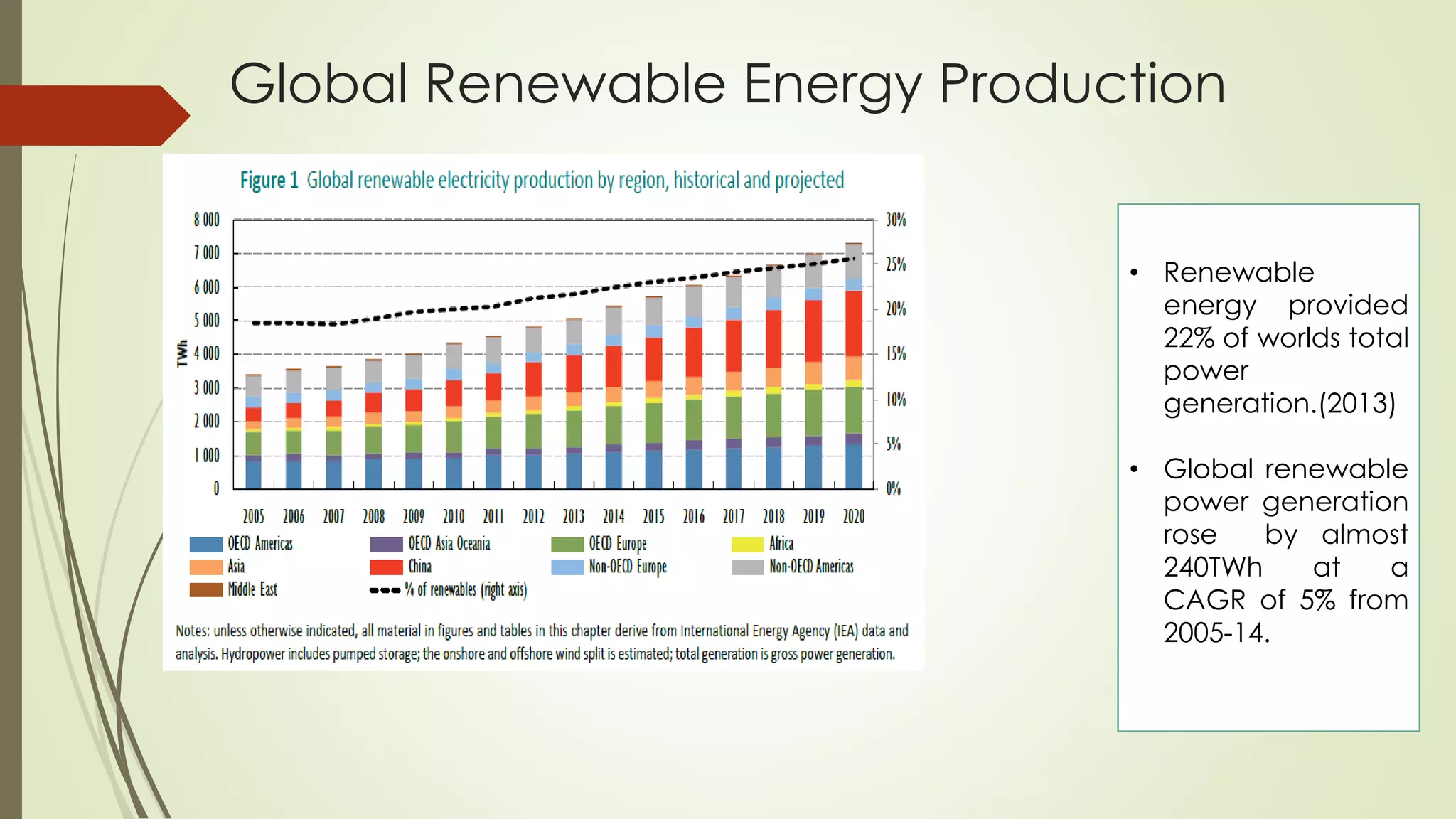
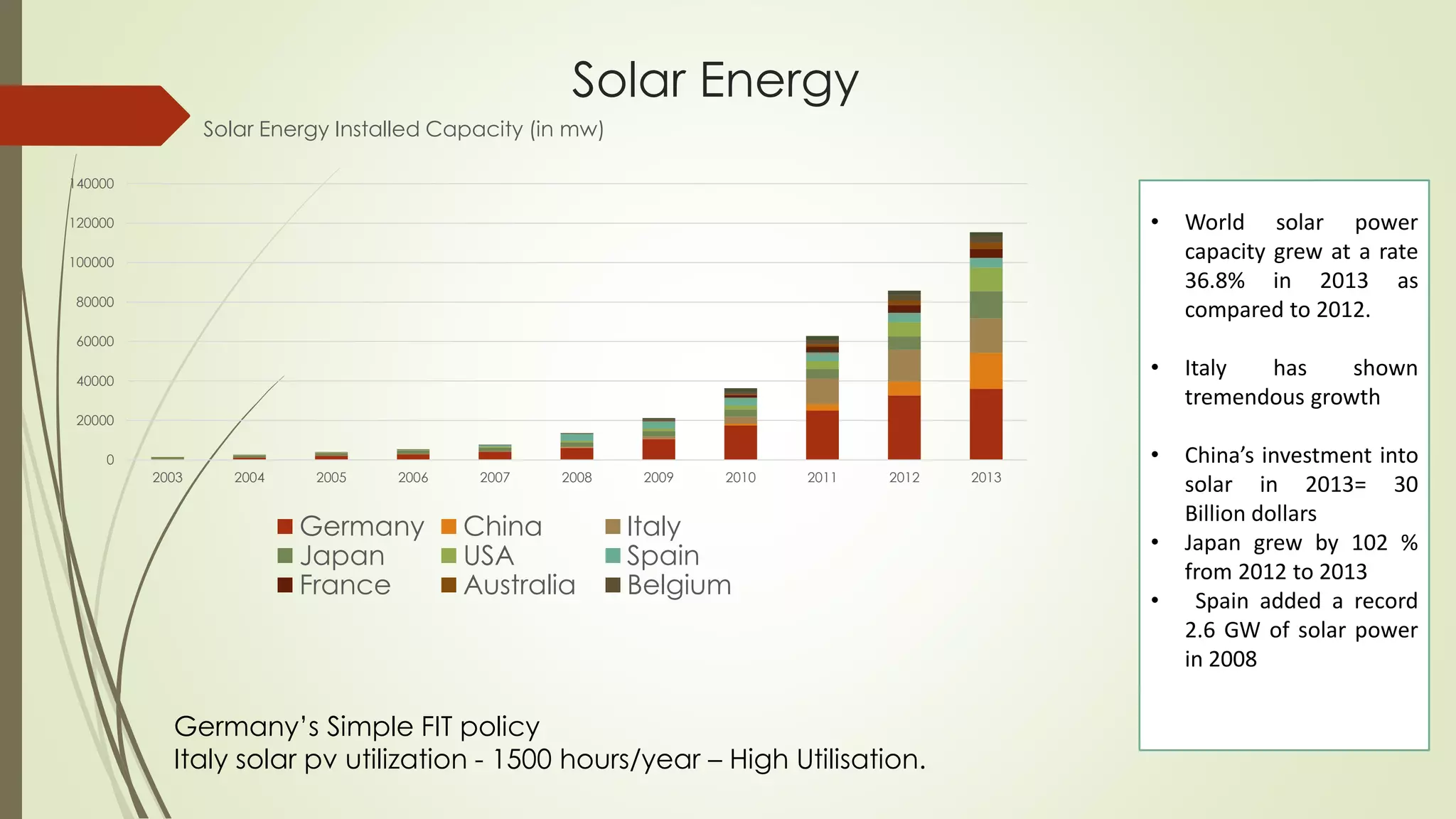
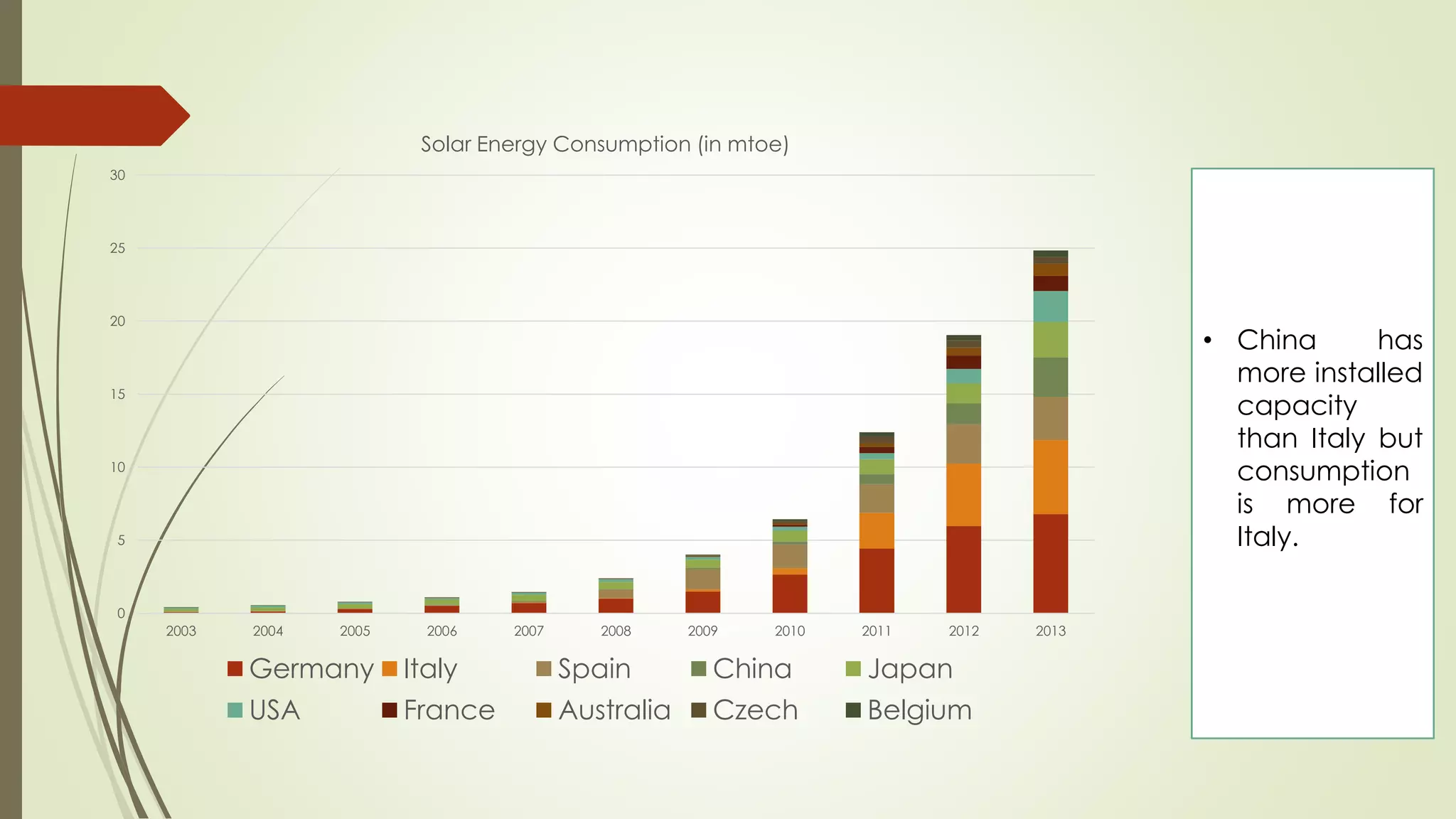
