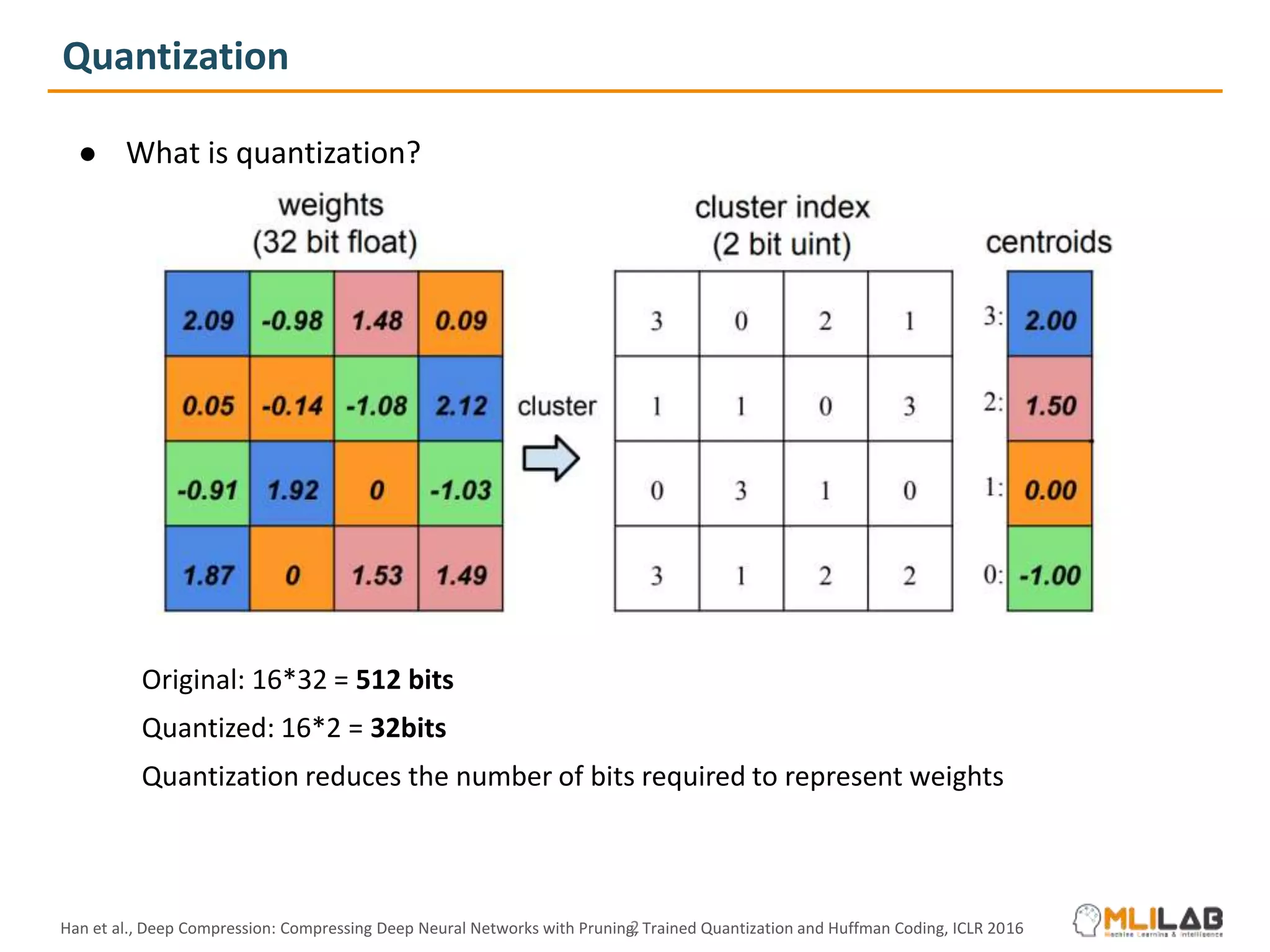
