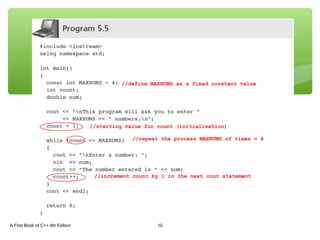
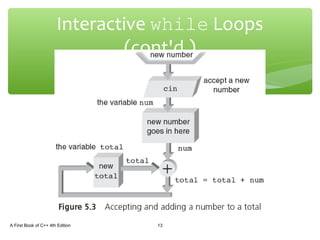
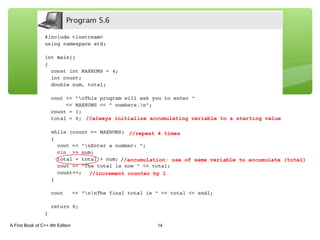
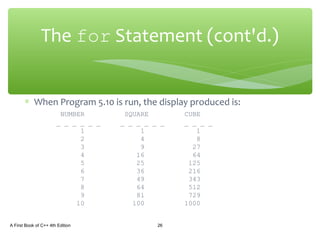
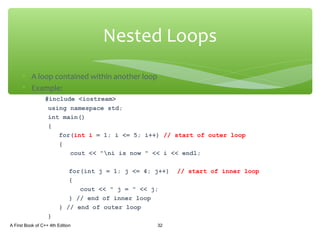
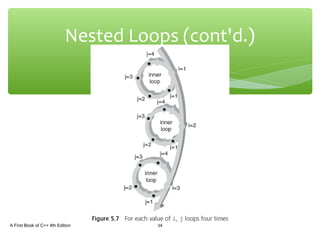
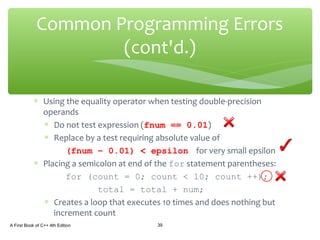
The document discusses repetition structures in C++ including while, for, do-while loops, and nested loops. It covers the basic syntax of each loop, how they evaluate conditional expressions, and examples of using loops to repeat tasks like input/output or calculations. Common errors like off-by-one issues or accidentally changing loop counters are also reviewed.