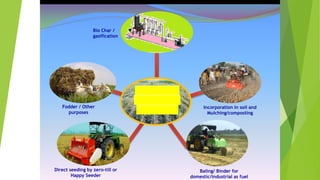
The document discusses the problem of crop stubble burning, particularly in Punjab and Haryana, where farmers resort to this practice due to time constraints and economic pressures. Stubble burning contributes significantly to air pollution, causing health issues and environmental degradation, including soil fertility loss and greenhouse gas emissions. The text also presents alternatives to burning, such as the use of happy seeders for direct sowing, biogas generation, composting, and production of biochar to promote sustainable practices.