This document provides an overview of dams and rivers, including:
1) An introduction to dams, their purposes of irrigation, hydropower, flood control, and more.
2) Reasons for building dams such as power generation, irrigation, flood control, drinking water, recreation, and transportation.
3) Details on ancient dams from around the world dating back to 3000 BC.
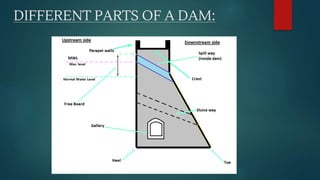
4) The different parts of a dam including the heel, crest, parapet wall, toe, abutments, conduits, cutoffs, galleries, diversion tunnels, and spillways.
5) The main types of dams classified by structure, use, and material including arch dams, gravity dams, buttress dams