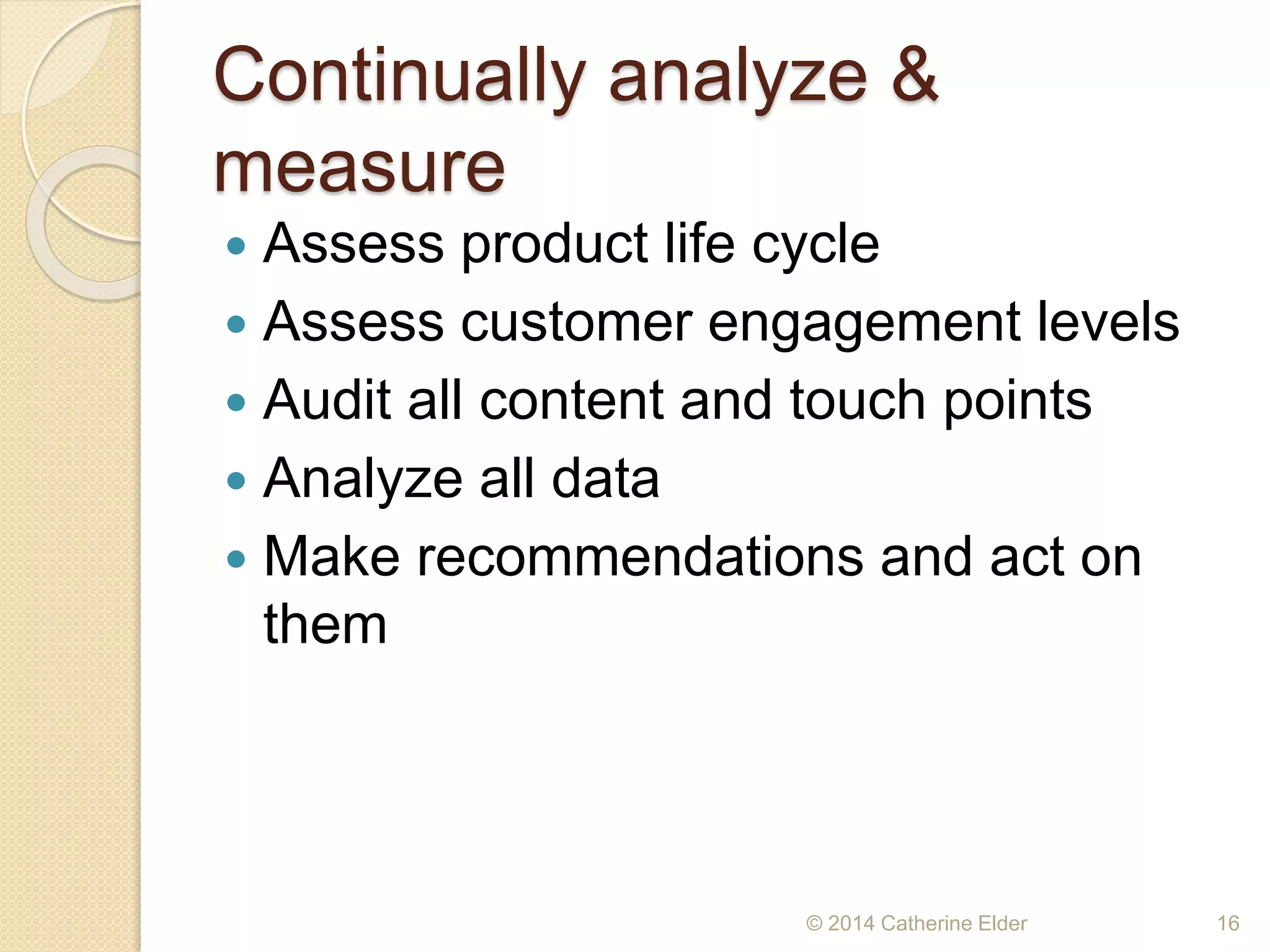
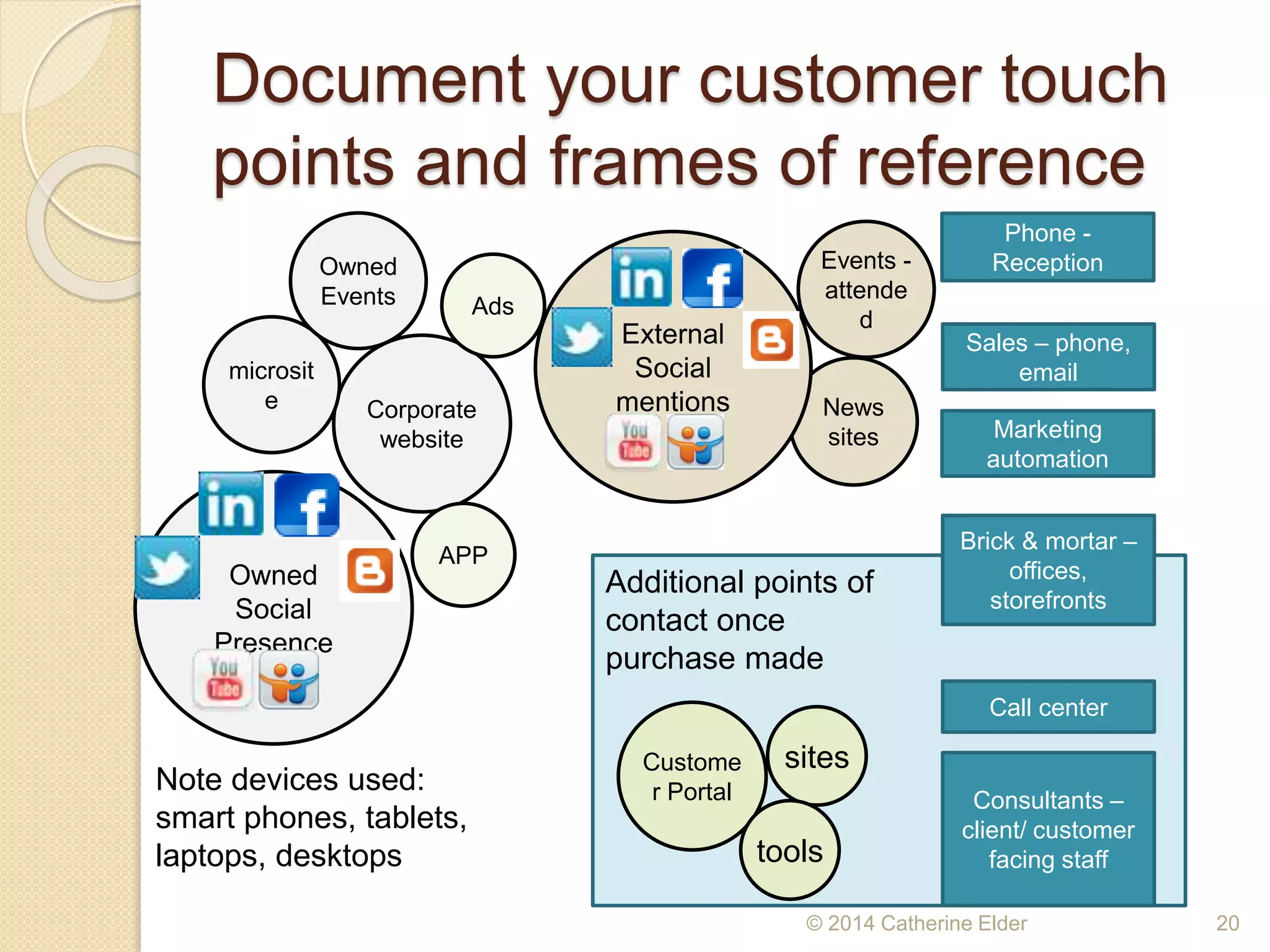
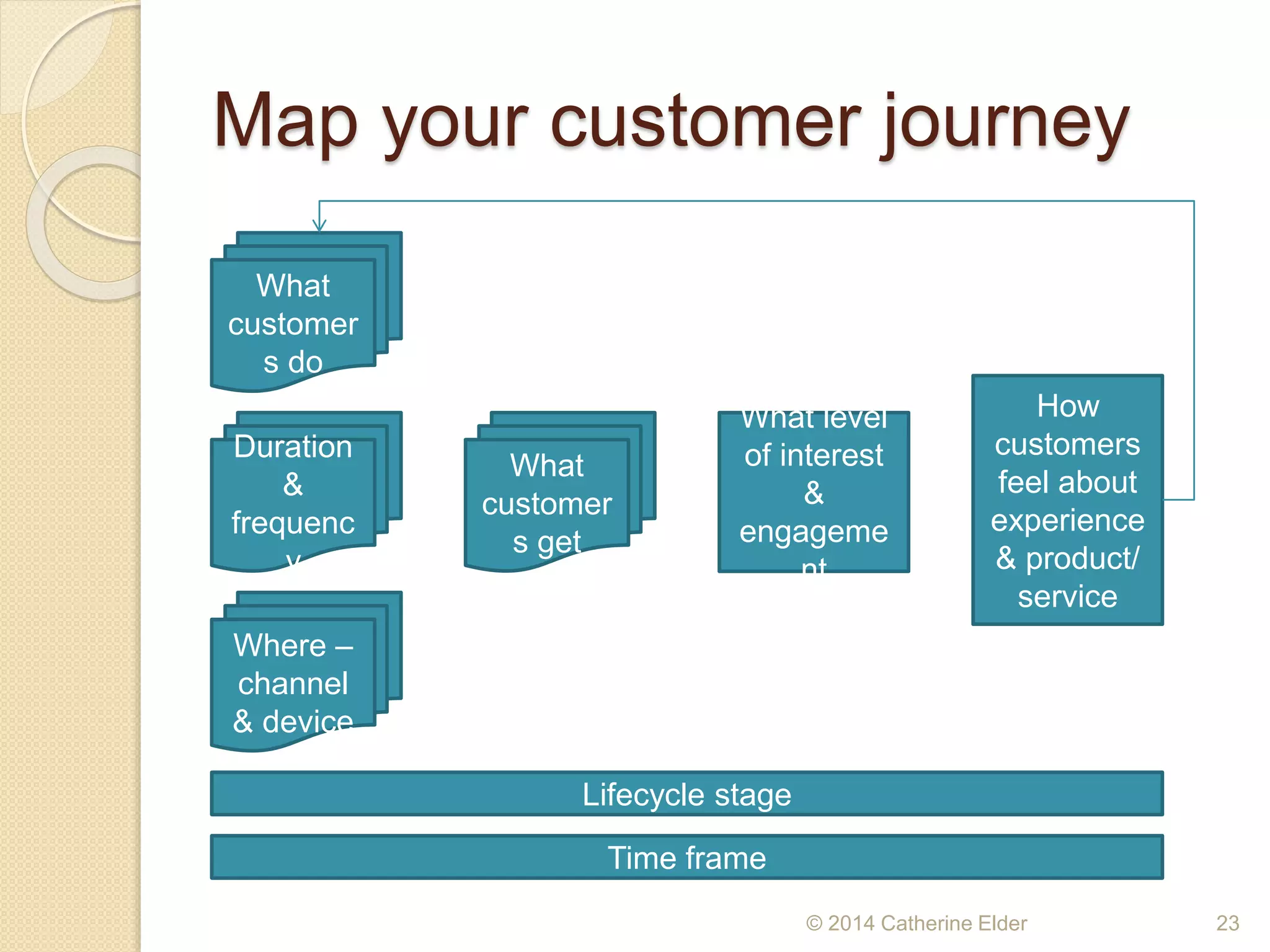
The document outlines the importance of customer journey mapping to enhance understanding of the customer experience from prospect to repeat purchase. It details stages of the customer journey, key attributes influencing purchase decisions, touchpoints for customer interaction, and emphasizes the need for ongoing analysis of customer engagement and product lifecycle. Strategies for improving customer experience and service post-purchase are also discussed to foster loyalty and advocacy.