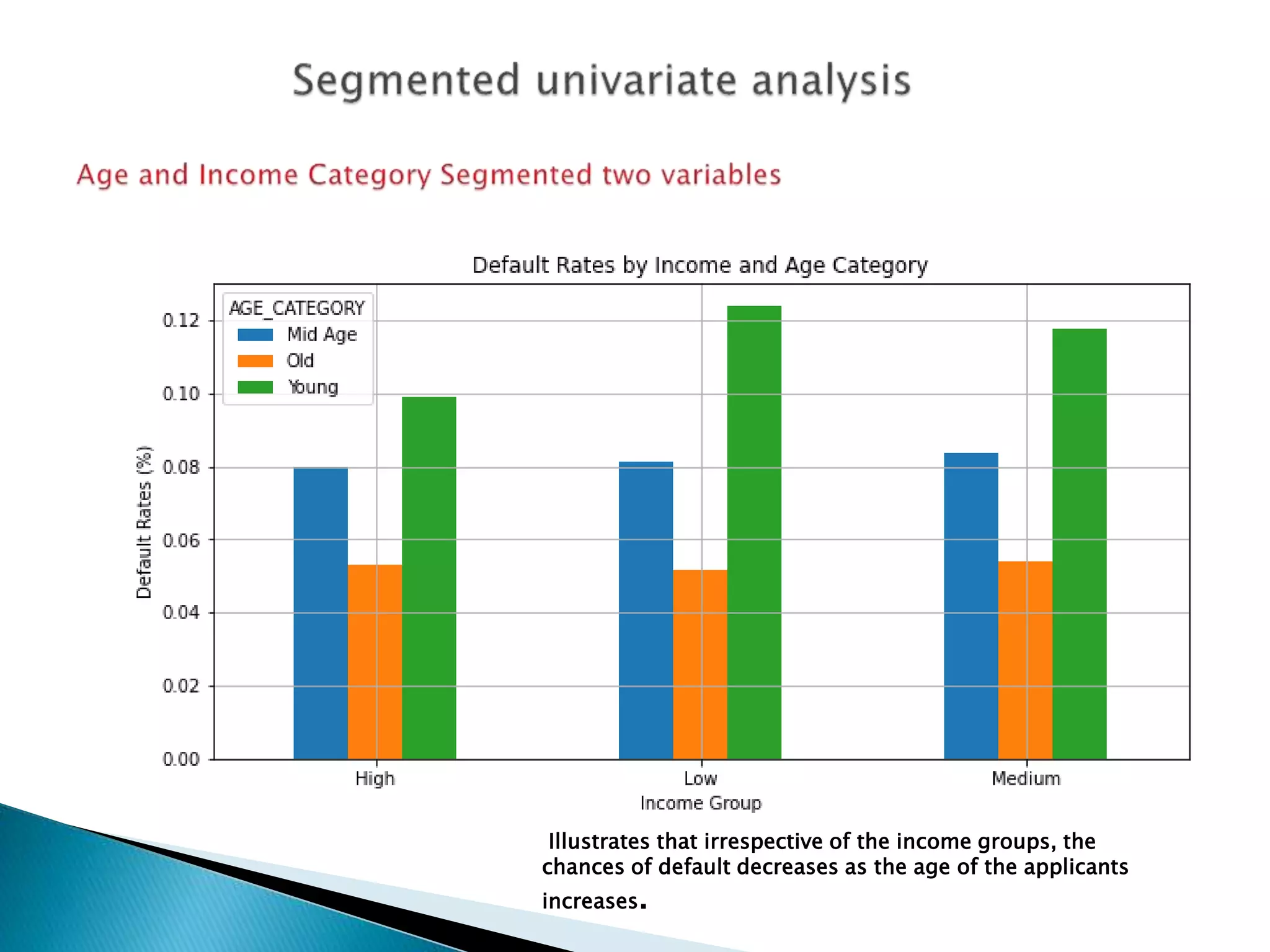
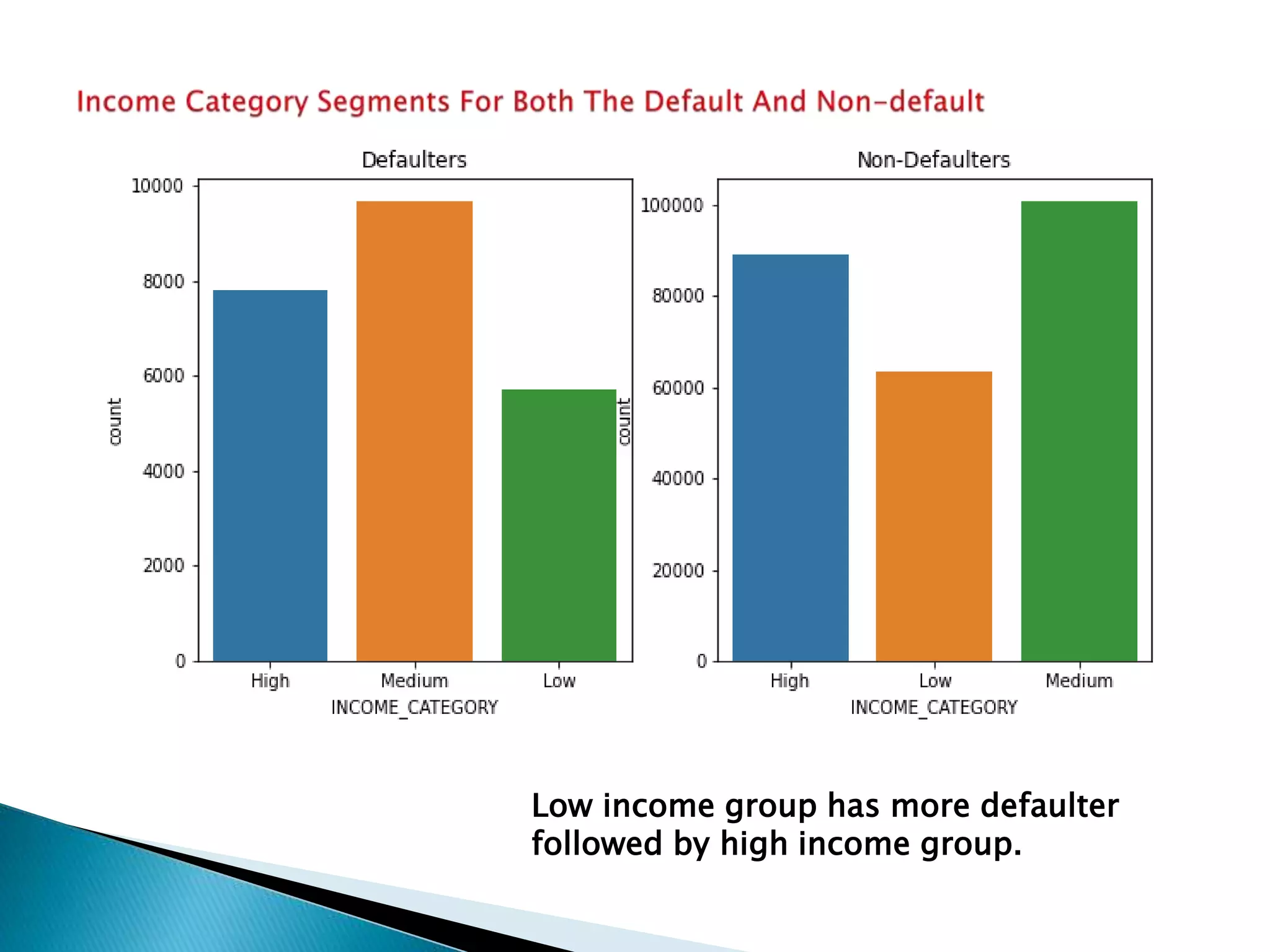
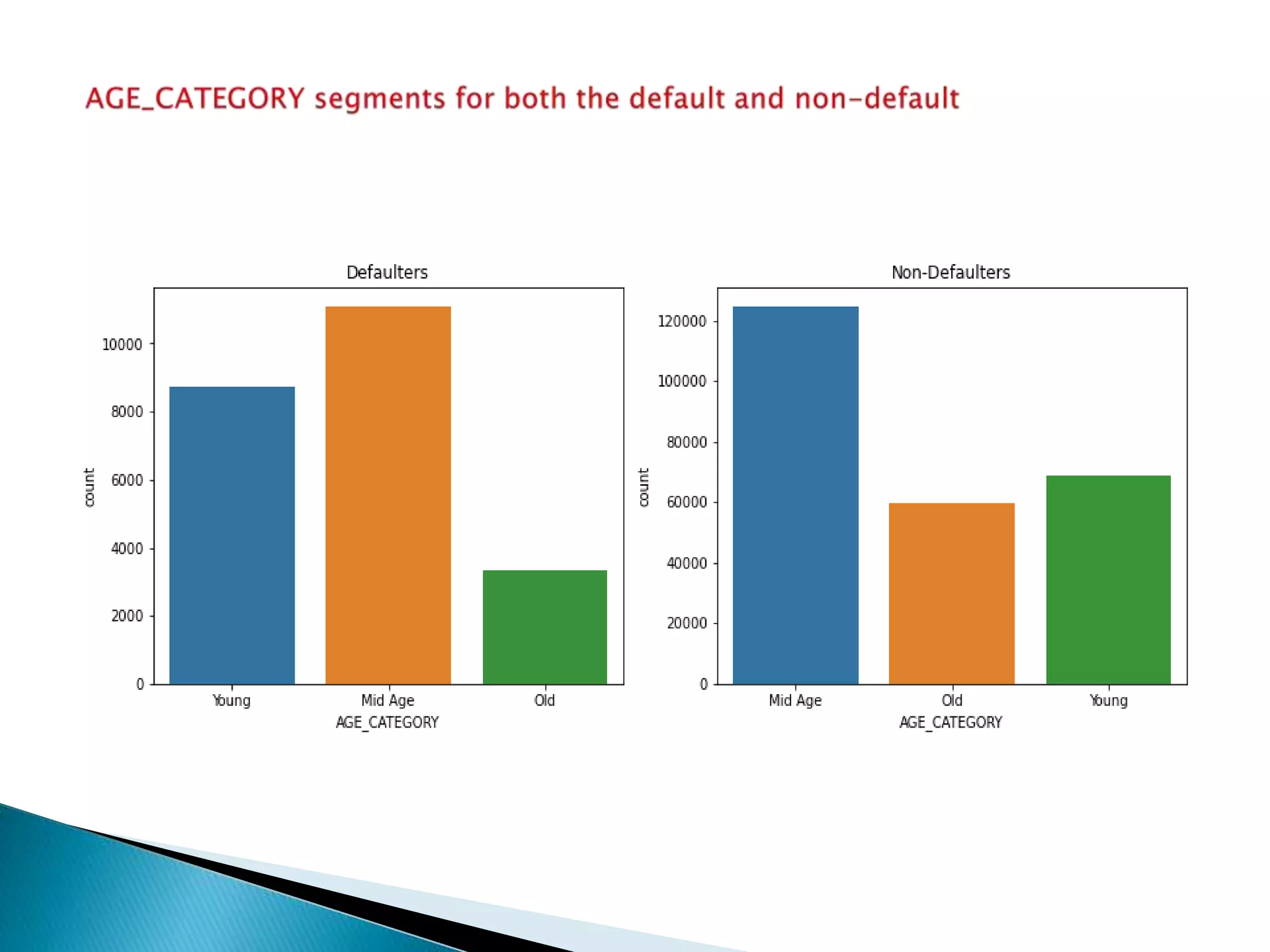
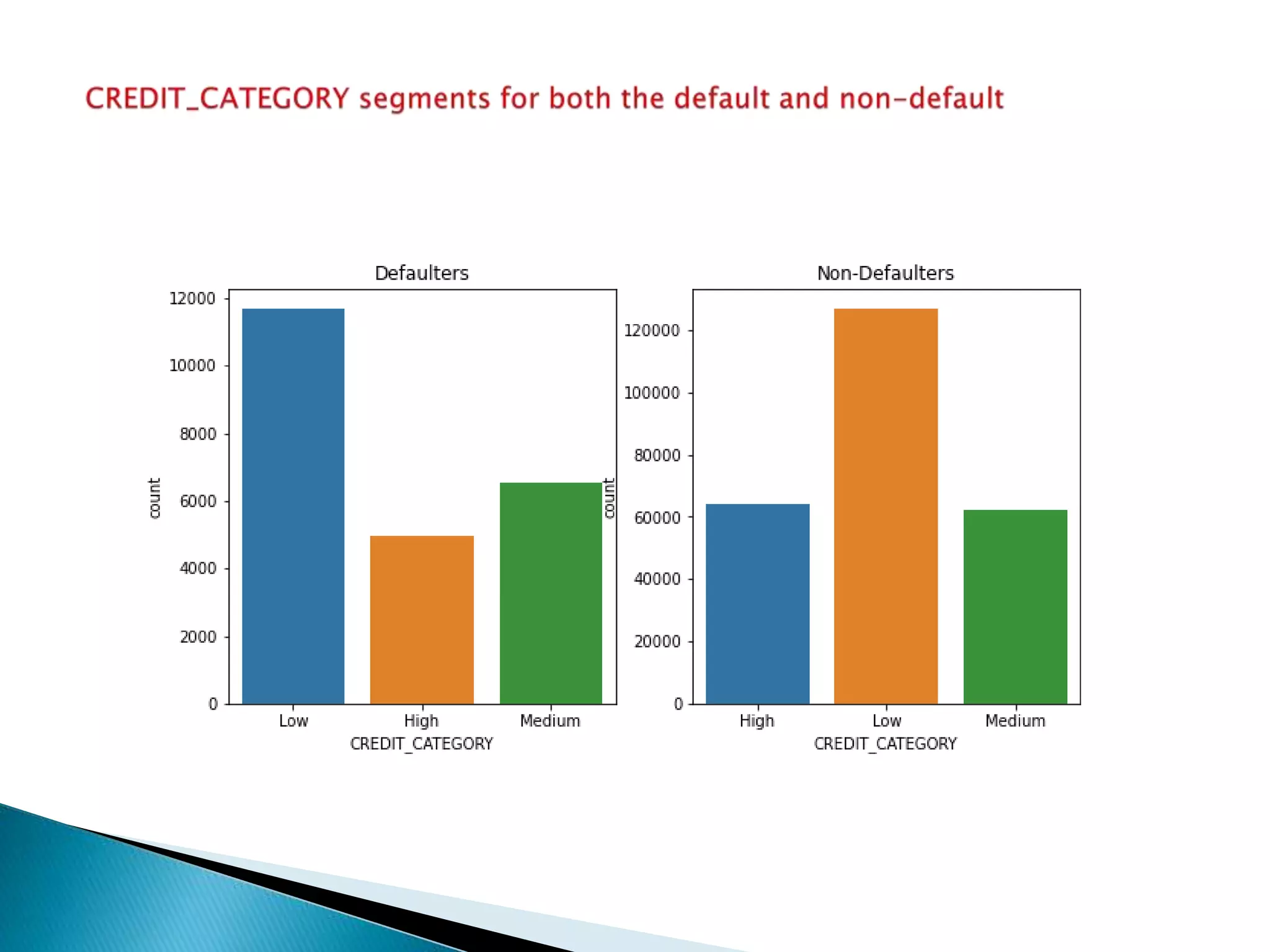