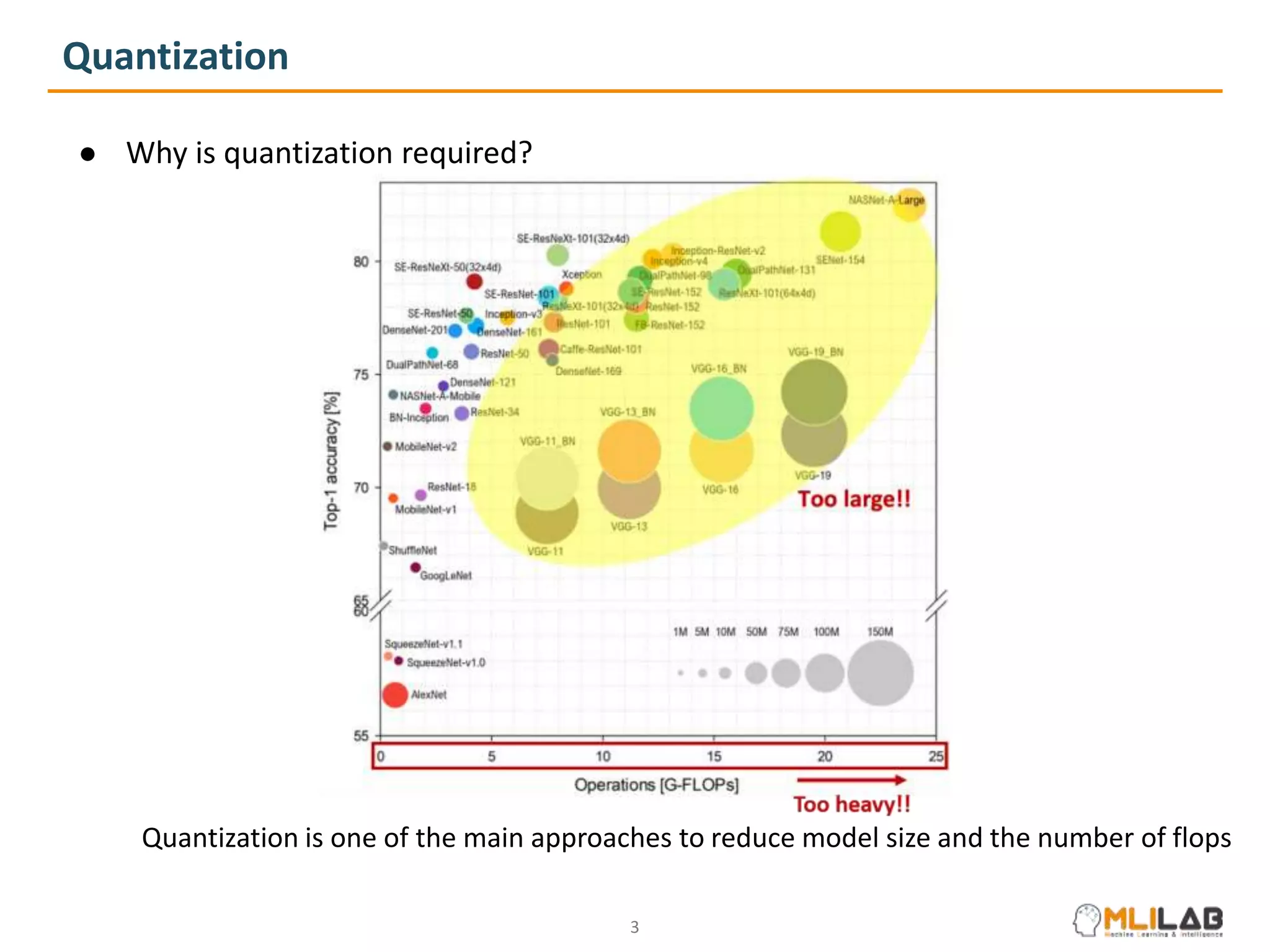
