The document provides an overview of Bitcoin, including:
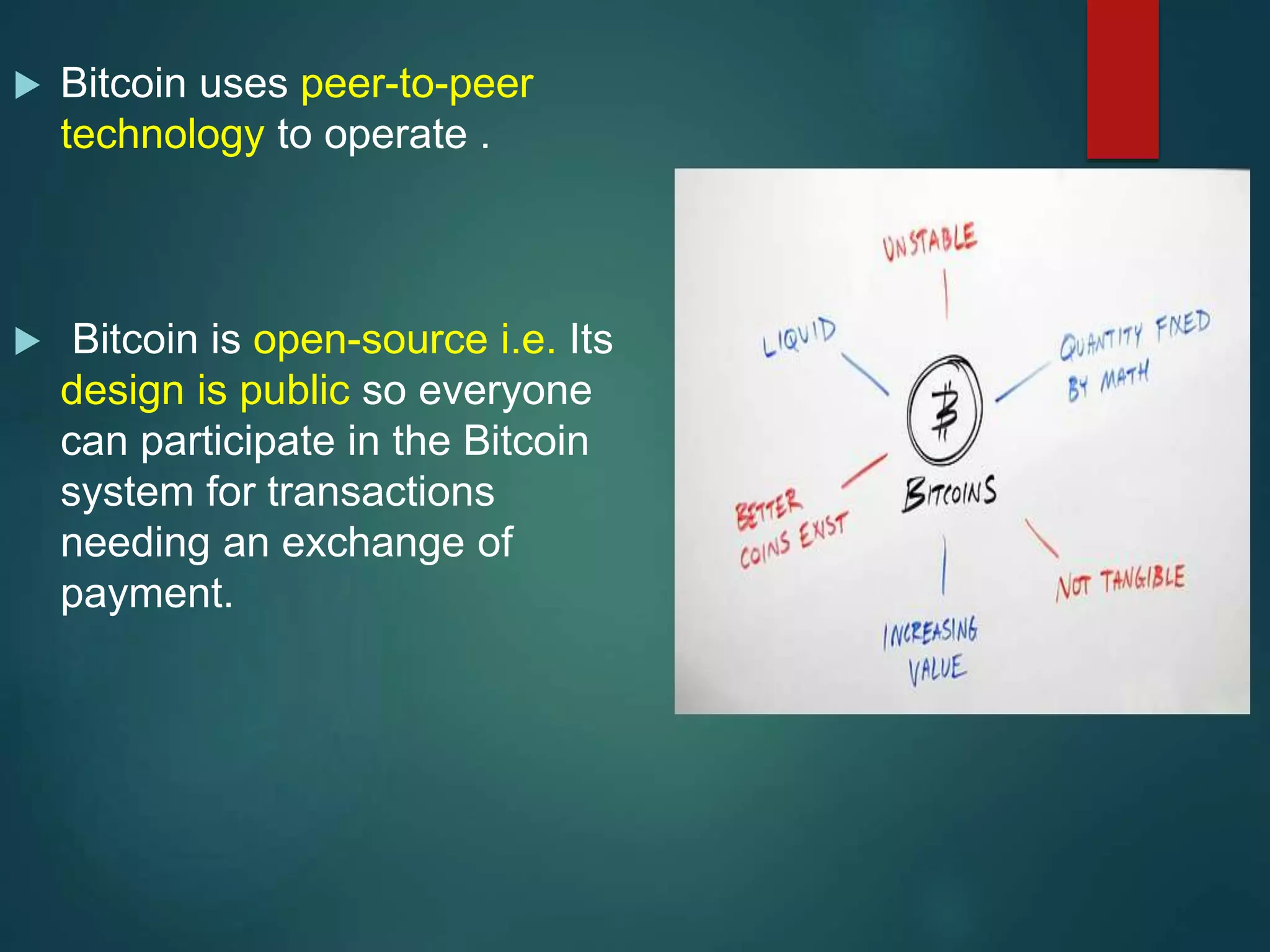
- Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency created by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008.
