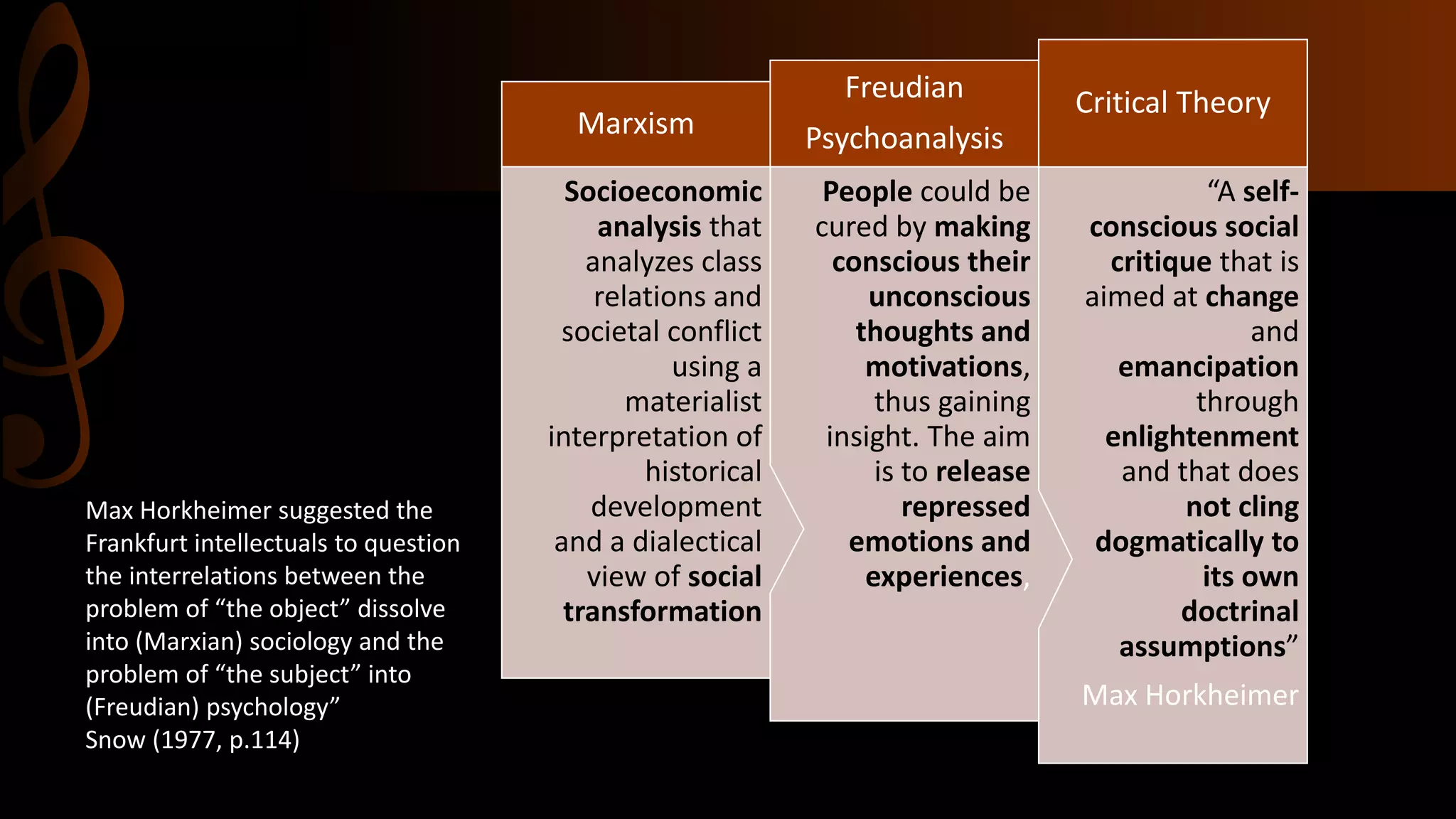
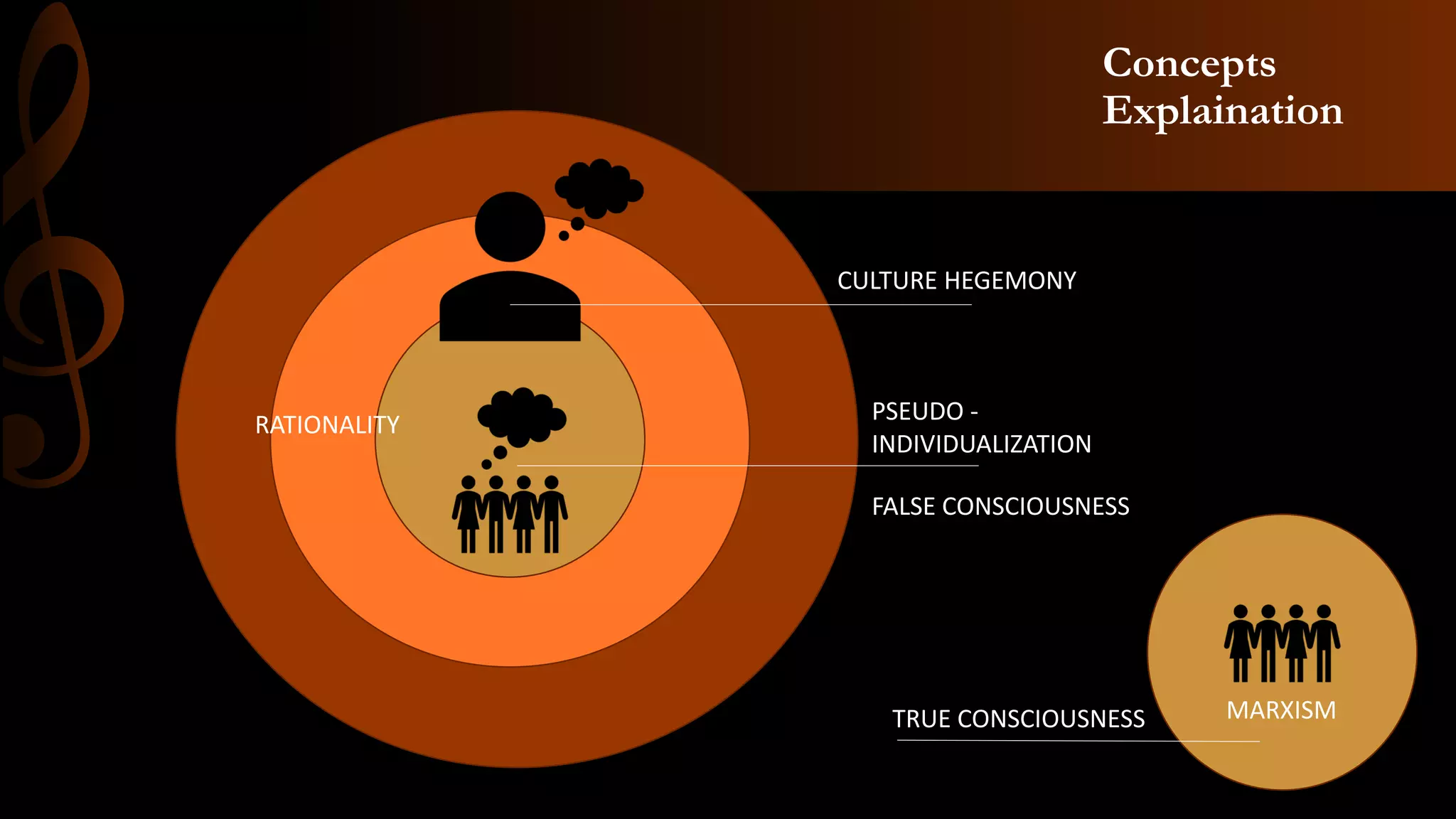
The document discusses Critical Theory and its contributions to Media Studies and Media Education. It begins by outlining three main questions to address regarding Critical Theory, its role in Media Studies, and how it can benefit media education students. It then provides background on Critical Theory, noting it originated from the Frankfurt School and opposes capitalism and domination. Key concepts from Critical Theory are also listed. The document focuses on Theodor Adorno's theories around mass culture, the culture industry, and the standardization and commodification of culture through capitalism. It argues Critical Theory continues to be relevant today across various fields and can help media educators develop a critical pedagogy.