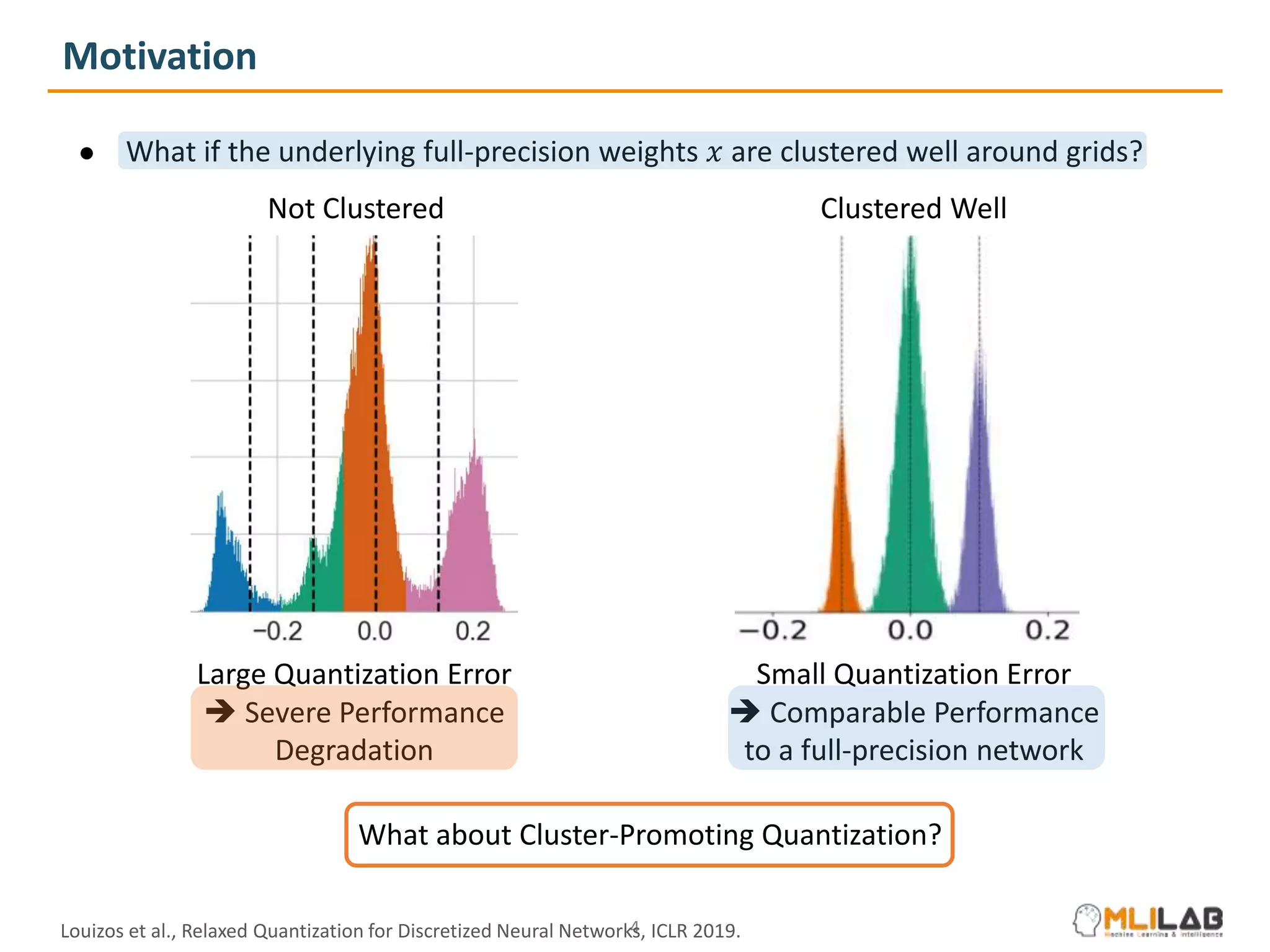