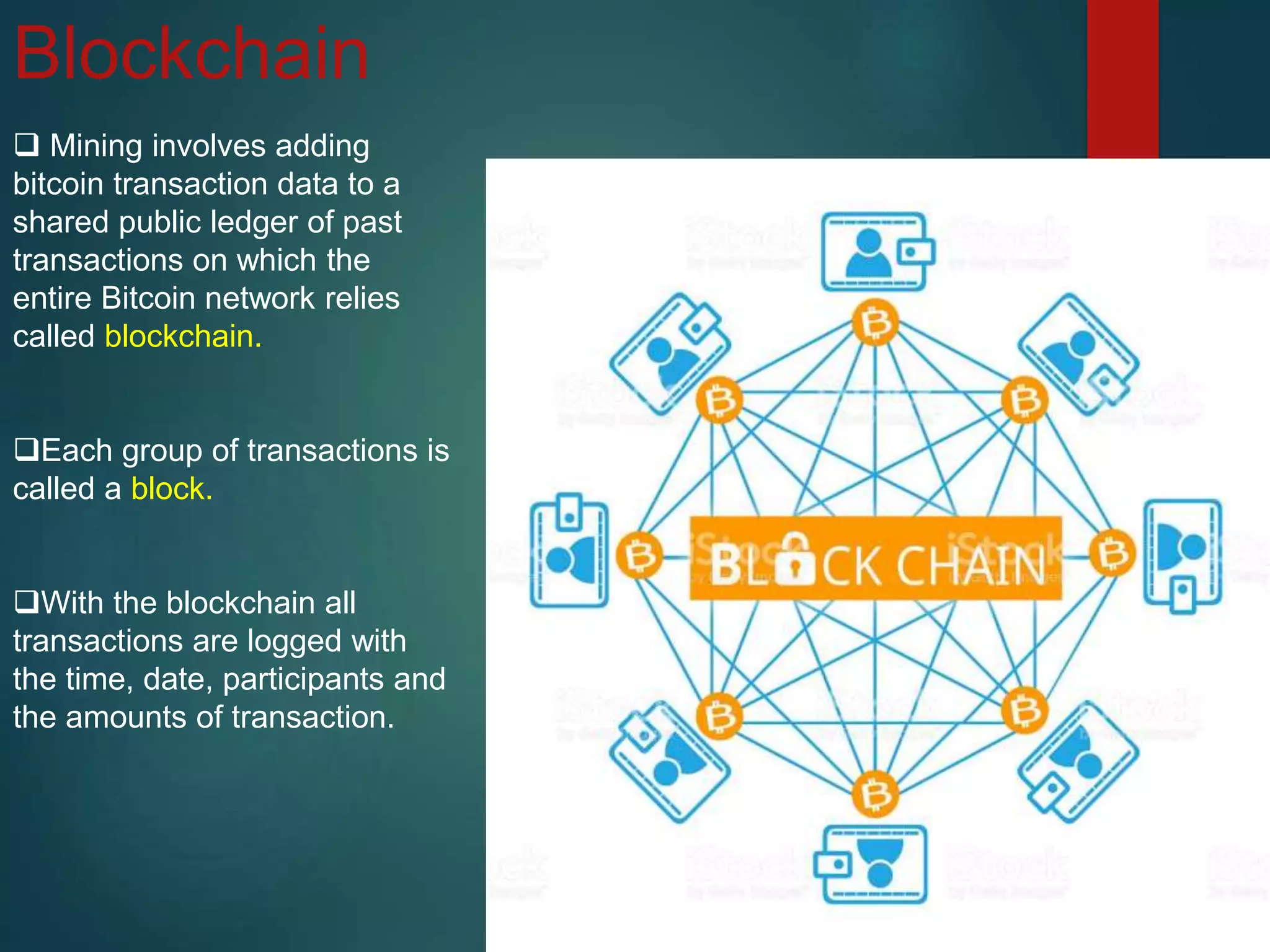
- It works using a peer-to-peer network and blockchain technology to record all transactions.
