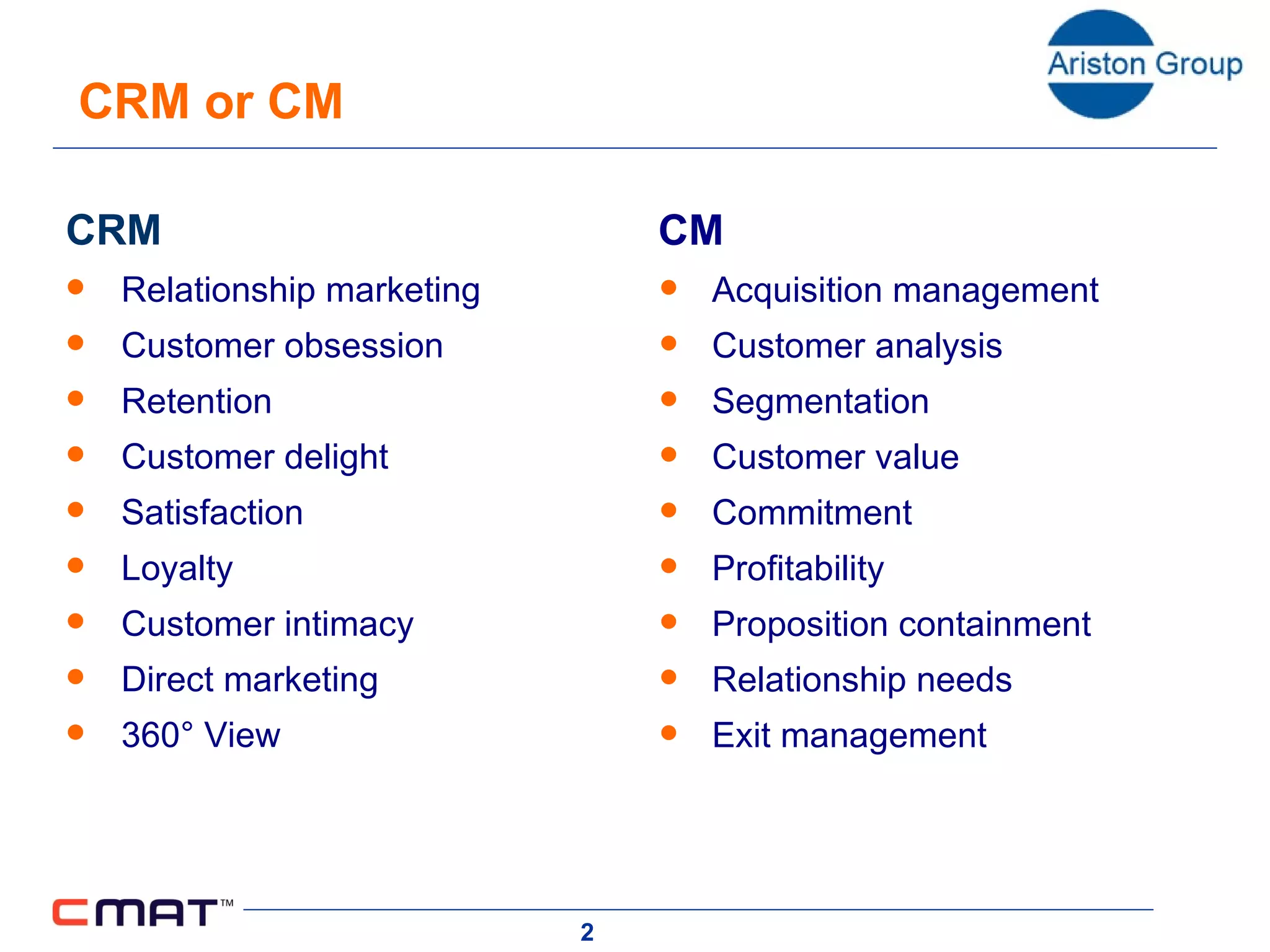
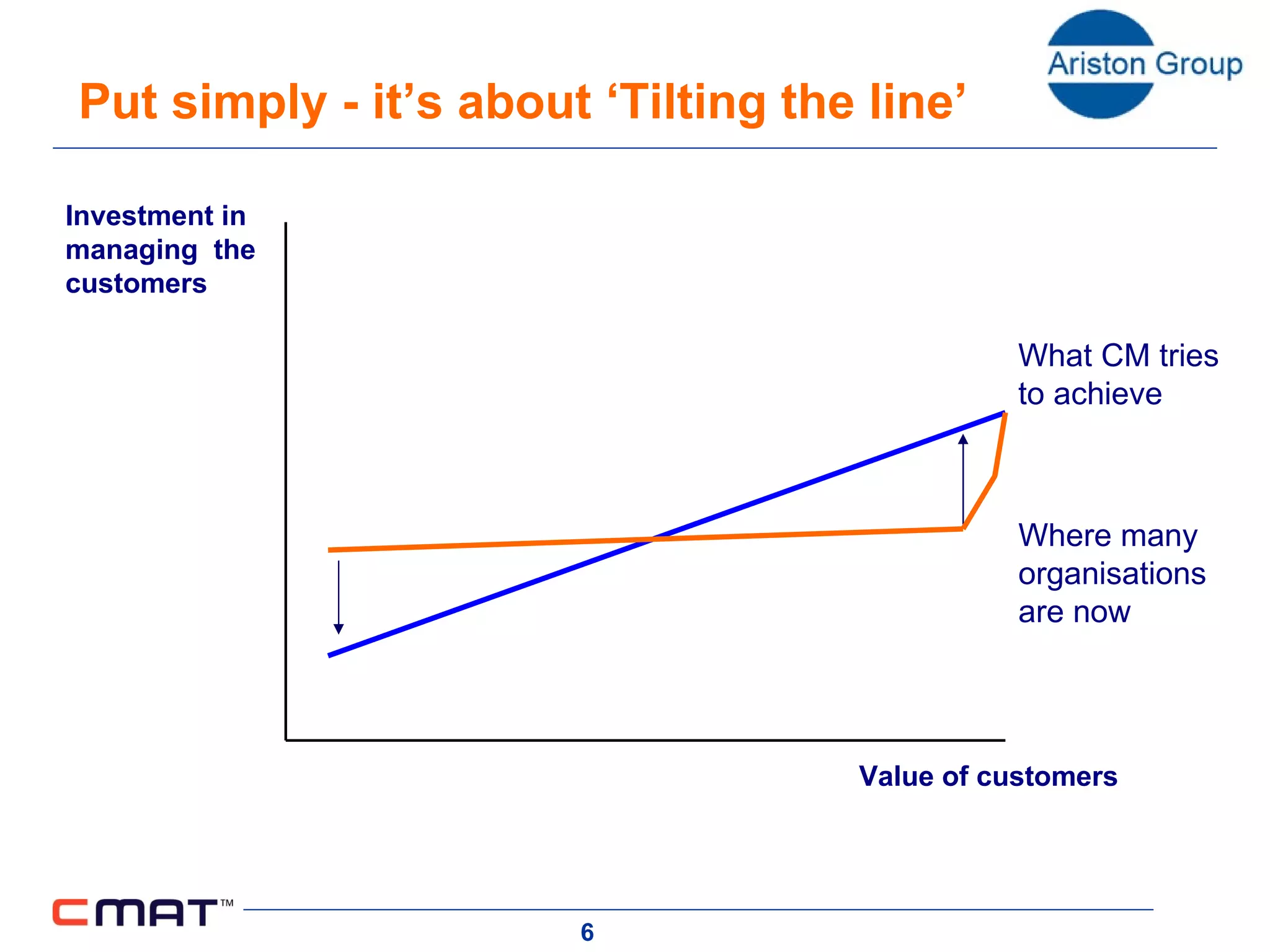
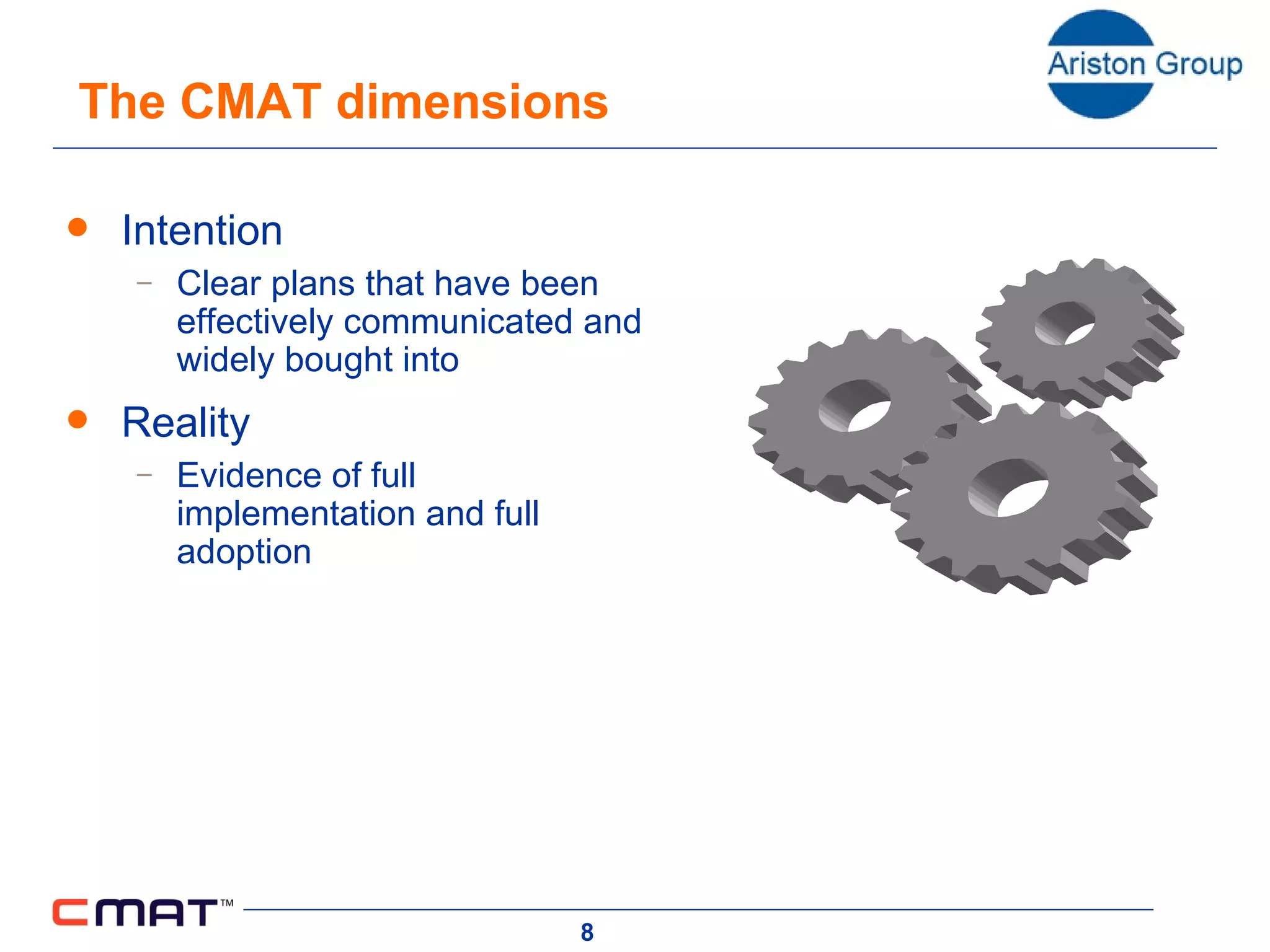
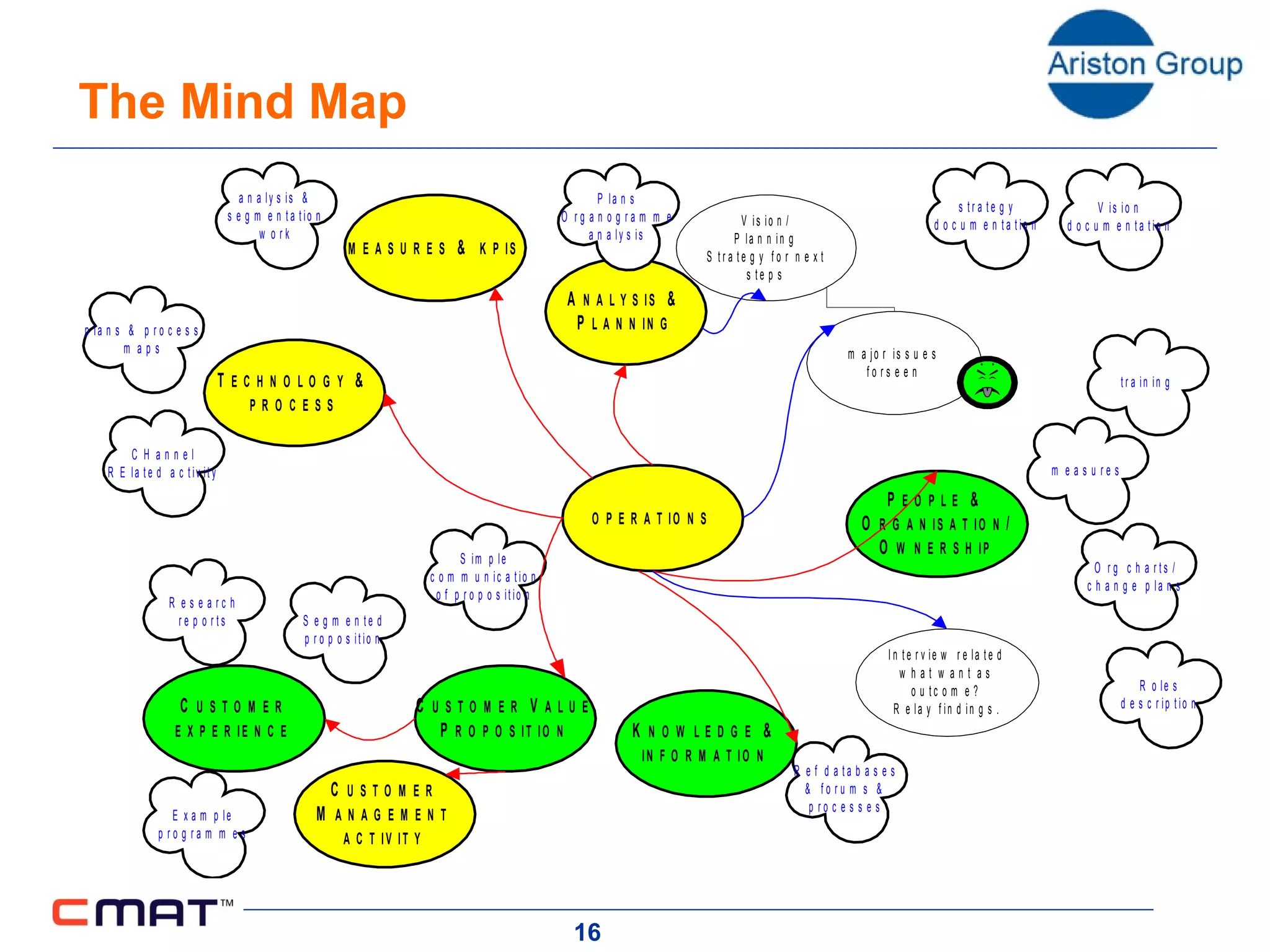
