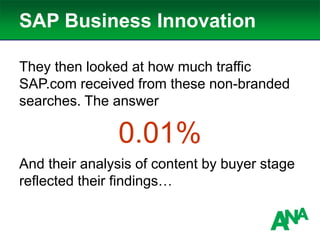
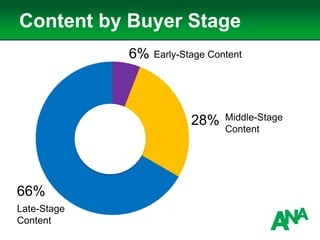
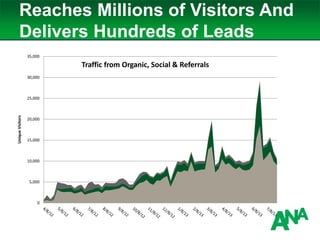
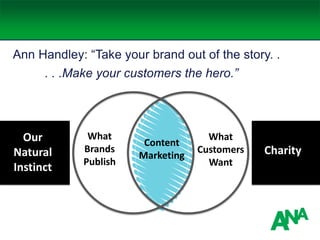
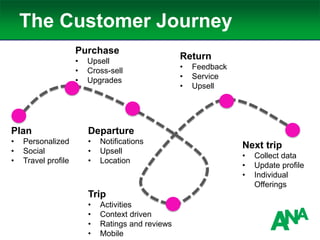
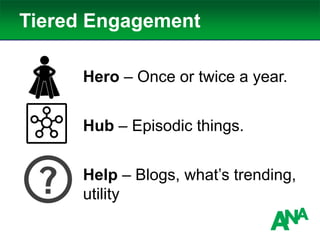
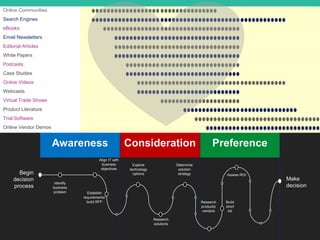
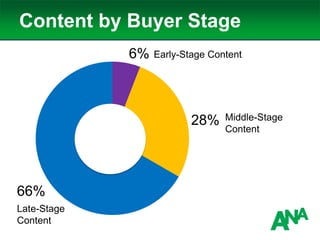
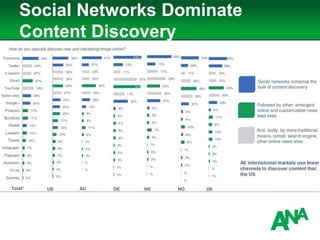
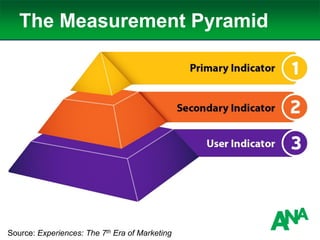
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to developing a business-driven content strategy, emphasizing the importance of storytelling and understanding audience needs. Key components include establishing a documented strategy, mapping content to the consumer journey, utilizing effective distribution channels, and measuring content marketing ROI. The content is designed to guide businesses in creating meaningful connections with their audience while achieving specific business objectives.


















![Exercise: Content + Objectives
1. What’s your content
mission?
Become a destination for [target
audience] interested in [topics]. To
help them [describe customer
value].
2. Who’s your target
audience?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anamastersofmarketing-151023041053-lva1-app6891/85/Creating-a-Business-Driven-Content-Marketing-Strategy-26-320.jpg)
























![My L.E.A.D. Action Plan
Actionable goal name:
Desired state (90 days from now): By [ _ /_ / _ ], I/we will:
Current state:
Key milestones to reach goal:
How will it be measured:
Who are you accountable to:
After the 90 days, assess your progress:
1. Did you accomplish your goal?
2. How were you supported in achieving your goals?
3. Did anything prevent you from achieving your goals?
4. What ongoing goals are you now driving to achieve?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anamastersofmarketing-151023041053-lva1-app6891/85/Creating-a-Business-Driven-Content-Marketing-Strategy-66-320.jpg)