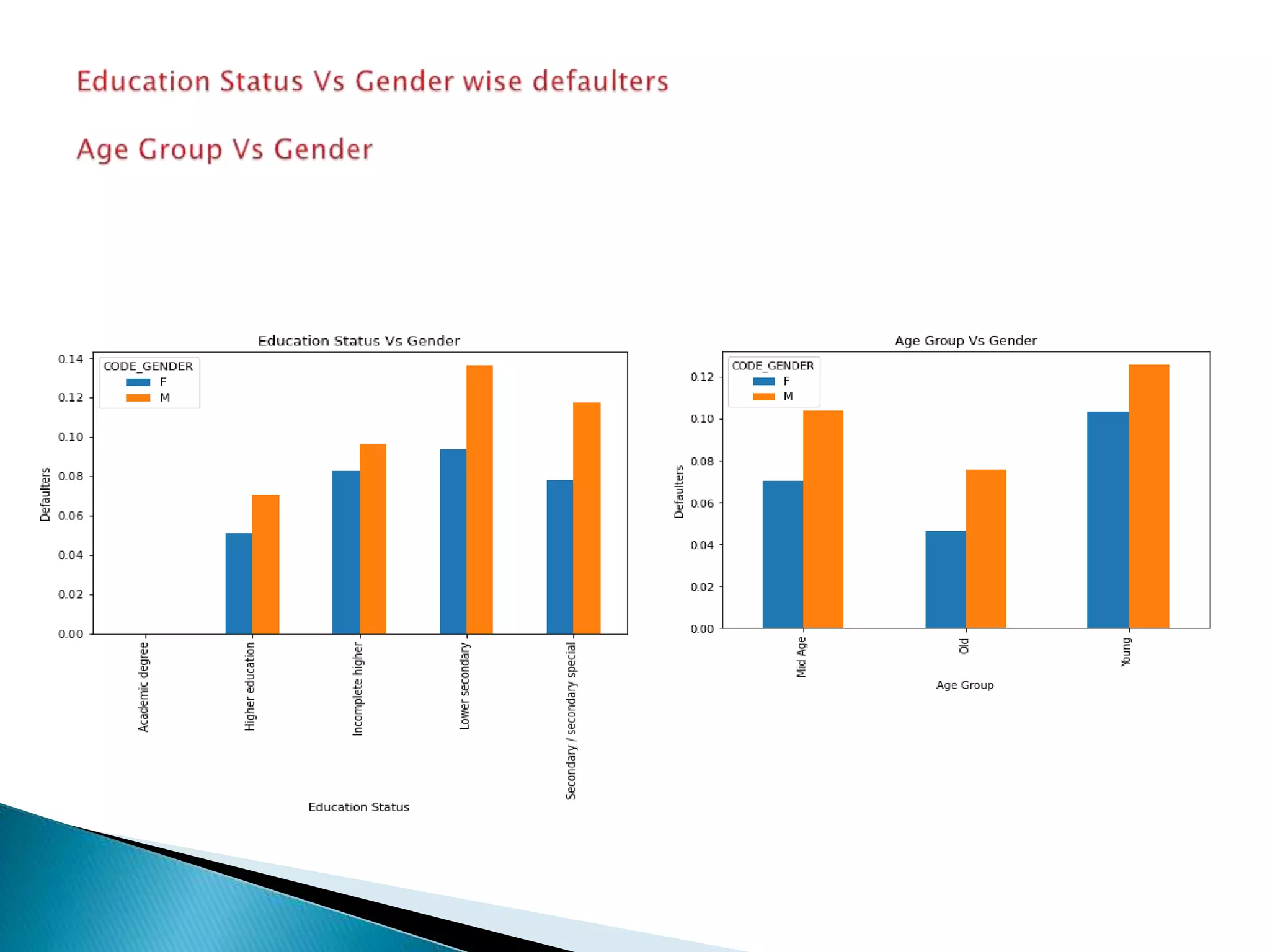
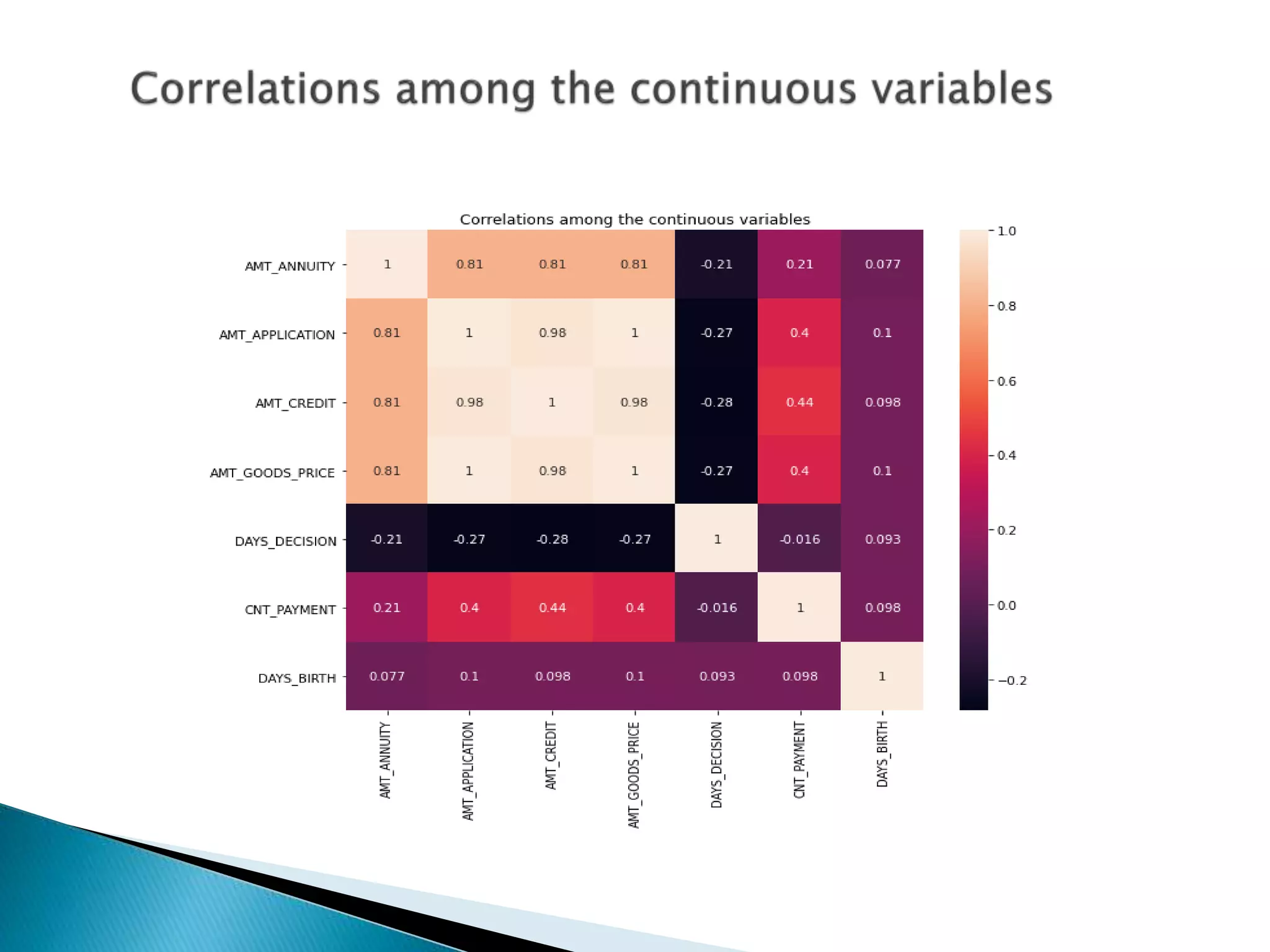
The document discusses credit risk analysis for loan approvals. It outlines the steps in the analysis, which include data understanding, checking for data quality issues, identifying data imbalances, and conducting univariate, bivariate, and correlation analyses. The analyses found that the chances of default decrease with increased applicant age but increase with higher credit amounts. Low income groups had higher default rates than high or medium income groups. Certain applicant attributes like being a state servant, older, higher income, or having a previous approved loan were associated with lower risk of default.