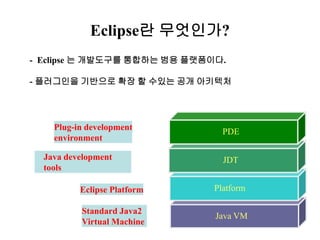
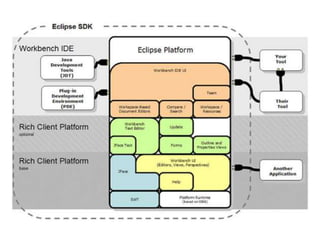
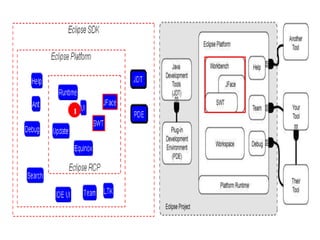
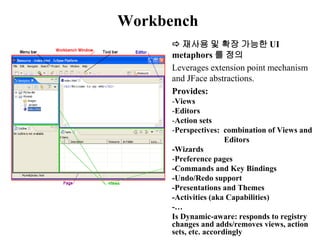
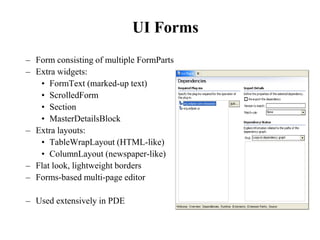
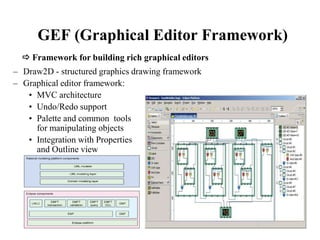
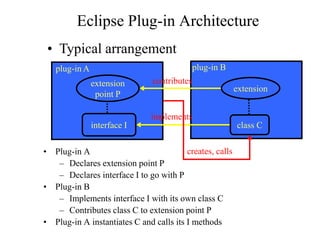
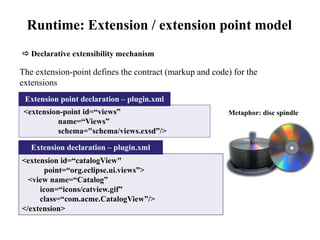
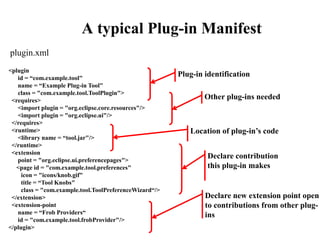
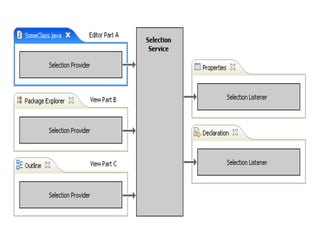
This document provides an overview of the Eclipse plugin architecture and framework. It describes Eclipse as an extensible platform based on plugins that can integrate development tools. It outlines key Eclipse UI frameworks like SWT, JFace, the workbench, text editor framework, and GEF. It explains that plugins contribute extensions to extension points and how this enables extensibility. The document also provides details on the plugin manifest and how it specifies a plugin's code, dependencies, and contributions.