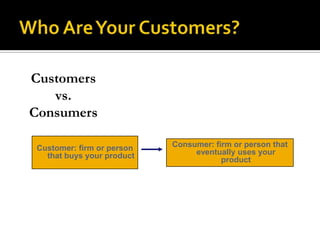
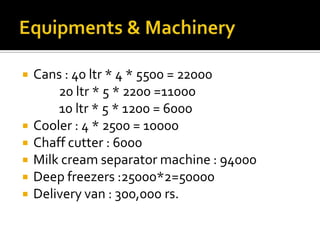
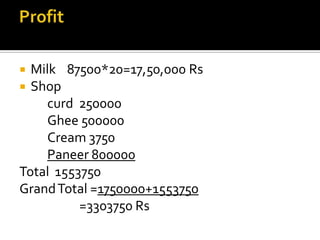
The document discusses establishing a dairy farm business in Varanasi, India. It provides details on the production, marketing, financials, operations, and human resource management of the dairy farm. Key points include producing over 125,000 liters of milk annually, earning over Rs. 30 lakhs in revenue, employing 7 people, and involving milking cows twice daily.