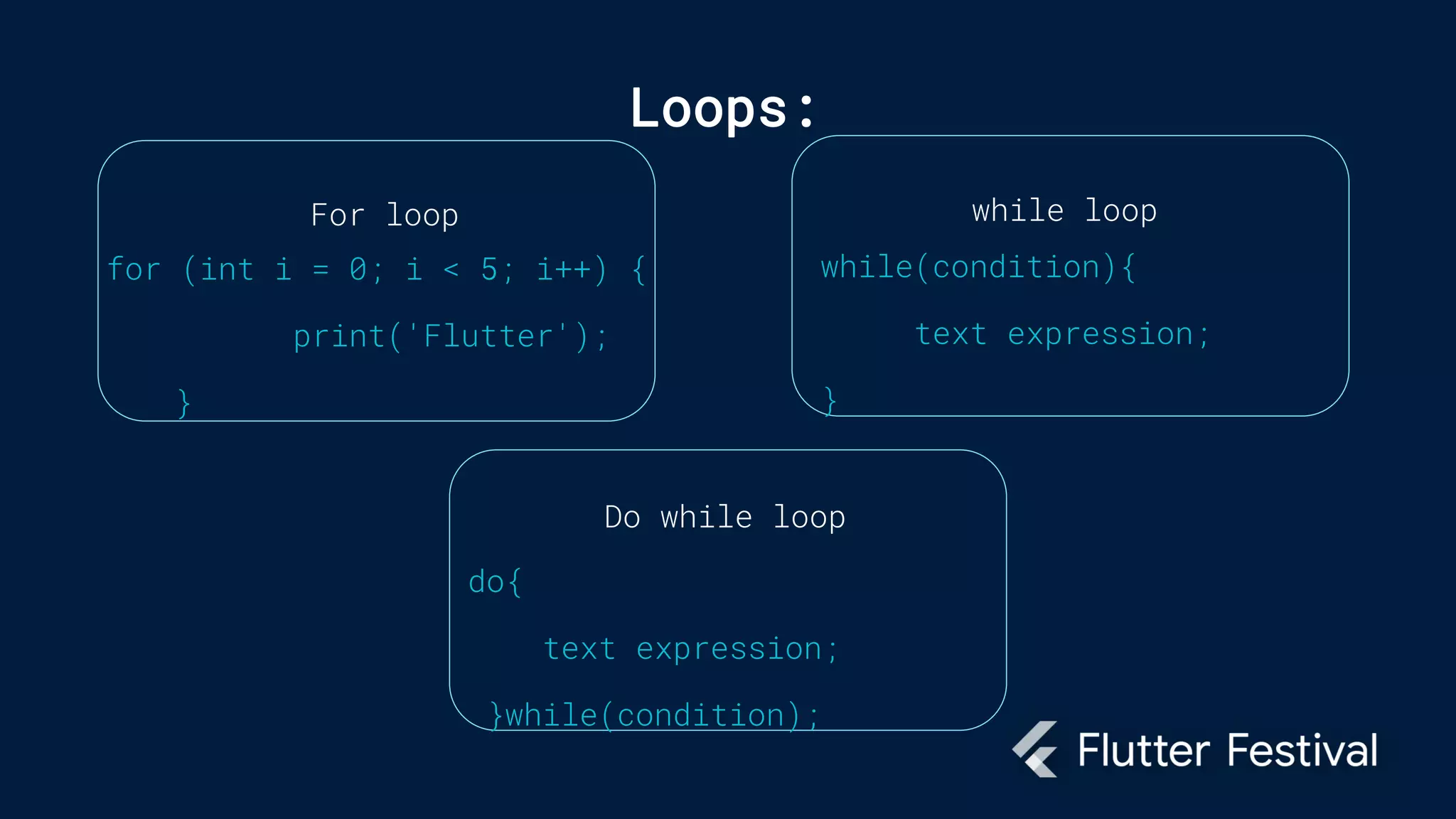
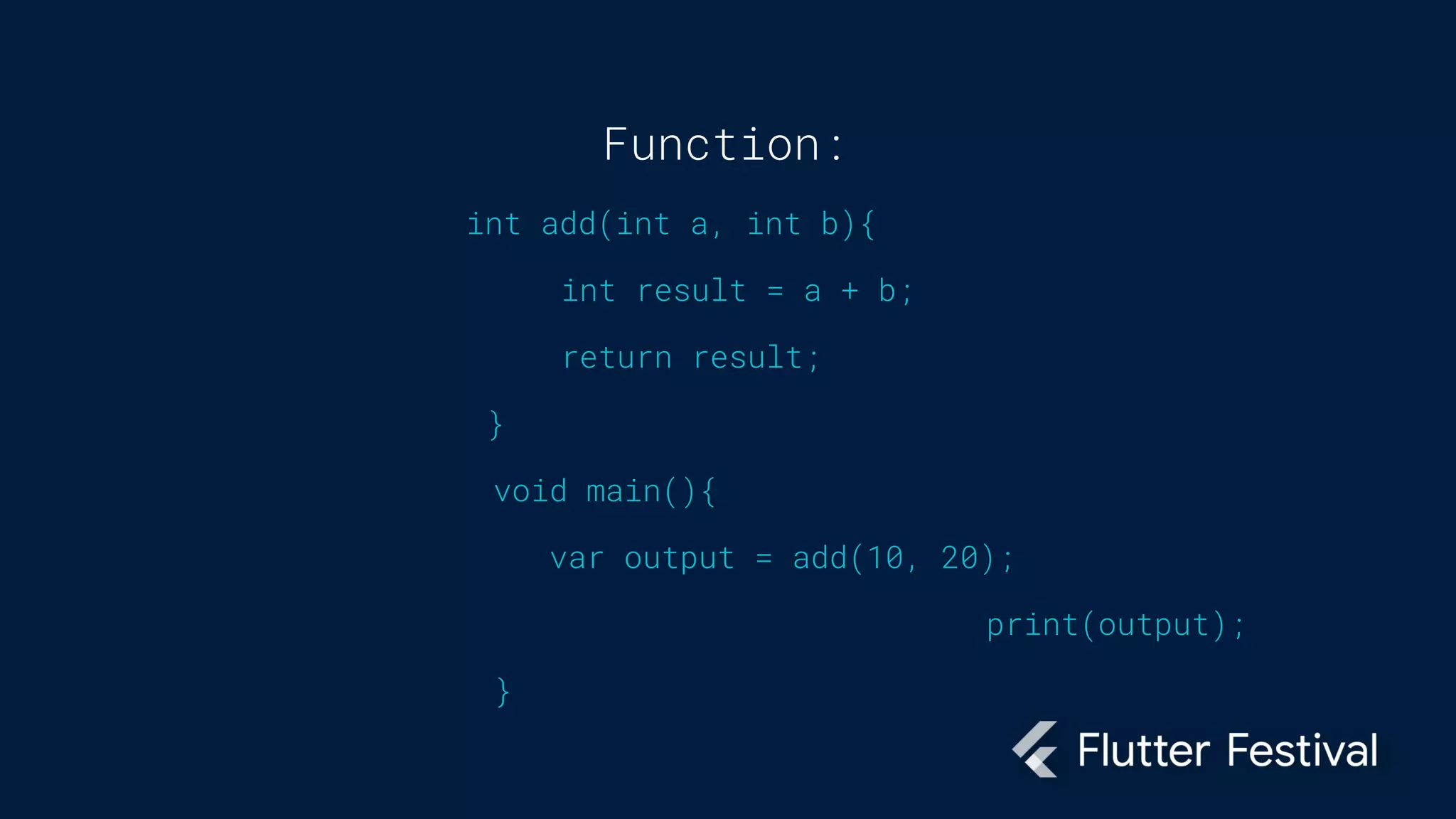
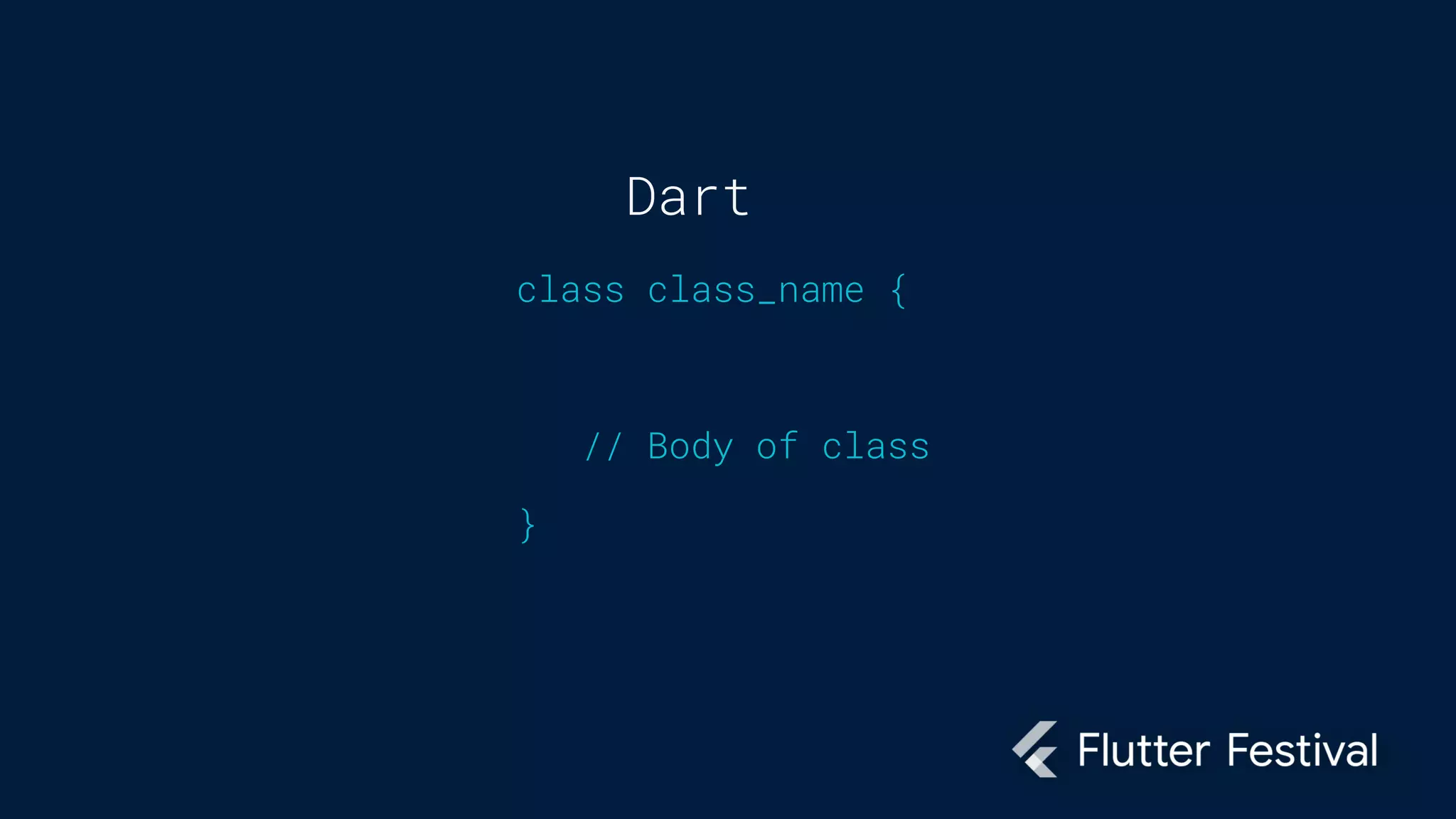
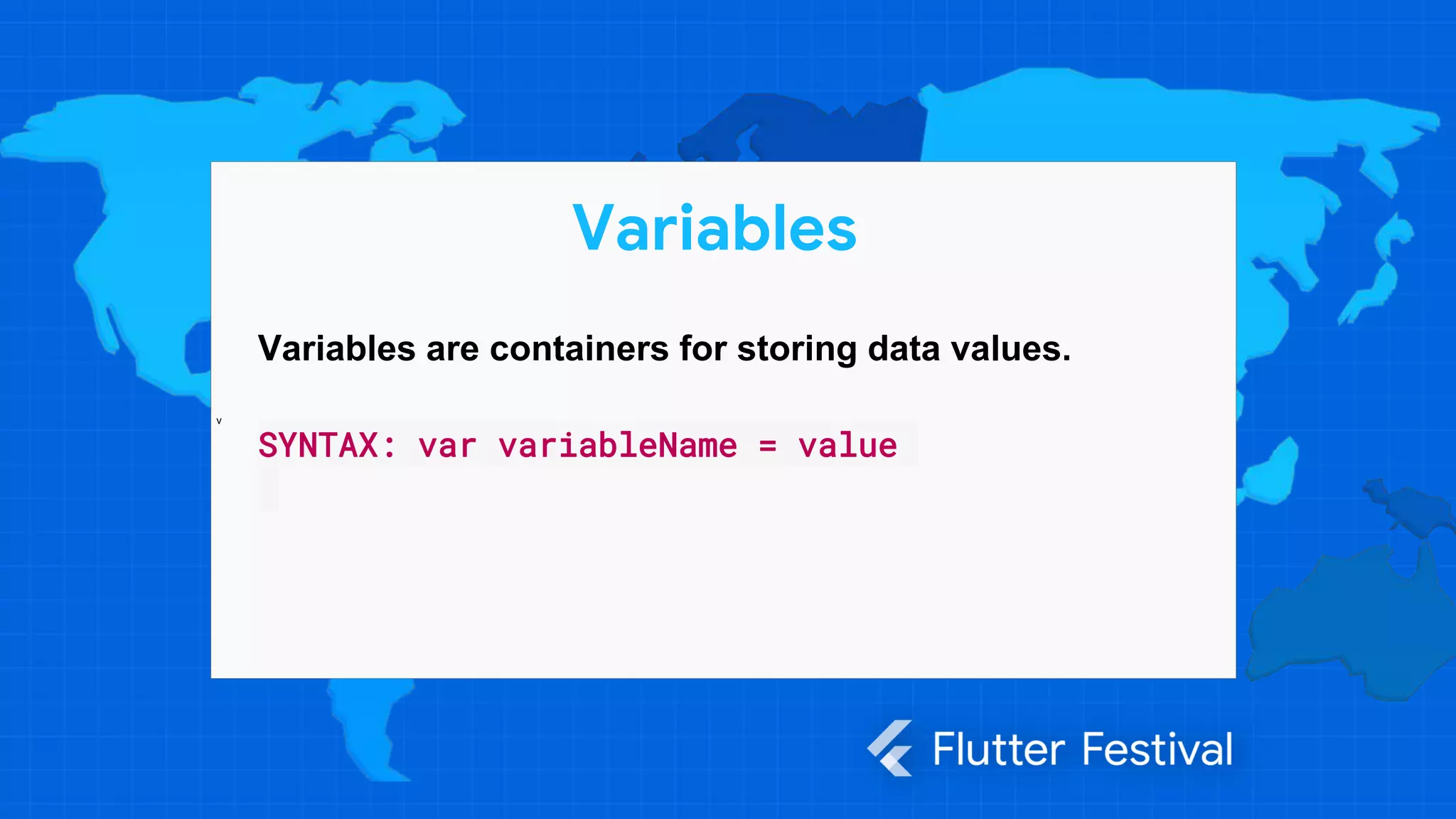
Dart is a programming language developed by Google, primarily for client development in web and mobile apps, and is integral to coding Flutter applications. Key concepts include variables, data types, conditional statements, loops, functions, and object-oriented programming, which utilize classes to create identifiable objects with specific behaviors. The document also provides syntax examples and fundamental programming concepts to guide new Dart programmers.




