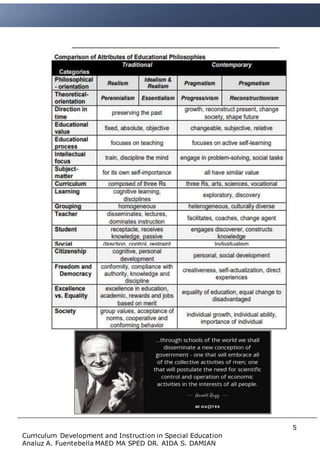
The document discusses the implications of using an outdated curriculum for 10 years without updating it. It notes that science and our understanding of learning progresses rapidly, so keeping the same curriculum for a decade without changes is not good practice. The pace of new discoveries about learning processes, environments, teaching methods, and sociocultural factors that influence learning mean the knowledge base for education is constantly evolving. An outdated curriculum that does not incorporate current research may not support students in reaching deep understanding or effective teaching. Schools need curricula that reflect the best scientific data on human learning to create supportive environments that optimize student learning.