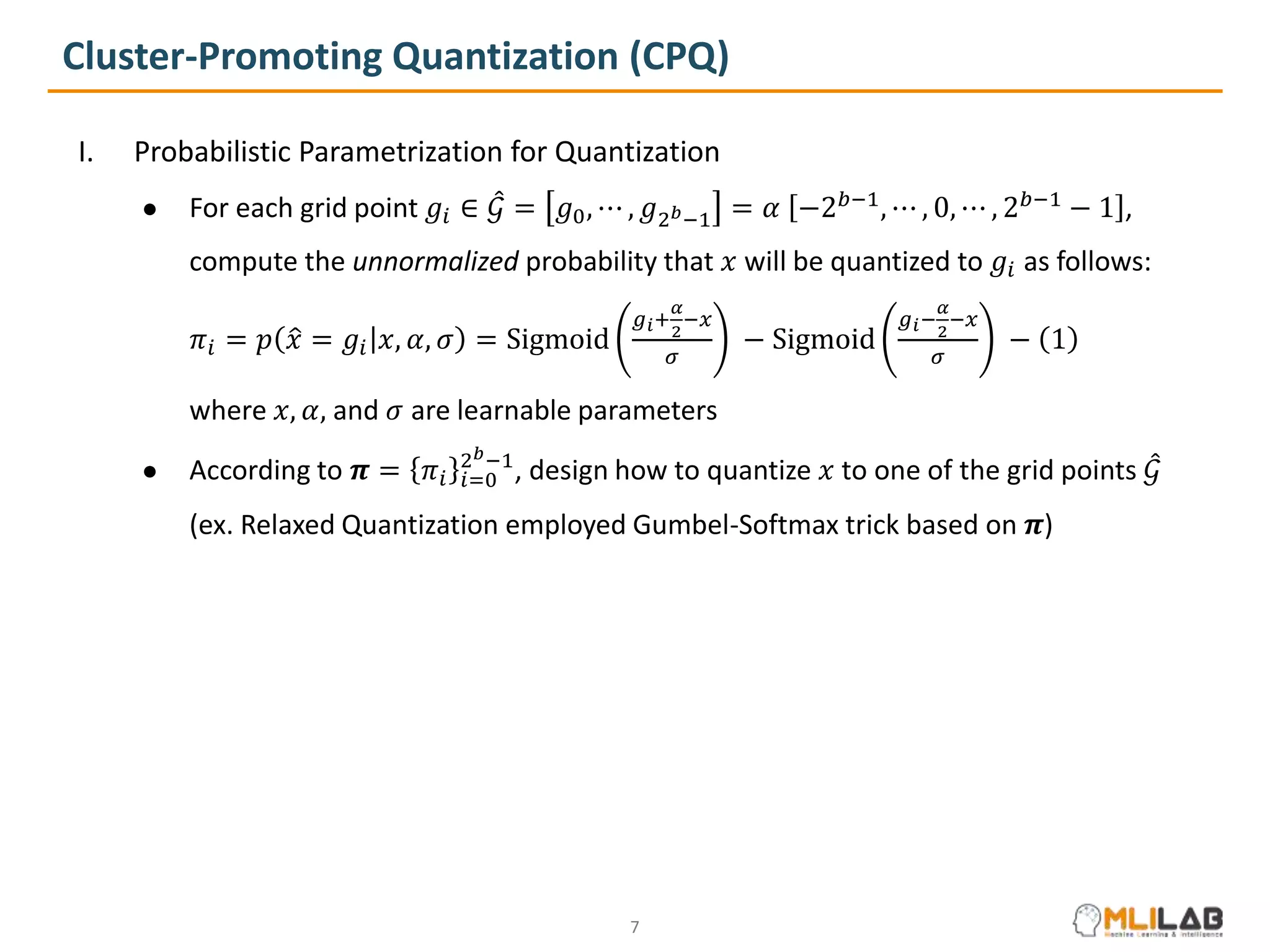
