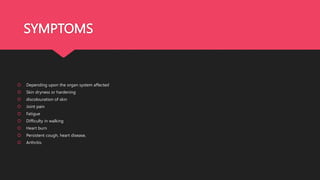
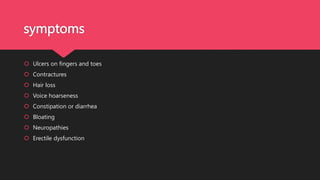
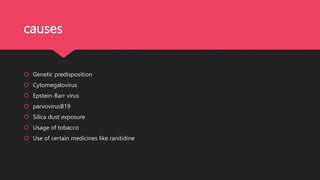
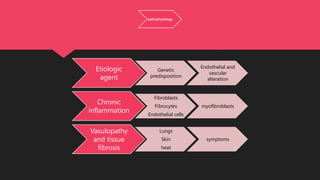
Crest syndrome is a limited form of systemic sclerosis characterized by calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, esophageal dysfunction, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia, which affects various organ systems. Symptoms vary depending on the organs involved and may include skin changes, joint pain, and gastrointestinal issues. While there is no universal treatment, management options include immunosuppressants, vasodilators, and symptomatic support.