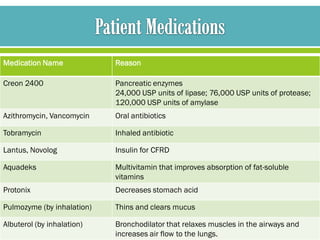
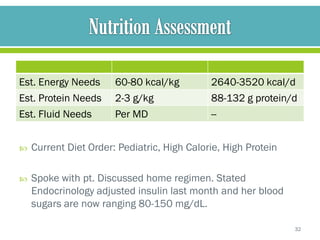
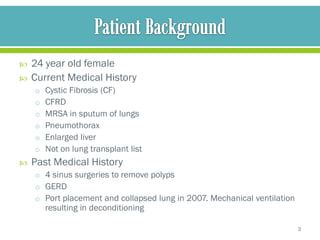
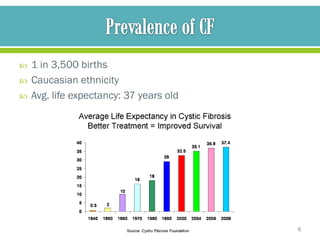
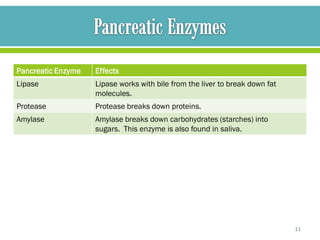
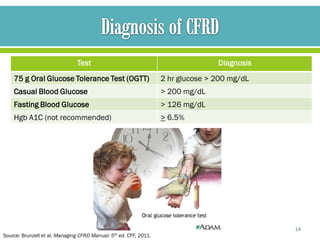
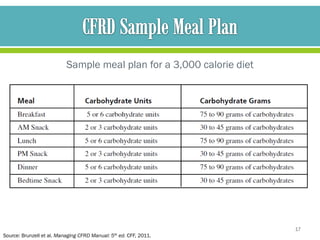
The document discusses cystic fibrosis and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes (CFRD), outlining their causes, symptoms, and treatment, including medical nutrition therapy. It also provides details of a specific 24-year-old female patient's history and condition, including her diagnosis of CFRD, and outlines her nutrition assessment, diagnosis, and prescribed nutrition interventions and monitoring.











![Step 3: Calculate Daily Energy Expenditure,
taking into account the degree of steatorrhea
• For pancreatic sufficient pts (including pts w/ a coefficient of fat
absorption [CFA] >93%)
• Daily energy requirement equals the daily energy expenditure
• For pancreatic insufficient pts
• Daily energy requirement equals the daily energy expenditure
time 0.93/CFA
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cysticfibrosiscasestudypresentationpdf-120926153431-phpapp02/85/Cystic-Fibrosis-Nutritional-Case-Study-Presentation-23-320.jpg)