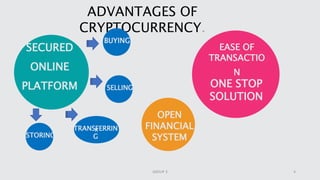
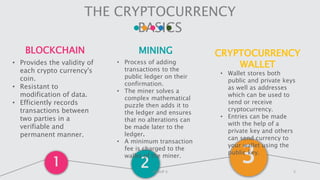
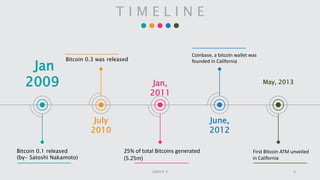
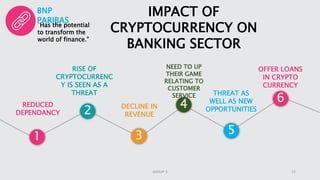
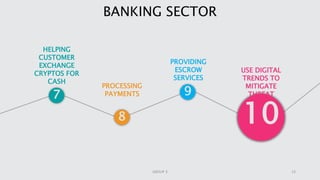
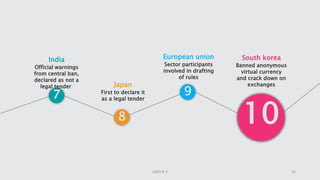
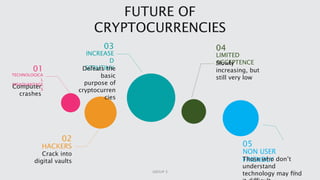
Cryptocurrency is a digital asset utilizing blockchain technology for secure transactions and operates independently from central authorities. The document covers the fundamentals of cryptocurrency, including its definition, how it works, advantages, and methods for buying and selling. It also discusses the impact of cryptocurrencies on the banking sector and the legal landscape in various countries, as well as potential future challenges and opportunities.