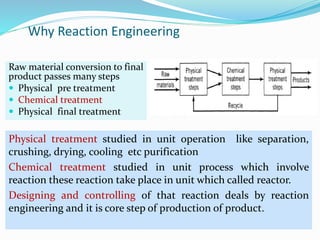
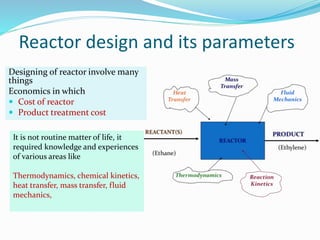
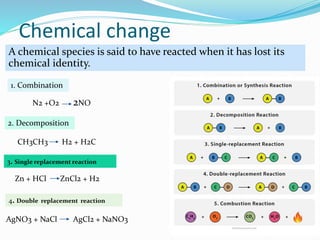
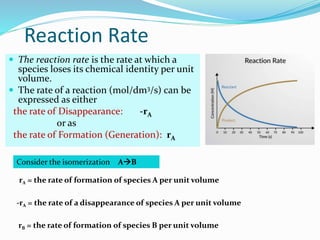
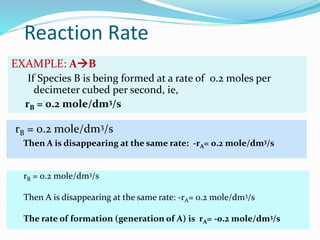
This document provides an introduction to chemical reaction engineering (CRE). CRE studies the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions and the design of reactors. It is important because it involves converting raw materials into products through both physical and chemical treatment steps. Reactions take place in reactors, so CRE focuses on designing and controlling reactions. Reactor design considers economics, kinetics, heat and mass transfer, and other factors. Reactions are classified as homogeneous or heterogeneous. The rate of a reaction is the rate at which a chemical species loses its identity per unit volume and can be expressed as the rate of formation or disappearance of that species.