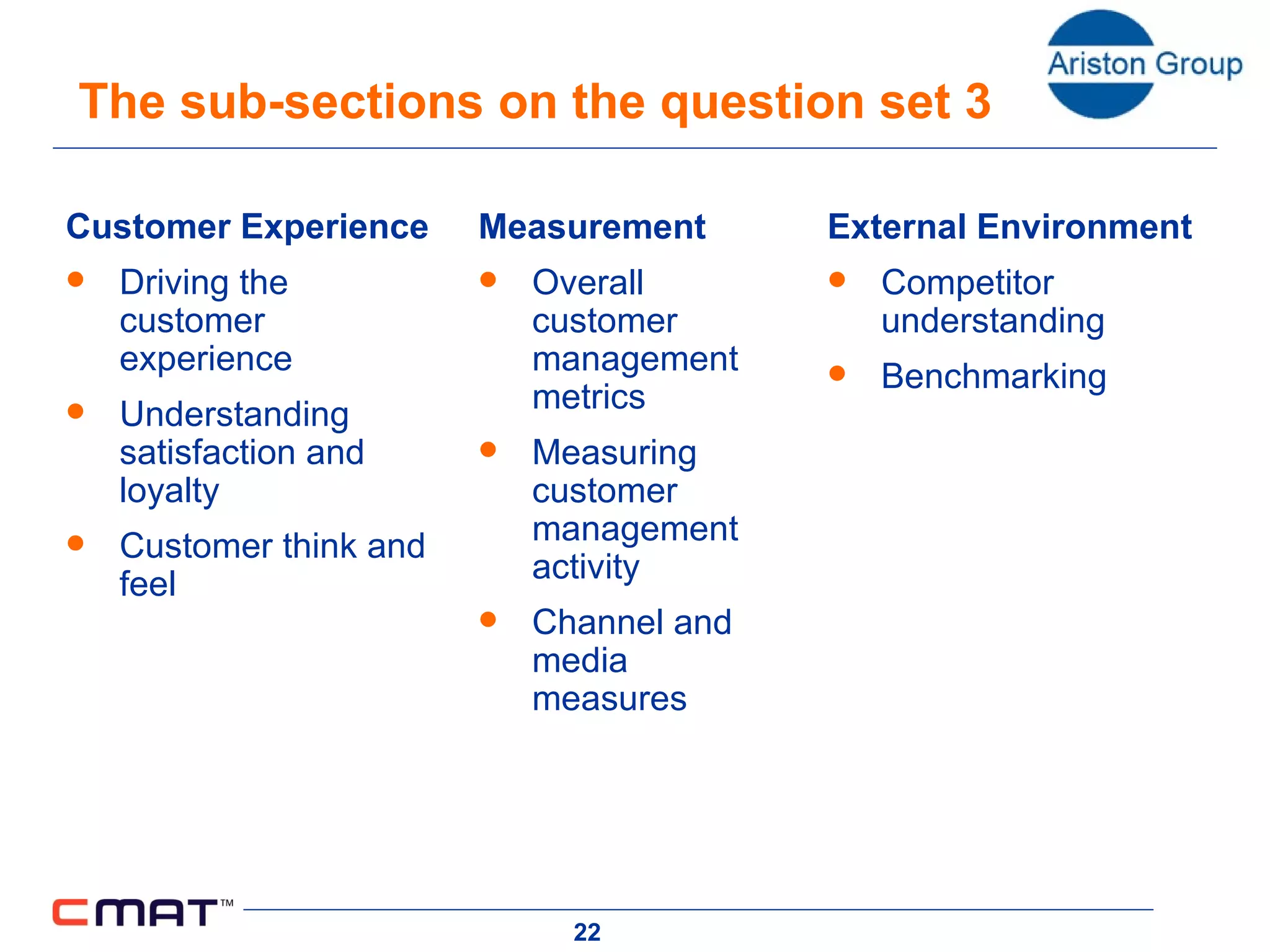
The document outlines a customer management assessment (CMAT) tool that organizations can use to evaluate how effectively they manage customers. The CMAT examines an organization's intentions, plans, and implementation of customer management practices across multiple dimensions. It provides a scored assessment against a clear model and benchmarks, identifies areas for improvement, and can be used as a planning and change tool. On average, organizations score 35% on the CMAT, with a best score of 67% and worst of 17%. Scores are not improving significantly over time.