dailylessonlog_science_ 9_quarterweek_7.docx
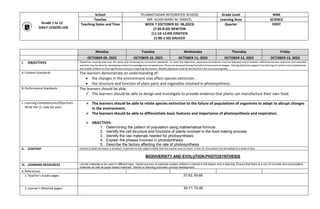
- 1. Grade 1 to 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School TELABASTAGAN INTEGRATED SCHOOL Grade Level NINE Teacher MR. ALVIN MARC M. DANCEL Learning Area SCIENCE Teaching Dates and Time WEEK 7 (OCTOBER 02- 06,2023) (7:30-8:20) NEWTON (11:10-12:00) EINSTIEN (1:00-1:50) GALILEO Quarter FIRST Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday OCTOBER 09, 2023 OCTOBER 10, 2023 OCTOBER 11, 2023 OCTOBER 12, 2023 OCTOBER 13, 2023 I. OBJECTIVES Objectives must be met over the week and connected to curriculum standards. To meet the objectives, necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are assessed during Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. A.Content Standards The learners demonstrate an understanding of: the changes in the environment may affect species extinction. the structure and function of plant parts and organelles involved in photosynthesis. B.Performance Standards The learners should be able: The learners should be able to design and investigate to provide evidence that plants can manufacture their own food. C.Learning Competencies/Objectives Write the LC code for each The learners should be able to relate species extinction to the failure of populations of organisms to adapt to abrupt changes in the environment. The learners should be able to differentiate basic features and importance of photosynthesis and respiration. OBJECTIVES: 1. Determining the pattern of population using mathematical formula 2. Identify the cell structure and functions of plants involved in the food making process 3. Identify the raw materials needed for photosynthesis 4. Explain the phases involved in photosynthesis 5. Describe the factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis II. CONTENT Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach. In the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. BIODIVERSITY AND EVOLUTION;PHOTOSYNTHESIS III. LEARNING RESOURCES List the materials to be used in different days. Varied sources of materials sustain children’s interest in the lesson and in learning. Ensure that there is a mix of concrete and manipulative materials as well as paper-based materials. Hands-on learning promotes concept development. A.References 1.Teacher’s Guide pages 37-53; 55-68 2.Learner’s Material pages 50-71; 72-85
- 2. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday OCTOBER 09, 2023 OCTOBER 10, 2023 OCTOBER 11, 2023 OCTOBER 12, 2023 OCTOBER 13, 2023 3.Textbook pages 4.Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) portal B.Other Learning Resources IV. PROCEDURES These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn things, practice their learning, question their learning processes and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. A.Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson DAY 1 Population pertains to the number of organisms of the same species living in a certain place. Biodiversity refers to the variety of life in an area. Communities with many different species (a high index of diversity) will be able to withstand environmental changes better than communities with only a few species (a low index of diversity). Population sizes vary among organisms. They change with the number of births and when they move into an ecosystem. They also change when members die or move out of an ecosystem. Limiting factors are environmental conditions that keep a population from increasing in size and help balance ecosystems. The carrying capacity is affected by changes in the environment Extinction occurs when the last member of that species dies. When the population of a species begins declining rapidly, the species is said to be a threatened species. A species is endangered when its population has become so low that it is possible of becoming extinct. Human actions have resulted in habitat loss and degradation that have accelerated the rate of extinction. The principal causes of deforestation are illegal logging, kaingin farming, forest fires, and conversion of agricultural lands to housing projects and typhoons. The effects of deforestation include soil erosion, floods, and depletion of wildlife resources. The major cause of wildlife extinction is the loss of habitat. Coral reef destruction is caused by dynamite fishing and muro-ami, while mangrove destruction is caused by overharvesting and conversion of the area into other uses. In eutrophication, nutrients are washed away from the land to enrich bodies of water. It causes excessive growth of aquatic plants and algae and results in algal bloom, which eventually die and decompose. The process depletes the oxygen dissolved in water, causing fish and other aquatic organisms to die. Acid rain is a result of air pollution mostly from factories and motor vehicles. Sustainable development means that a society should live under the carrying capacity of the environment.
