The document proposes using homomorphic encryption to encrypt controllers in networked control systems. It aims to conceal both signals and parameters within the controller to protect against hacking and theft. The approach divides linear control operations to apply homomorphic properties of encryption schemes like RSA and ElGamal. Simulation results show the encrypted controller successfully regulates the plant while hiding system dynamics from identification attempts. Future work will incorporate attack detection and evaluate computation costs of the encrypted controller approach.


![Introduction
3
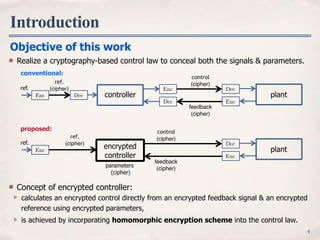
Controller device is important, but exposed to threats of hacking and targeted attacks.
signals: modeling, stealing recipe, management policy and know-how
parameters: knowledges about system designs and operations
Attacks on networked control system
plantcontroller
ref. (recipe)
control signals
feedback signals
parameters
[1] Sandberg et al., 2015. [2] Sato et al., 2015. [3] Pang et al., 2011
Related works
aiming to conceal the signals
control-theoretical approach: detection[1], positive use of noises[2]
cryptography-based approach: encryption of communication links[3]
no studies considering encryption of the controller or its inside…
control
(cipher)
feedback
(cipher)
EncDec
Enc Dec
plantcontroller
ref.
ref.
(cipher)
Enc Dec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-3-320.jpg)
![Problem Statement
5
Encryption of linear controller
Consider a linear controller: f
Controller Encryption Problem:
Given an encryption scheme , for a control law realize an encrypted law .fE fE
Define an encrypted control law , given an encryption scheme , satisfyingfE E
x[k + 1]
u[k]
=
A B
C D
x[k]
y[k]
:= ⇠[k] := f( , ⇠[k])
: parameter matrix
: plant output
: control inputu
y
5
control
(cipher)
feedback
(cipher)
Enc
Dec
plant
parameters
(cipher)
Enc(y)
Enc(u) u
y
Enc( )
fE (Enc( ), Enc(⇠))
fE (Enc( ), Enc(⇠)) = Enc(f( , ⇠))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-5-320.jpg)
![RSA encryption[4,5] (deterministic) & ElGamal encryption[6] (stochastic)
ElGamal encryption scheme[4]
key generation: public , and private (random)
encryption:
decryption:
Controller Encryption 1/3
6[4] Rivest, “A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystem”, 1978. [5] Rivest, “On Data Banks and Privacy Homomorphisms”, 1978.
Homomorphic encryption schemes
RSA: Rivest-Shamir-Adelman
Dec(c1, c2) = c2 ⇥ c s
1 mod p
g, p, s 2 N(g, p) s
r 2 N: randomEnc(m) = (gr
mod p, m ⇥ gsr
mod p)
= c1 = c2 m: integer in plaintext space
: integer in ciphertext spacec1, c2
Homomorphism
definition
Enc(m1 • m2) = Enc(m1) ⇤ Enc(m2)
in the case of ElGamal
·: multiplication ⇤ : modulo operation
plaintext
space
ciphertext
space
m1
m2
⇥
⇥
⇥
m2•m1
⇥
⇥
⇥
Enc(m1)
Enc(m2)
N N2
Enc
Enc
Enc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-6-320.jpg)
![Controller Encryption 2/3
7
Idea for controller encryption
Divide the linear operation to apply the homomorphism.
f = f+
f⇥
f⇥
( , ⇠) =
⇥
1⇠1 2⇠2 · · · L⇠L
⇤
=:
← executed after the decryption
← executed in the controller device
modification of the decryption process to update the decryption algorithm with “Dec+
”.
Dec+
Configuration using ElGamal encryption scheme
signals
(cipher)
feedback
(cipher)
Enc
Dec
plant
parameters
(cipher)
Enc( )
Enc( )
f+
f⇥
Enc(⇠)
x[k + 1]
u[k]
⇠
fE (Enc( ), Enc(⇠))
f+
( ) =
LX
l=1
l](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-7-320.jpg)
![with and sufficient large, rounding (quantization) error can be made small.a
encrypted
controller
u[k]
y[k]
Enc
Enc(KpM)
Enc(yM[k])
Enc(uM[k])
a 2
yM[k]
uM[k]
ba•e
plant
Dec+
n
Controller Encryption 3/3
8
a 2 N
b•e : round function
KpM = ba ⇥ Kpe
yM[k] = ba ⇥ y[k]e
uM[k] = KpMyM[k]
Kp
y[k]
u[k] = Kpy[k]
example: , then .Kp = 0.83, a = 1000 KpM = b1000 ⇥ 0.83e = 830
Remarks
Signals & parameters are real; Plaintext is integer.
need a map: multiplying by a natural number and rounding off to an integer, i.e.,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-8-320.jpg)
![Simulation: Controller Encryption
9
(key length 25bit)
Things seen in controller
encrypted
controller
normal:
proposed:
u[k]
y[k]
controller
n = 67108913 g = 3
Enc( )
=
2
4
1 0.0063 0
0 0.3678 0.0063
10 99.90 3
3
5
=
Enc(x[k])
Enc(y[k])
Enc(⇠[k])
Enc( [k])
0 1 2 3 4 5
-3
-2
-1
0
1
0 1 2 3 4 5
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
time [s] time [s]
control output
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
6 signals related to control
2 signals related to output
0 1 2 3 4 5
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
0 1 2 3 4 5
-3
-2
-1
0
1
Enc( )2 =
2
4
14170023 24305287 4114472
24817983 26559389 33379406
29922594 31813162 24125985
3
5
Enc( )1 =
2
4
16354115 11333831 12428094
25939844 22437363 17650745
23018684 228286 8037052
3
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-9-320.jpg)
![Validation: Protection from Stealing
10
System identification (n4sid)
-150
-100
-50
0
50
10-2
100
102
-270
-225
-180
-135
-90
-45
0
frequency [rad/s]
gain[dB]phase[deg]
original closed loop system
without encryption
with encryption(RSA)
with encryption(ElGamal)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-10-320.jpg)
![Conclusion
11
Introduction
Problem Statement
controller encryption problem
Encrypted Controller
homomorphism of specific encryption scheme
remarks in quantization error
Simulation & Validation
enable to conceal signals & parameters inside
the controller device in terms of cryptography.
enable to hide dynamics of the control system.
Future works
incorporate an attack detection method.
validate computation cost of encrypted controller.
-150
-100
-50
0
50
10-2
100
102
-270
-225
-180
-135
-90
-45
0
frequency [rad/s]
gain[dB]phase[deg]
original closed loop system
without encryption
with encryption(RSA)
with encryption(ElGamal)
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
time [s]
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
× 107
0 1 2 3 4 5
0
1
2
3
4
× 107](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/151215cdcencctrller-151218105831/85/Cyber-Security-Enhancements-of-Networked-Control-Systems-Using-Homomorphic-Encryption-11-320.jpg)