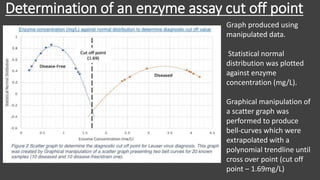
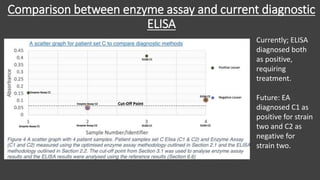
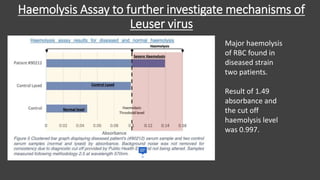
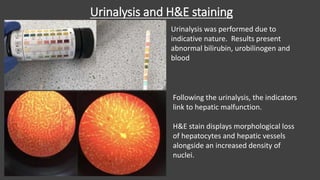
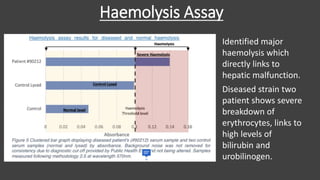
The main purpose of this research project was to develop a quantitative serological diagnostic enzyme assay to detect and differentiate between the two strains of Yellow Eye Disease. The research optimized an enzyme assay that achieved a 97.5% diagnostic success rate compared to the current ELISA method. Investigation into the pathogenesis through urinalysis, haemolysis assays, and H&E staining indicated hepatic malfunction and haemolysis in diseased patients. The results provide a foundation to improve both treatment and diagnosis of the more severe strain two of the virus.