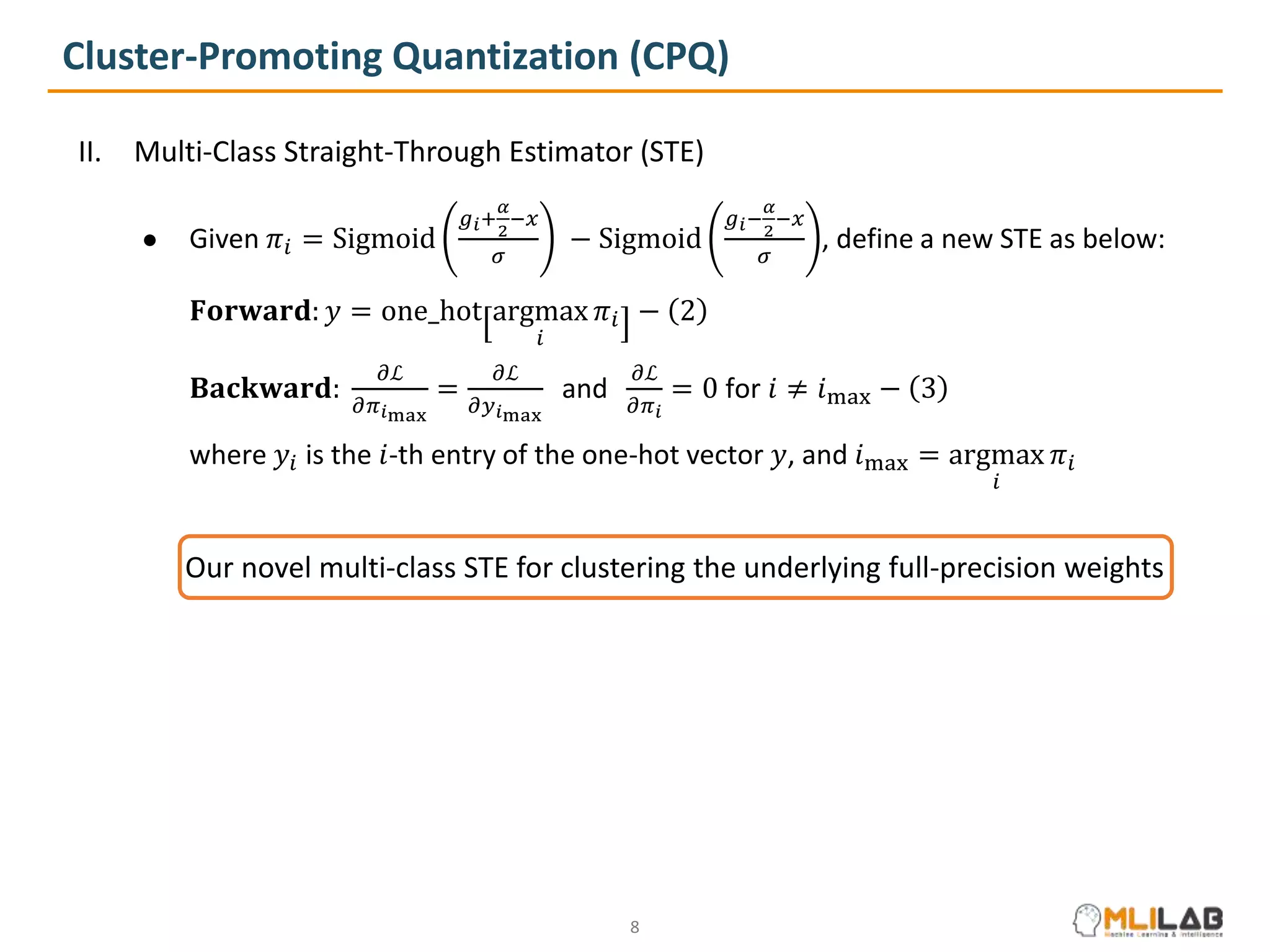