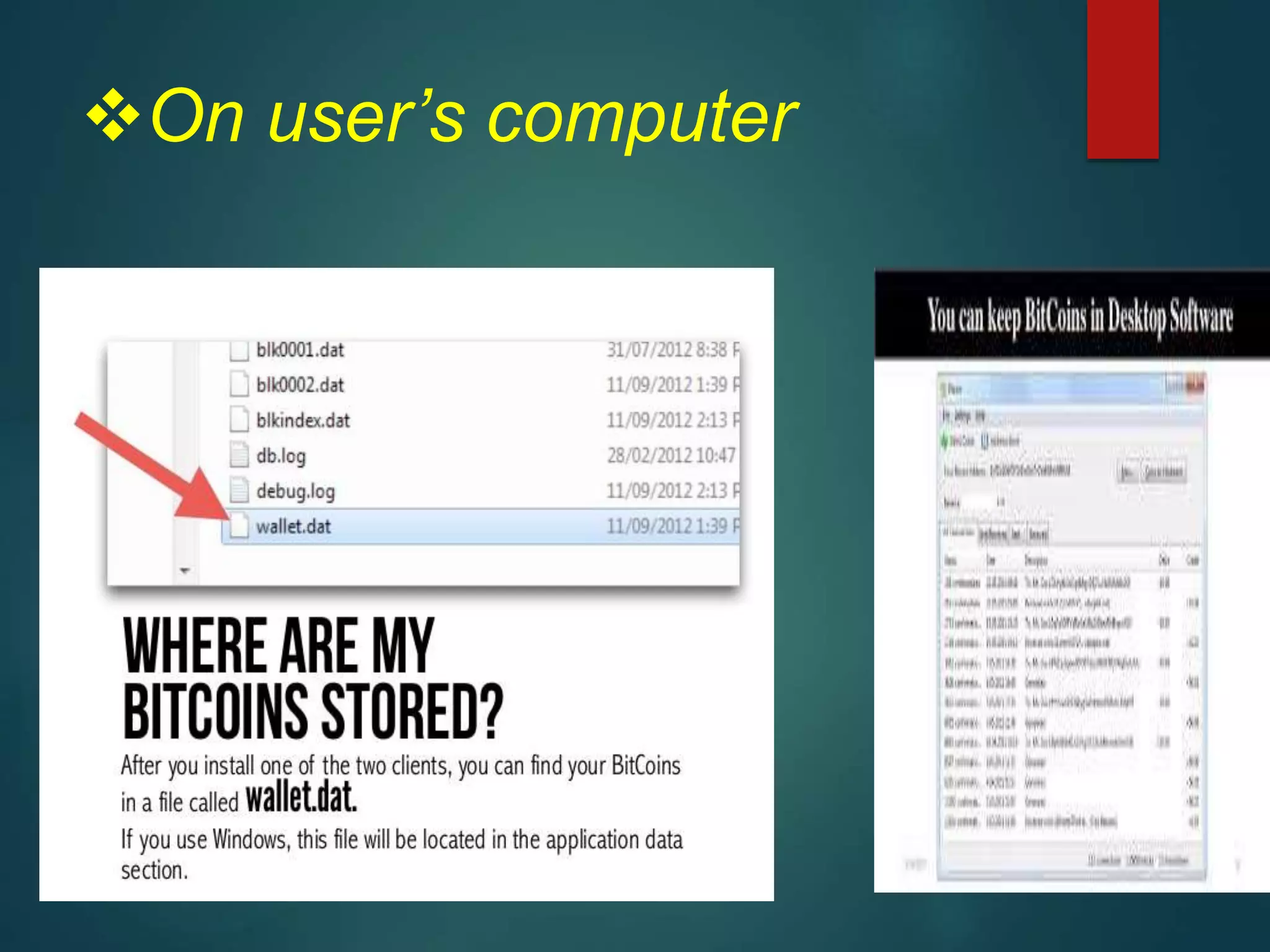
- Users can buy, sell, and trade bitcoins through exchanges or person-to-person using digital wallets stored on their devices or in the cloud.
- While Bitcoin offers anonymity and lack of oversight, it also faces risks of volatility, limited acceptance, and potential use for illicit activities.