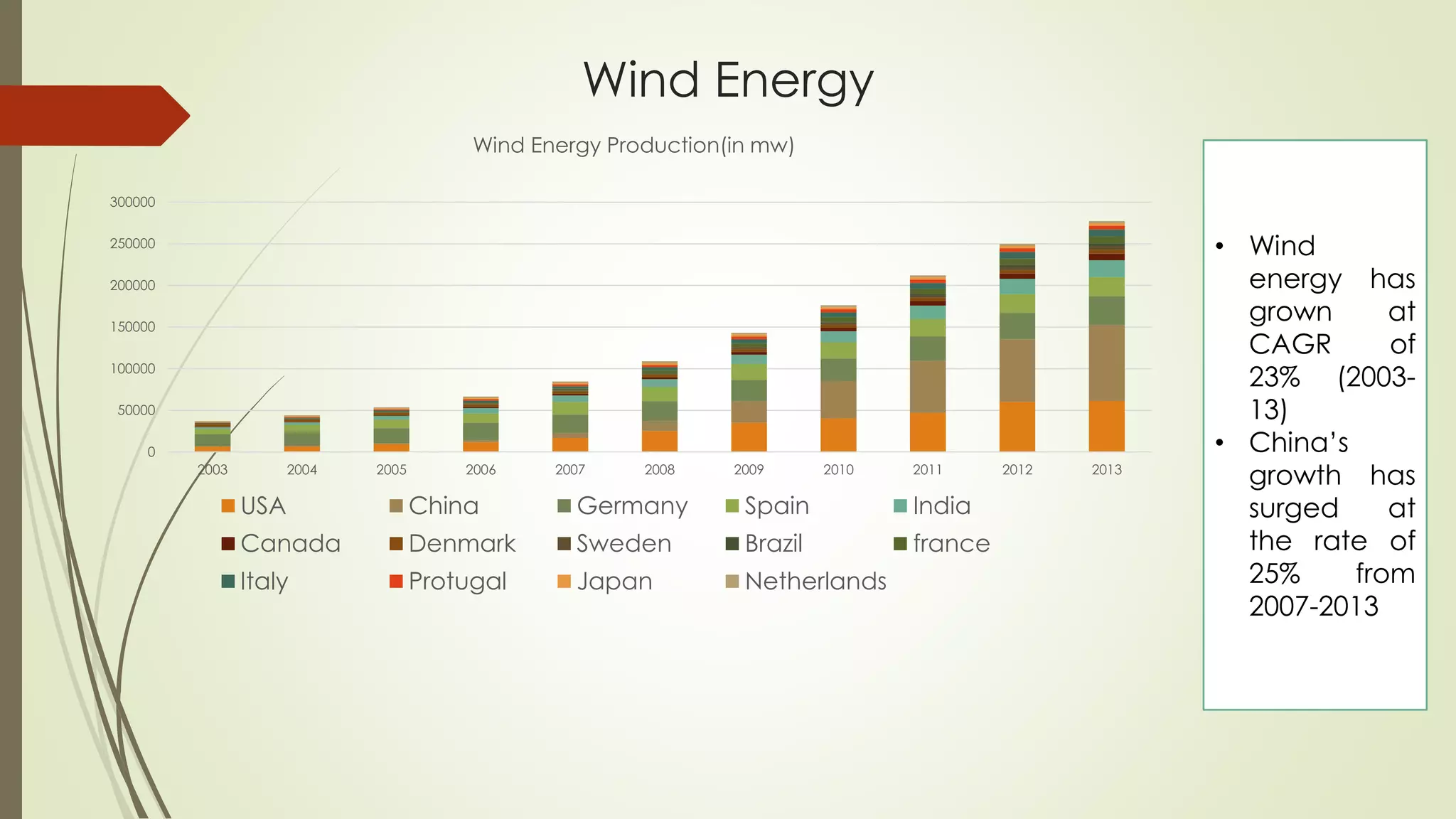
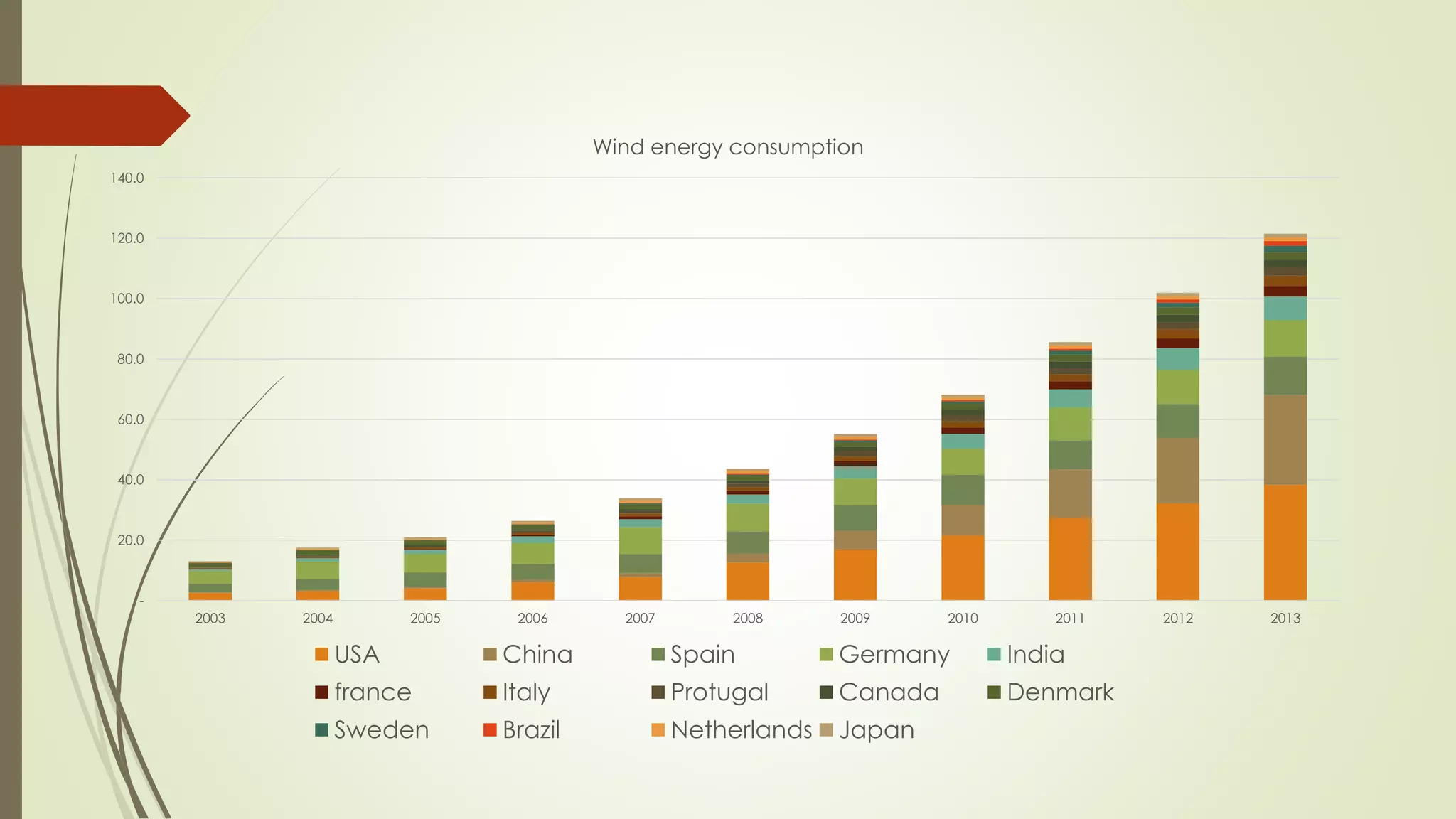
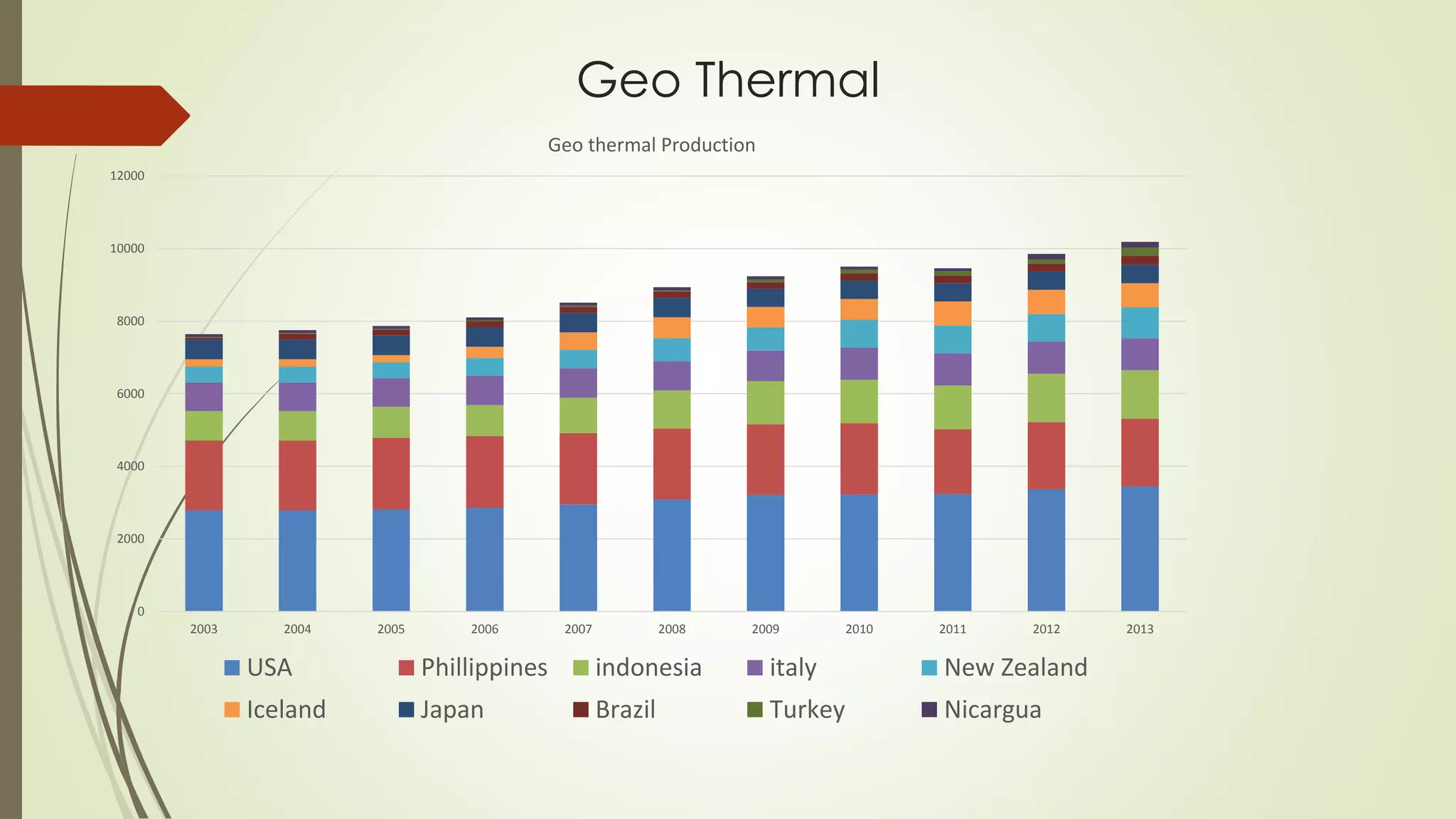