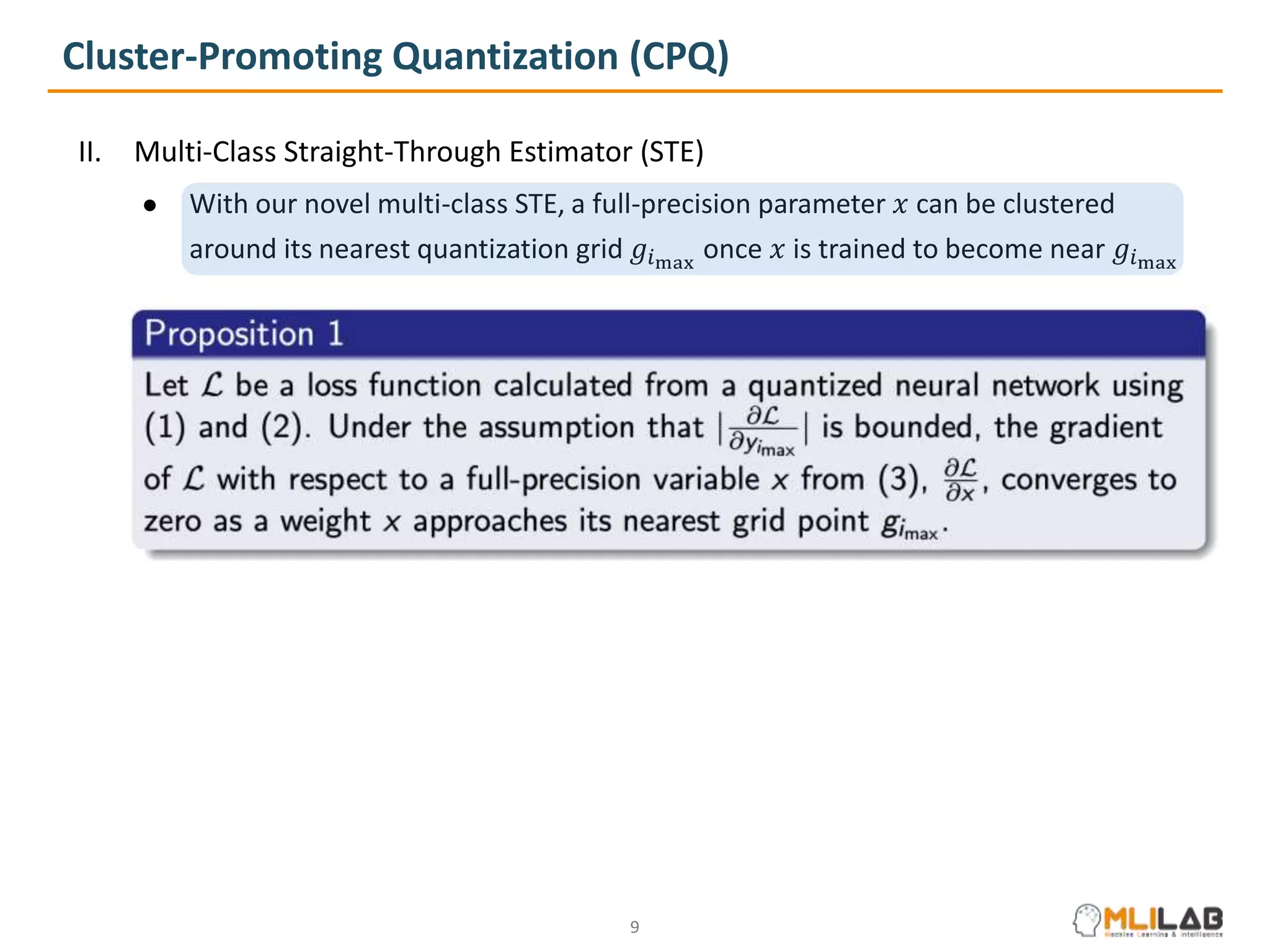
