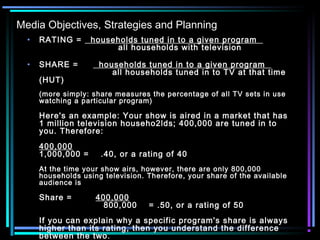
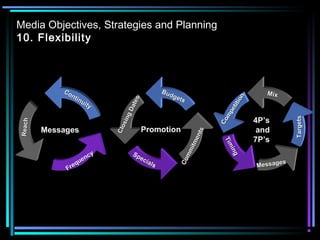
1. Media planning involves selecting the right media vehicles to direct marketing messages to targeted consumer audiences. This includes choosing between types of media like TV, radio, print, and non-traditional outlets.
2. When developing a media plan, factors to consider include the target market, product distribution channels, advertising budget, competitive strategies, desired messaging attributes, and metrics like reach, frequency and continuity of scheduling.
3. An effective media mix and schedule must account for seasonality, opportunities for synergies with other promotional activities, and cost efficiency considerations.