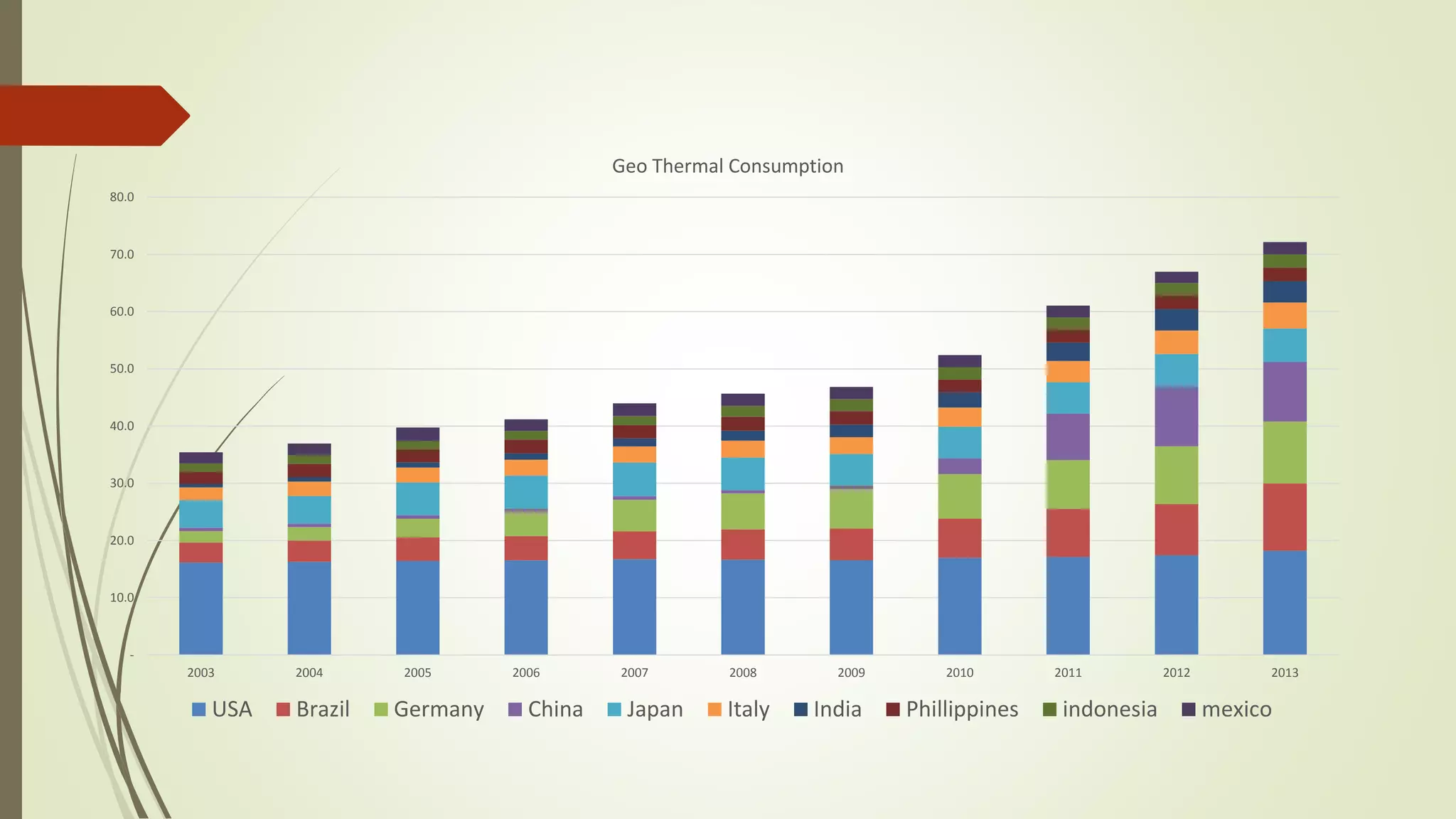
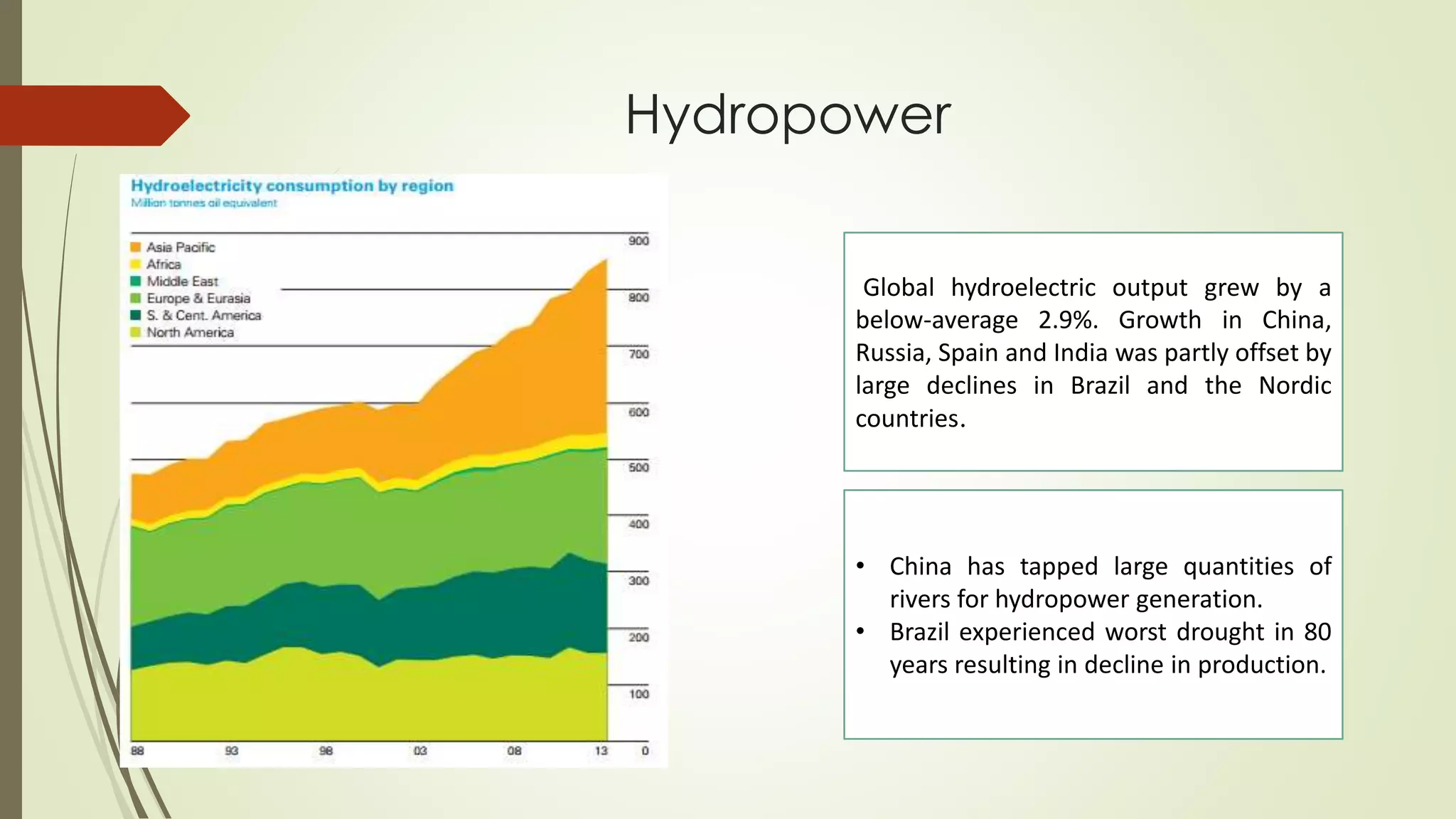
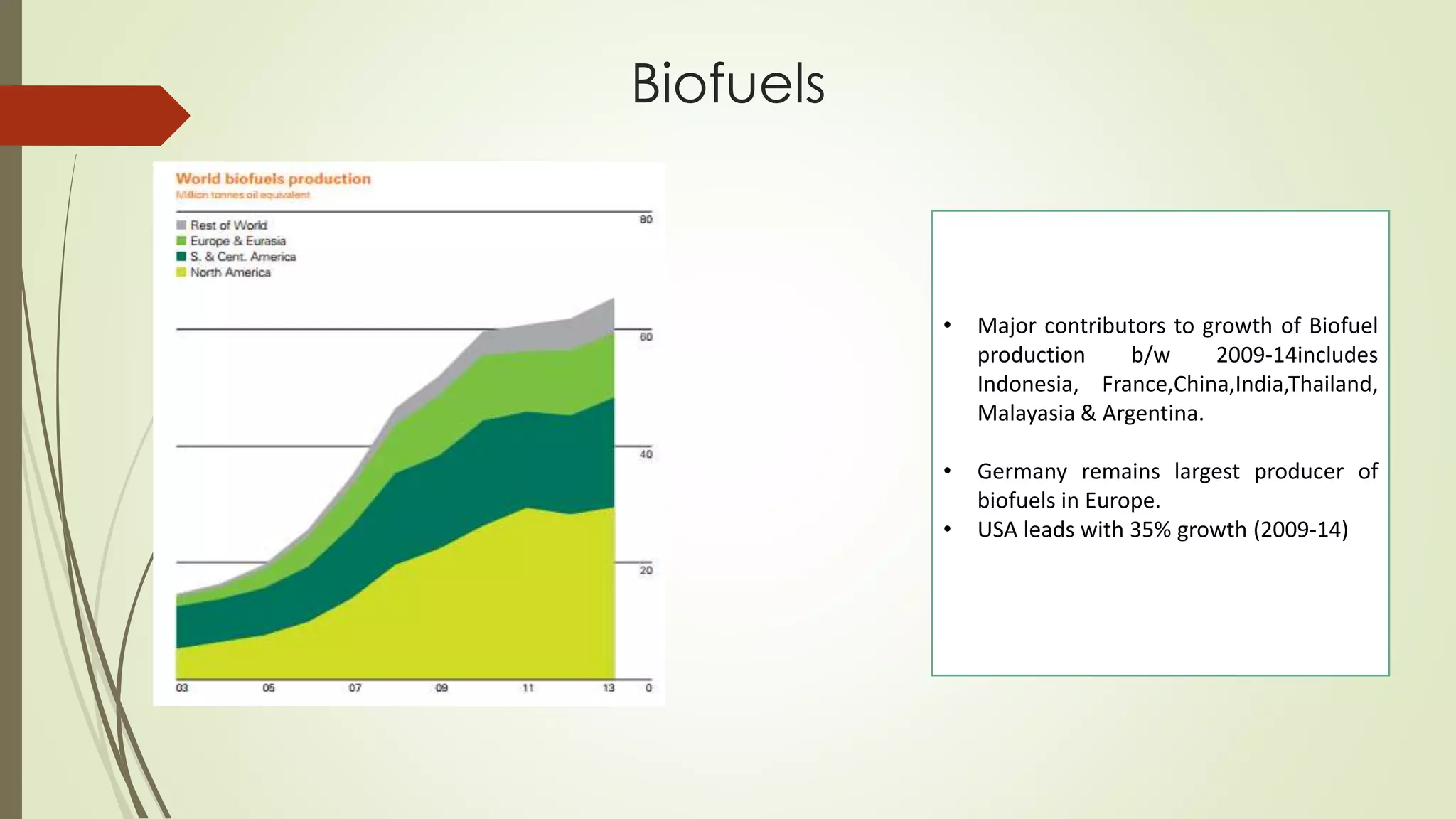
This document provides an outline and analysis of various renewable energy sources including solar, wind, geothermal, hydroelectric, and biofuels. It details global trends in renewable energy production from 2003-2013, finding that renewable sources provided 22% of global power in 2013 and capacity grew 5% annually over that period. The largest growth was seen in solar and wind energy. China is a leader in renewable energy capacity and production while Germany pioneered solar energy policies. Hydropower remains the largest renewable source but growth has slowed in recent years.