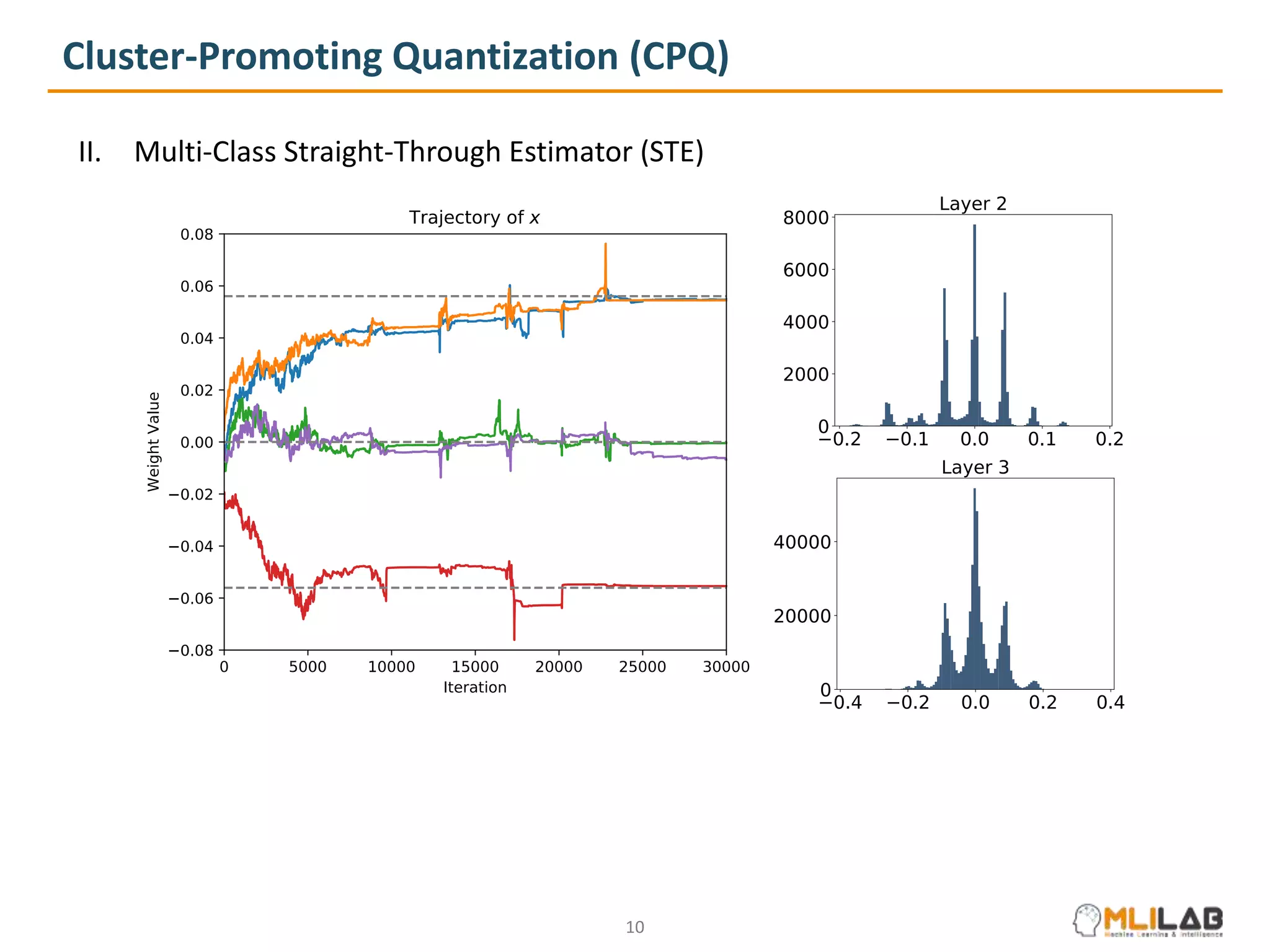
