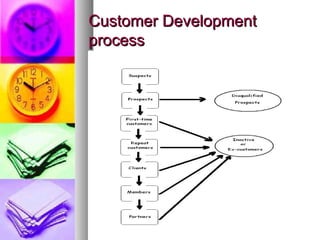
This document discusses customer relationship management (CRM) strategies. It defines CRM as a process that seeks to build long-term customer relationships through carefully managing customer information and touchpoints. It outlines a four-step CRM framework involving identifying, interacting with, differentiating between, and customizing for customers. The document also discusses increasing customer lifetime value, attracting and retaining customers, handling complaints, building loyalty, and provides examples from Apple and Harley-Davidson.