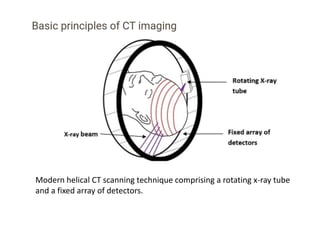
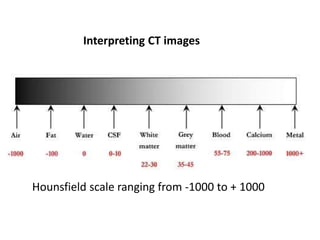
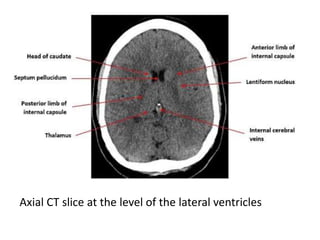
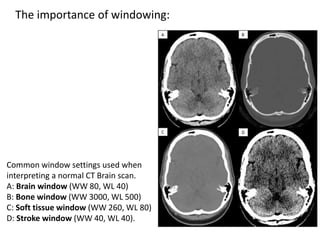
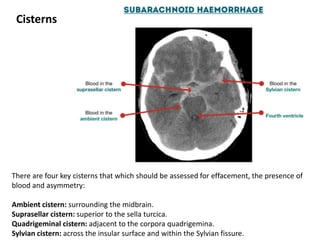
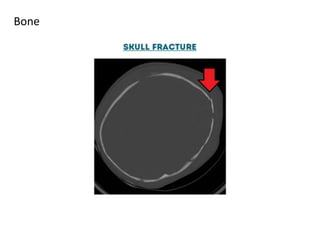
A CT head scan uses rotating x-rays and detectors to produce axial slices of the brain at different levels, which are interpreted using different window settings to highlight soft tissues, bones, and other structures. Key features examined include the lateral and third ventricles, pituitary fossa, pons, cisterns, and bones. Conditions like hydrocephalus and blood in the cisterns or ventricles can be identified.