- 3. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday OCTOBER 09, 2023 OCTOBER 10, 2023 OCTOBER 11, 2023 OCTOBER 12, 2023 OCTOBER 13, 2023 B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson DAY 2 Use the words in the box to complete the paragraph below. carbon dioxide chlorophyll oxygen gas photosynthesis starch sugar sunlight water 1.)_____________ is the process by which plants produce their own food in the presence of 2.)________, 3.)________and 4.)_______. Plants contain a green pigment called 5.)________ that absorbs sunlight. The raw materials coming from the atmosphere and roots react to produce 6.)_______ which is stored as food in other parts of the plant in the form of 7.)_______.Furthermore, 8.)________ is released into the environment for animals and humans to breathe. Presenting examples/instances of the new lesson Then discuss the following: Plant Structures for Photosynthesis In plants, photosynthesis mainly takes place in the leaves and little or none in stems, depending on the presence of chlorophyll. A waxy layer known as cuticle covers the leaves of all plant species. The upper and lower epidermis protect the leaves and has nothing to do with photosynthetic processes. The upper epidermis is a single layer of cells on the upper surface of the leaf, which aids the water conservation while the lower epidermis is a single layer of cells on the lower surface of the leaf, which contains stomata and guard cells. The palisade mesophyll layer is found below the upper epidermis. The spongy mesophyll is found above the lower epidermis and has the greatest number of chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll. They are important in trapping light energy from the sun. Vascular bundles (phloem and xylem) serve as transporting vessels of manufactured food and water. The xylem transports water and minerals to the leaves; the phloem transports the photosynthetic products to the other parts of the plants. Carbon dioxide and oxygen gas are collected in the spongy layer and enter and exit the leaf through the stomata. Chloroplasts are double membrane organelle with outer membrane, inner membrane, and intermembrane space. The outer membrane is permeable to small organic molecules, whereas the inner membrane is less permeable and studded with transport proteins. Intermembrane space is the space between outer and inner membrane. There are two distinct regions present inside the chloroplast known as the grana and stroma. Granum is made of stacks of disc- shaped structures known as thylakoids. The thylakoid consists of the thylakoid membrane and the enclosed region called the thylakoid lumen. Photosynthetic pigments (e.g., chlorophyll) are embedded into the thylakoid membrane, making it the site of the light dependent reaction in photosynthesis. The thylakoid lumen is used for photophosphorylation during photosynthesis. Stroma is the colorless fluid outside the thylakoid membranes in the chloroplasts. Lamella connects the stacks of thylakoids. C.Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 DAY 3 ACTIVITY: EVIDENCE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Page 79; 81-82 D.Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 DAY 4 The students will watch the video about Light- independent and light- dependent reaction the let them answer some questions. Guide Questions: 1.What are the two processes involved in photosynthesis? 2. Differentiate the two processes.
- 4. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday OCTOBER 09, 2023 OCTOBER 10, 2023 OCTOBER 11, 2023 OCTOBER 12, 2023 OCTOBER 13, 2023 3.Where do the light reactions and Calvin cycle? 4. Where do the light reactions take place? 5. Why is Calvin cycle also known as Dark Reactions? 6.What are the products of light reaction phase? 7.What are the two products of the light reactions that are needed for the Calvin cycle/Dark Reactions? 8. What are the products of the Calvin cycle/Dark Reactions? E. Developing mastery Give at least 3 important words and give its meaning in your own understanding. For example: Photosynthesis- is a process of food making done by plants and other autotrophic organisms. The presence of chlorophyll enables these organisms to make their own food. F. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living Your simple acts have a huge impact on the environment. Using Oslo/short bond paper, create a poster illustrating how you can help in taking good care of the environment. Then, write 5 sentences describing your poster. The rubrics is provided for you to be guided in achieving a remarkable score. G.Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson Plants have green pigments called chlorophyll stored in the chloroplast. This pigment aids in capturing light energy from the sun that enables plants to change it into chemical energy stored in the food. This process is called photo synthesis. There are two stages of photosynthesis: light reaction s and Calvin cycle (dark reactions) The factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis are temperature, carbon dioxide, water, and light. Providing the plant with the right amount of these materials will ensure good quality and quantity of the harvest. H.Evaluating learning ACTIVITY- EMBEDDED ASSESSMENT
- 5. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday OCTOBER 09, 2023 OCTOBER 10, 2023 OCTOBER 11, 2023 OCTOBER 12, 2023 OCTOBER 13, 2023 I. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your students’ progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A.No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B.No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C.Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D.No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did this work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I used/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Prepared by: Checked by: Noted: Alvin Marc M. Dancel Danica D. Guevarra Jennifer S. Lumanug,EdD Teacher III Master Teacher II Principal II