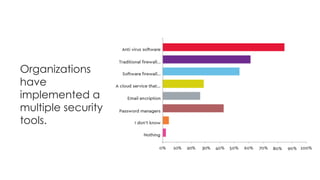
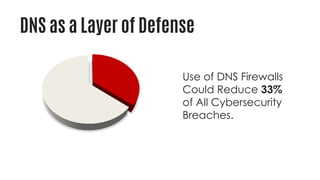
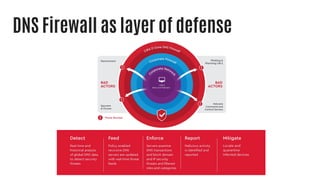
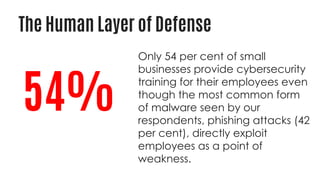
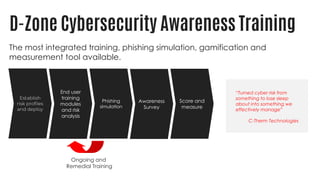
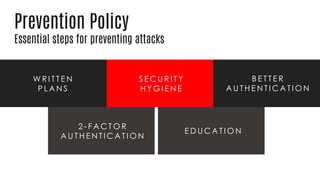
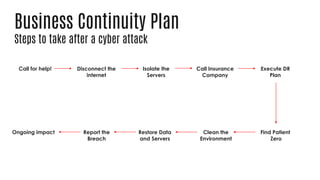
This document summarizes a cyber security planning panel discussion. The panelists discussed (1) the importance of cyber security for all organizations, even small and medium enterprises, as attackers target any organization that may have assets; (2) that all organizations have cyber security responsibilities to customers, stakeholders, and authorities; and (3) that organizations can take action to improve their cyber security through basic measures and defenses. The panel then covered specific cyber security threats like ransomware and weaponized artificial intelligence, trends showing small businesses and public sectors are increasingly targeted, and best practices for mitigation including having a plan, insurance, and a cyber security partner.