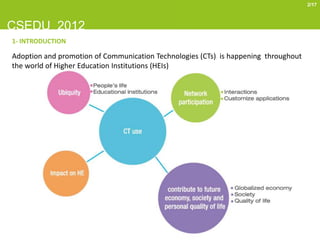
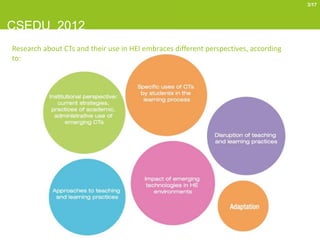
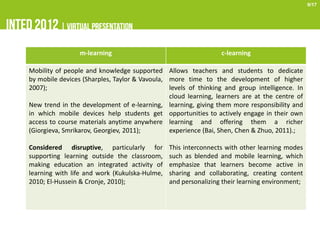
This document provides a literature review on the emerging use of communication technologies (CTs) in higher education. It summarizes that CTs, especially Web 2.0 tools, are increasingly being adopted in higher education to support teaching and learning. Popular tools include social networking sites, wikis, media sharing, virtual worlds, and personal learning environments. While CTs are disrupting traditional teaching methods, their integration into higher education is still a work in progress, with gaps in infrastructure and teacher training remaining barriers to adoption. The review aims to understand which CTs are used and how to inform the ongoing TRACER project analyzing CT adoption in Portuguese universities.