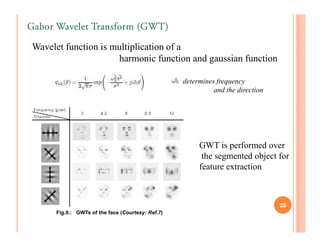
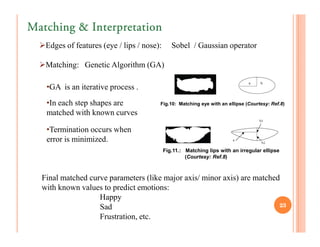
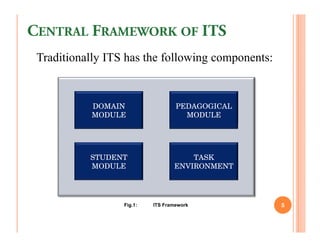
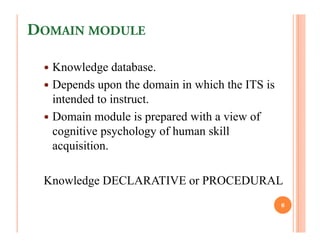
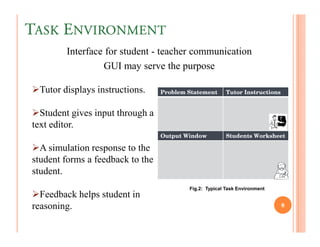
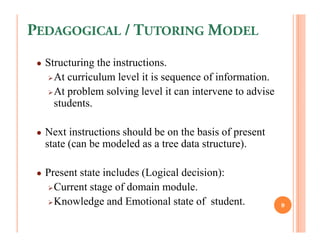
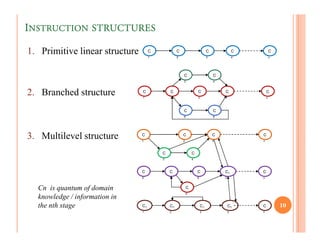
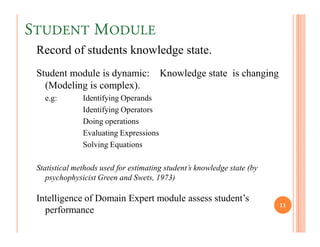
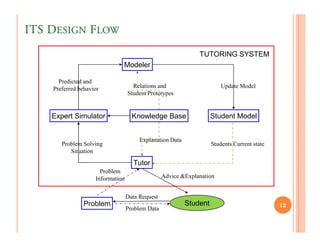
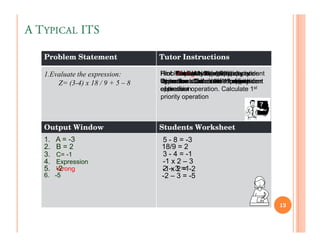
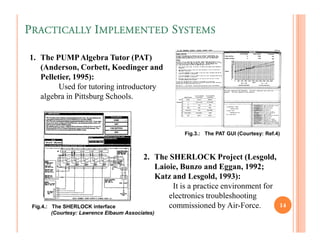
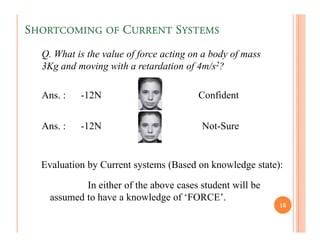
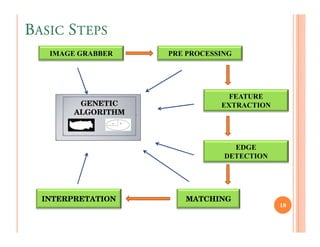
The document discusses intelligent tutoring systems and their components. It describes the typical framework of an ITS which includes domain, student, and pedagogical modules. The domain module contains the knowledge base, student module tracks the student's performance, and the pedagogical module structures instructions. Newer generations of ITS aim to enhance learning through emotional feedback analyzed from students' facial expressions.





![Resistive Fuse Network
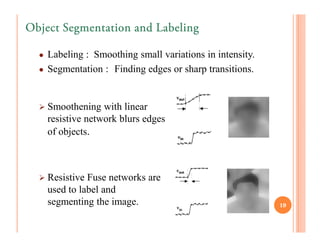
The resistive fuse acts as a linear resistor
for |Vdiff| < Voff
Acts as an open circuit for |Vdiff| > Voff
Fig.5.: Fuse Resistor
The change in voltage at each node
can be calculated from Kirchoff’s current law:
Vout2,2(t+1) – Vout2,2(t) =
v[ ∑ G(Vout i,j – Vout2,2) + σ(Vin2,2- Vout2,2) ]
i,j∈N
2,2
Fig.6.: Segmentation Circuit 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt11ec65r09-120423033641-phpapp02/85/Intelligent-Tutorial-System-20-320.jpg)
![The equation v[ ∑ G(Vout i,j – Vout2,2) + σ(Vin2,2- Vout2,2) ]
i,j∈N
2,2
can be realized in FPGA:
Fig.7.: Raster Scan of the image
(Courtesy: Ref.7)
e = sample pixel
a – i = neighbor pixel
Smem = pixel data Vin is stored
Dmem = Output data Vout is stored
LUT1 performs σ evaluation
LUT2 performs G (fuse value)
per channel (RGB)
21
Fig.8.: FPGA implementation (Courtesy: Ref.7)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt11ec65r09-120423033641-phpapp02/85/Intelligent-Tutorial-System-21-320.jpg)