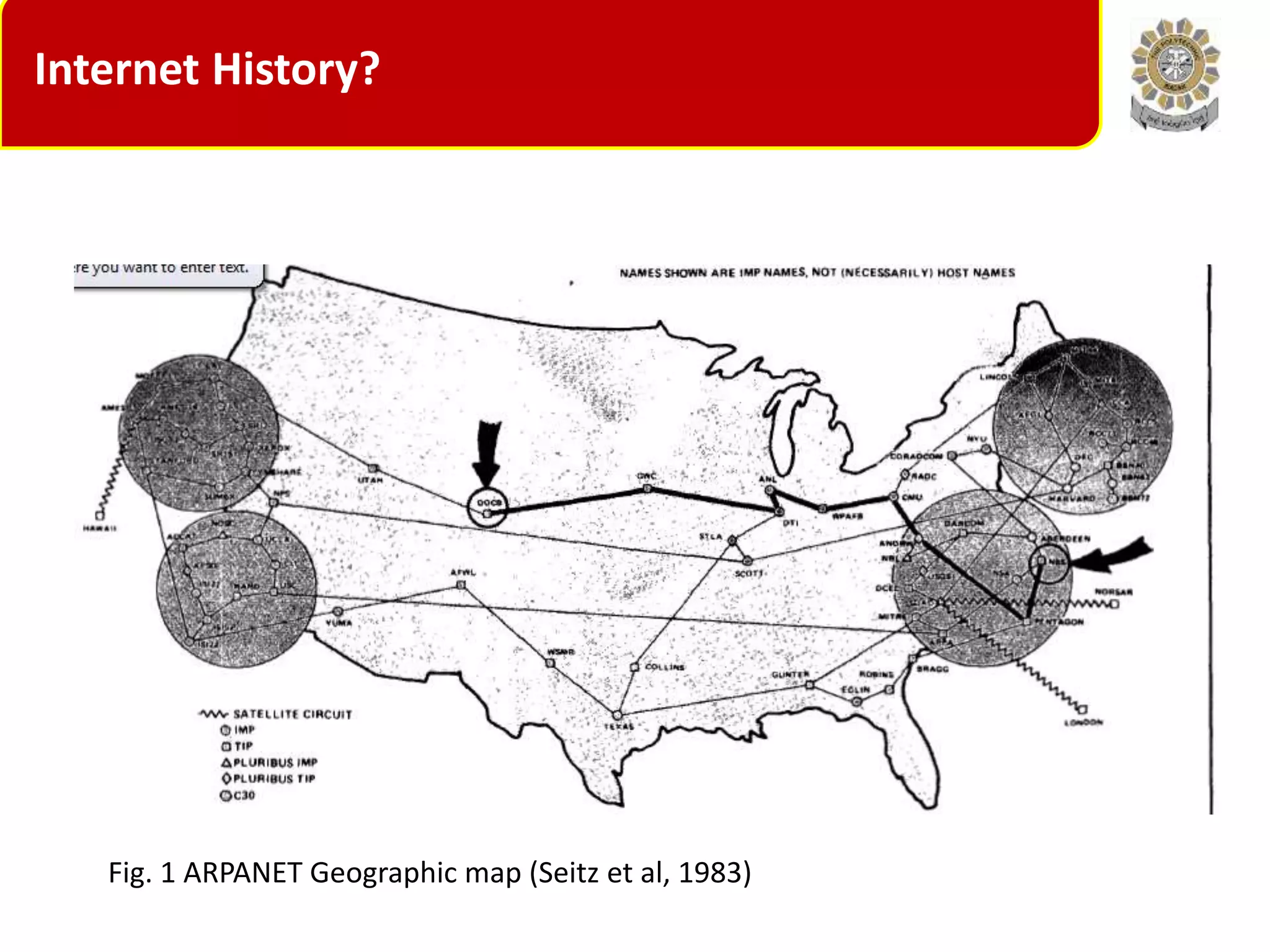
The document outlines the course content for CTE 216 on Internet Technology, covering topics such as internet history, ARPANET, NSFNET, and various network types. It also details course outcomes and the evolution of the internet, highlighting key figures and events in its development. Additionally, it includes review questions to reinforce understanding of essential concepts.