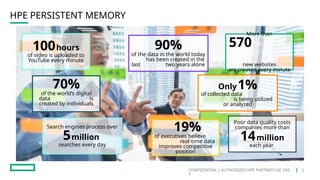
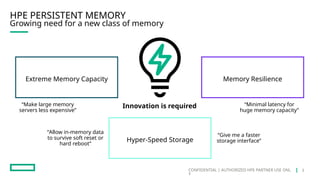
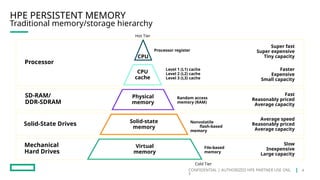
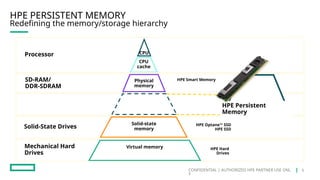
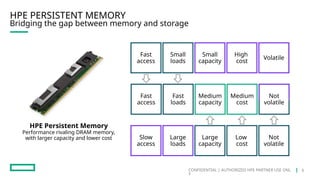
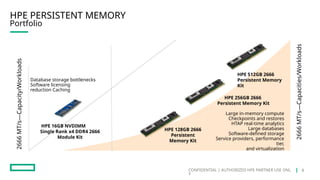
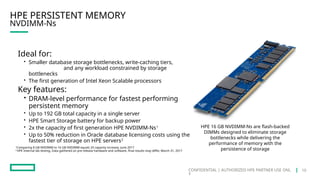
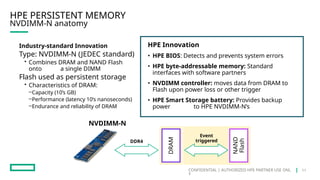
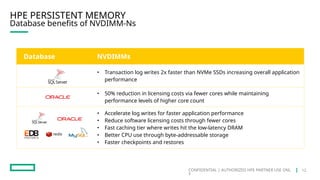
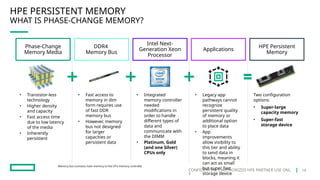
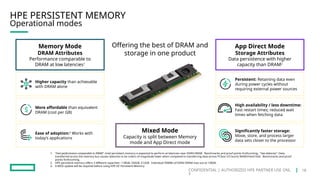
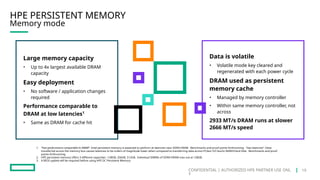
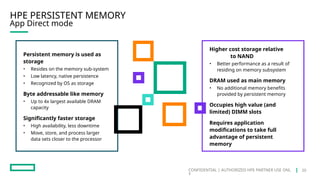
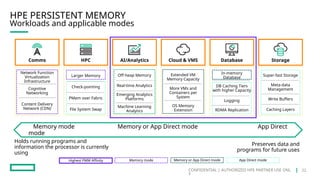
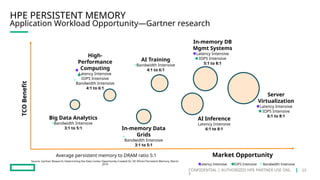
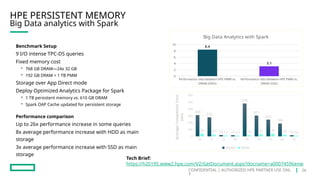
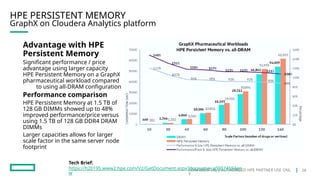
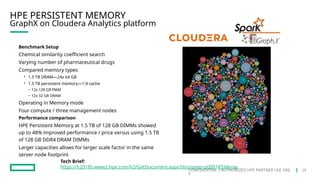
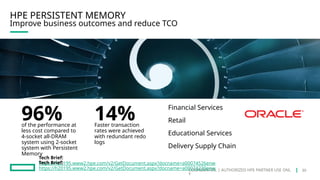
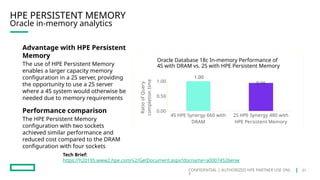
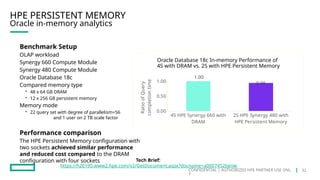
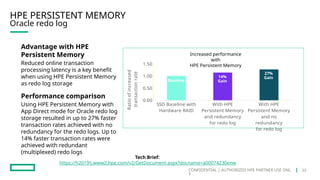
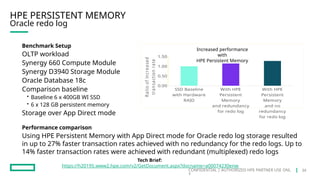
HPE's persistent memory portfolio provides innovative solutions that bridge the gap between memory and storage, enabling greater capacity and performance at lower costs. With technologies like NVDIMM-N and significant improvements in data processing speeds, HPE persistent memory enhances capabilities for real-time analytics, large database operations, and AI applications. This technology is designed for various workloads, offering flexible configurations and substantial performance benefits compared to traditional memory and storage solutions.