![v
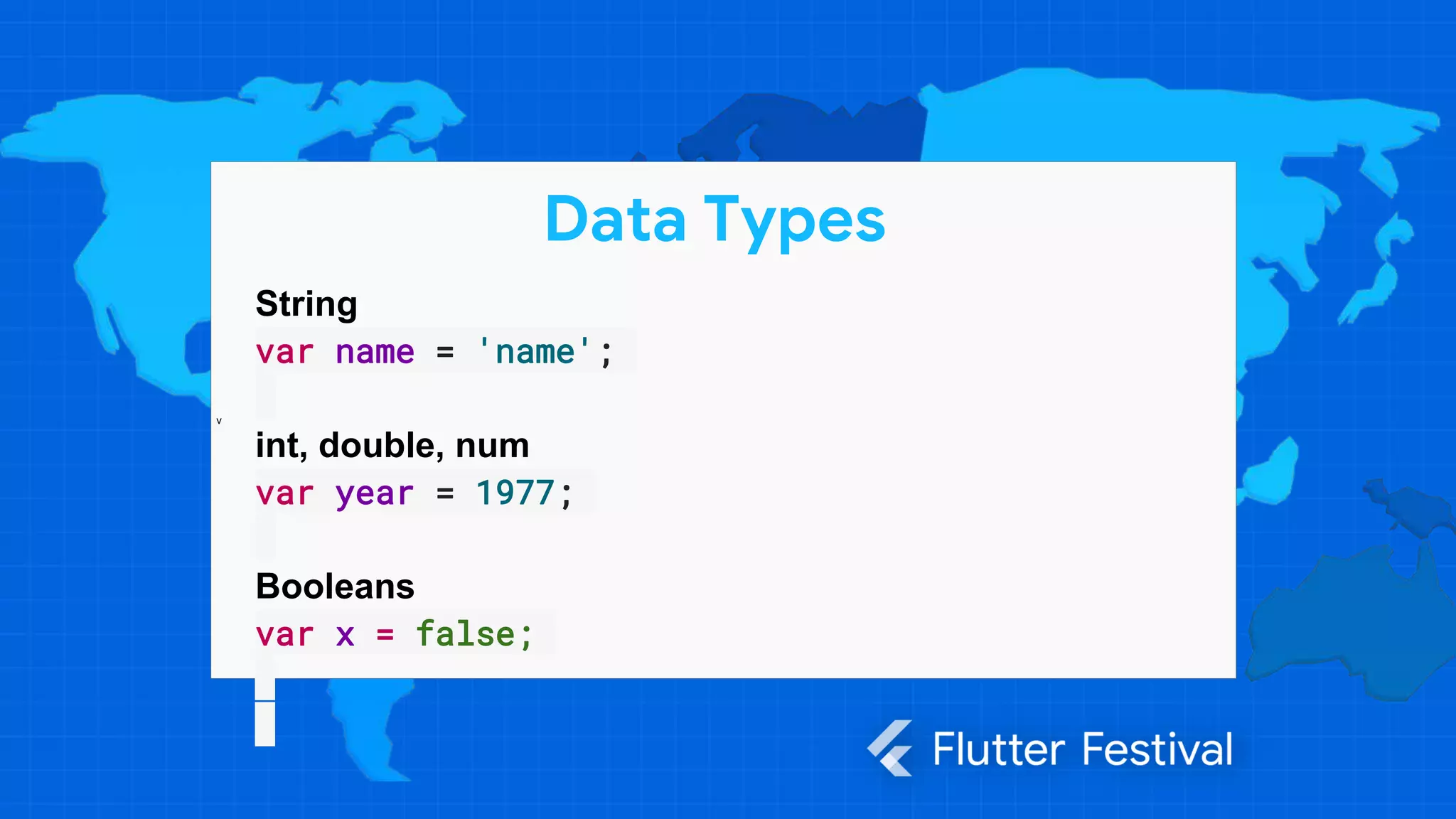
Data Types
List
var flybyObjects = ['Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune'];
map
var identifier = { key1:value1, key2:value2
[,…..,key_n:value_n] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dartppt-220324180828/75/Dart-PPT-pptx-10-2048.jpg)