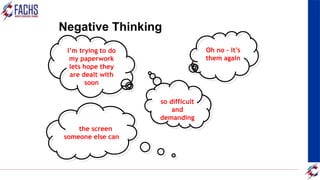
The document outlines a training program focused on communication skills and customer care, detailing its objectives, content, and key skills for effective customer service. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs, providing excellent service, and maintaining a professional image. Additionally, it discusses various metrics for measuring customer satisfaction and the significance of an efficient supply chain in enhancing customer experience.


![1. Green
- Who is a customer?
- Explain the assertion that: ‘
The Customer is always
right?’ [5 Marks]
Do Activity
Challenge (Spicy)
Extension:
List and explain 3 things
that make up an
organisations image.
(10 marks)
2. Amber
List 5 effective
communication skills a
customer services person
needs
[5] Marks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fachscustomercareday3-4autosaved-230603001239-5e59552e/85/CUSTOMER-CARE-pptx-3-320.jpg)












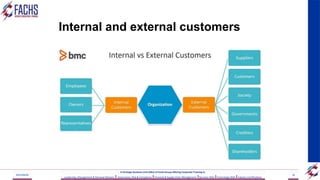






























































![TASK 5
• Question 5 (SO 5, AC 1, AC 4)
• Define supply chain management and indicate how
the components of supply chain management can
be used to improve customer service [10]
• Question (SO 2; AC 1, AC 2, AC 3, AC 4)
• In groups outline the main goods and services your
organisation(s) offer to their external clients. On
each of the identified goods and services indicate
how you would know that you have met the
customer’s expectations or exceeded them. [10]
2023/06/03
A Strategic Business Unit (SBU) of Fachs Group offering Corporate Training in:
Leadership, Management & Personal Mastery I Governance, Risk & Compliance I Financial & Supply Chain Management I Business Skills I Technology Skills I Industry Certifications
81](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fachscustomercareday3-4autosaved-230603001239-5e59552e/85/CUSTOMER-CARE-pptx-81-320.jpg)