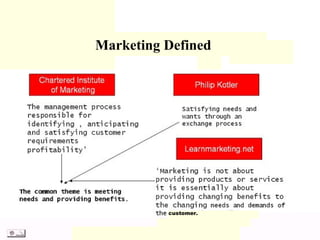
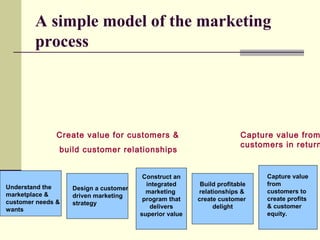
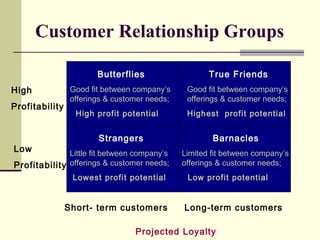
This document provides an overview of key marketing concepts from Philip Kotler's book "Principles of Marketing". It defines marketing as satisfying customer needs and building relationships to create value for customers and capture value in return. The goal of marketing is to attract and retain customers by delivering superior value and satisfaction. It discusses the production, product, selling, marketing, and societal concepts of organizing a business. It also covers customer relationship management, lifetime value, equity, and strategies for building relationships with different customer types.