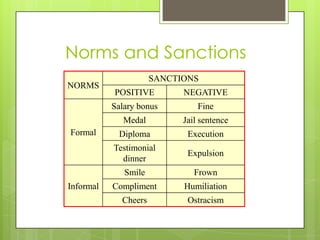
This document defines and discusses key concepts related to culture. It states that culture refers to the total way of life of a society and includes material and nonmaterial aspects. Material culture includes tangible objects while nonmaterial culture consists of intangible creations like beliefs and social norms. Some key components of culture discussed are norms, sanctions, values, symbols, and language. Norms establish standards of behavior while sanctions are rewards or penalties for following or violating norms. Values indicate what a culture deems good or bad. Symbols represent shared meanings, and language is a fundamental part of human social life and culture.