For the full video of this presentation, please visit: https://www.edge-ai-vision.com/2025/08/customizing-vision-language-models-for-real-world-applications-a-presentation-from-nvidia/
Monika Jhuria, Technical Marketing Engineer at NVIDIA, presents the “Customizing Vision-language Models for Real-world Applications” tutorial at the May 2025 Embedded Vision Summit.
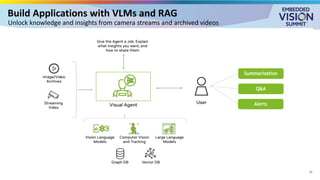
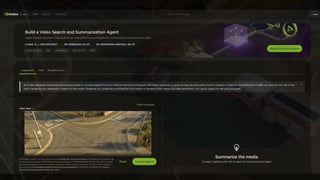
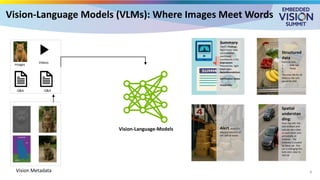
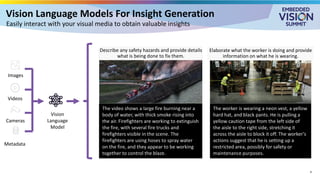
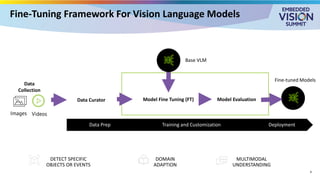
Vision-language models (VLMs) have the potential to revolutionize various applications, and their performance can be improved through fine-tuning and customization. In this presentation, Jhuria explores the concept and shares insights on domain adaptation for VLMs. She discusses the factors to consider when fine-tuning a VLM, including dataset requirements and the resources available to developers.
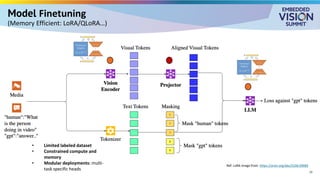
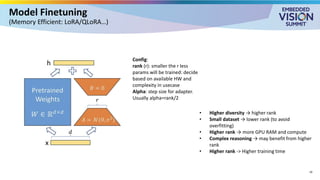
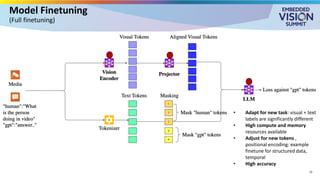
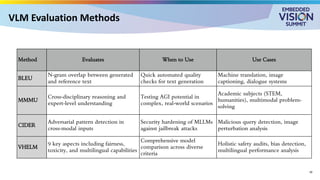
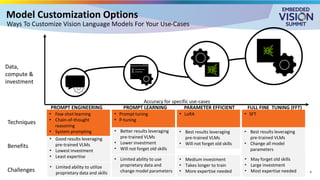
Jhuria explores two key approaches for customization: VLM fine-tuning, encompassing memory-efficient fine-tuning methods such as low-rank adaptation (LoRA) and full fine-tuning, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for enhanced adaptability. Finally, she discusses metrics for validating the performance of VLMs and best practices for testing domain-adapted VLMs in real-world applications. You will gain a practical understanding of VLM fine-tuning and customization and will be equipped to make informed decisions about how to unlock the full potential of these models in your own projects.



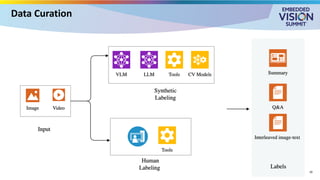
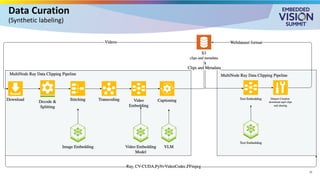
![Data Curation
(Type of Labels)
Q&A
Media
MCQ Style:
Questions: What Kind of anomaly
is present in this scene?
Options:
A: Pedestrian jaywalking
B: Vehicle running a red light
C: Pedestrian crossing at marked
crosswalk
GQA Style:
Questions: What unsafe action is
happening and why is it
dangerous?
Answer: The person is crossing
outside the designated
crosswalk….
Structured Style:
Question: Describe the occurred anomaly in the traffic
scene. Response in a json format: {“anomaly_type”: ,
“bbox”:.., “alert”:..}
Answer:
{
“anomaly_type”: “pedestrian jaywalking”,
“bbox”: [450, 300, 500, 600],
“alert”: “Pedestrian jaywalking detected”
}
Spatial Style:
Questions: “Describe the anomaly, including where
and how it’s occurring?”
Answer: “ A pedestrian is jaywalking at the bottom-
right of the frame (around 70% from the left, 85%
from the top), stepping onto the road outside the
marked crosswalk..”
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t1w11jhurianvidia2025-250818151246-5361a63e/85/Customizing-Vision-language-Models-for-Real-world-Applications-a-Presentation-from-NVIDIA-12-320.jpg)