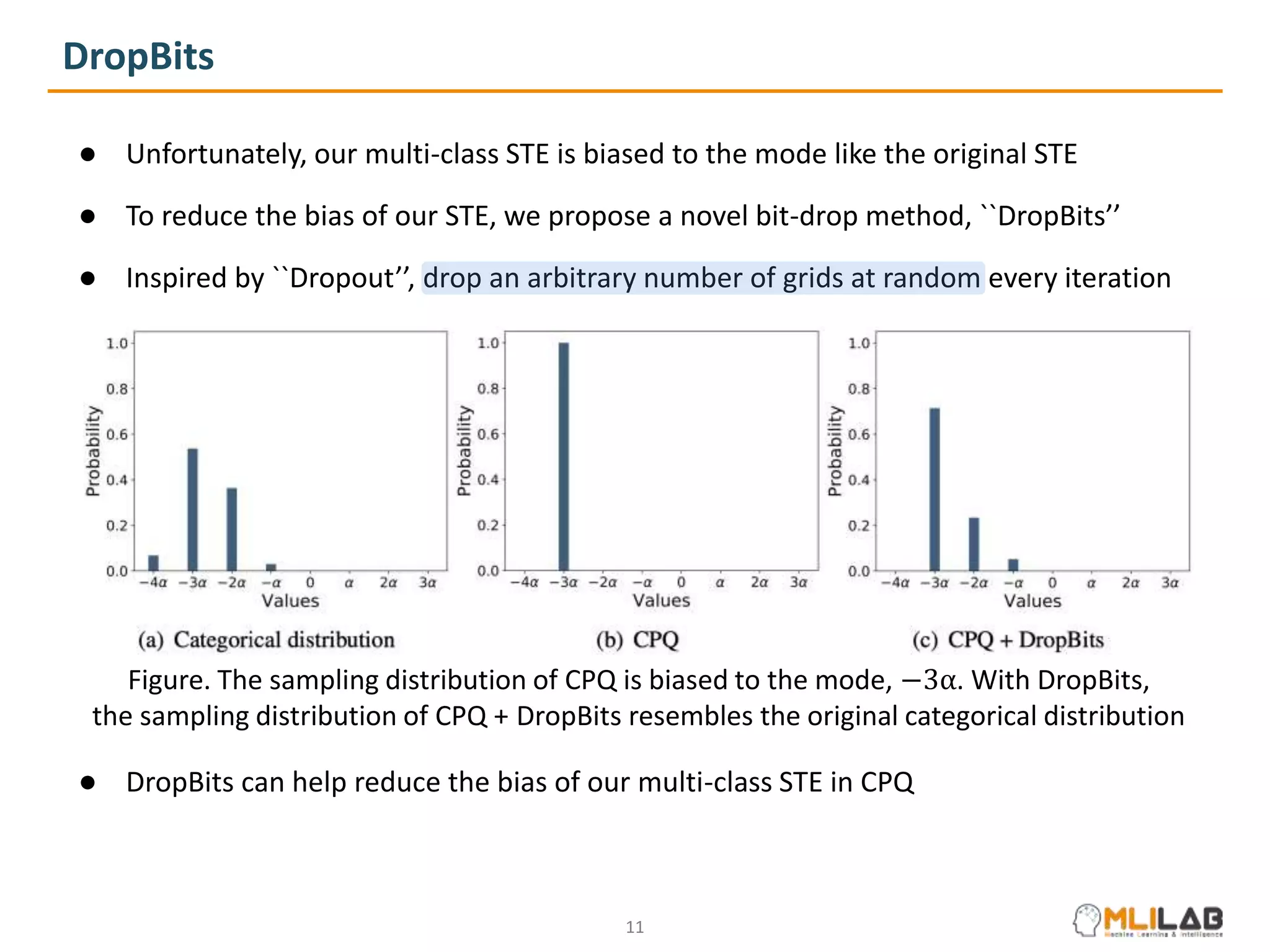
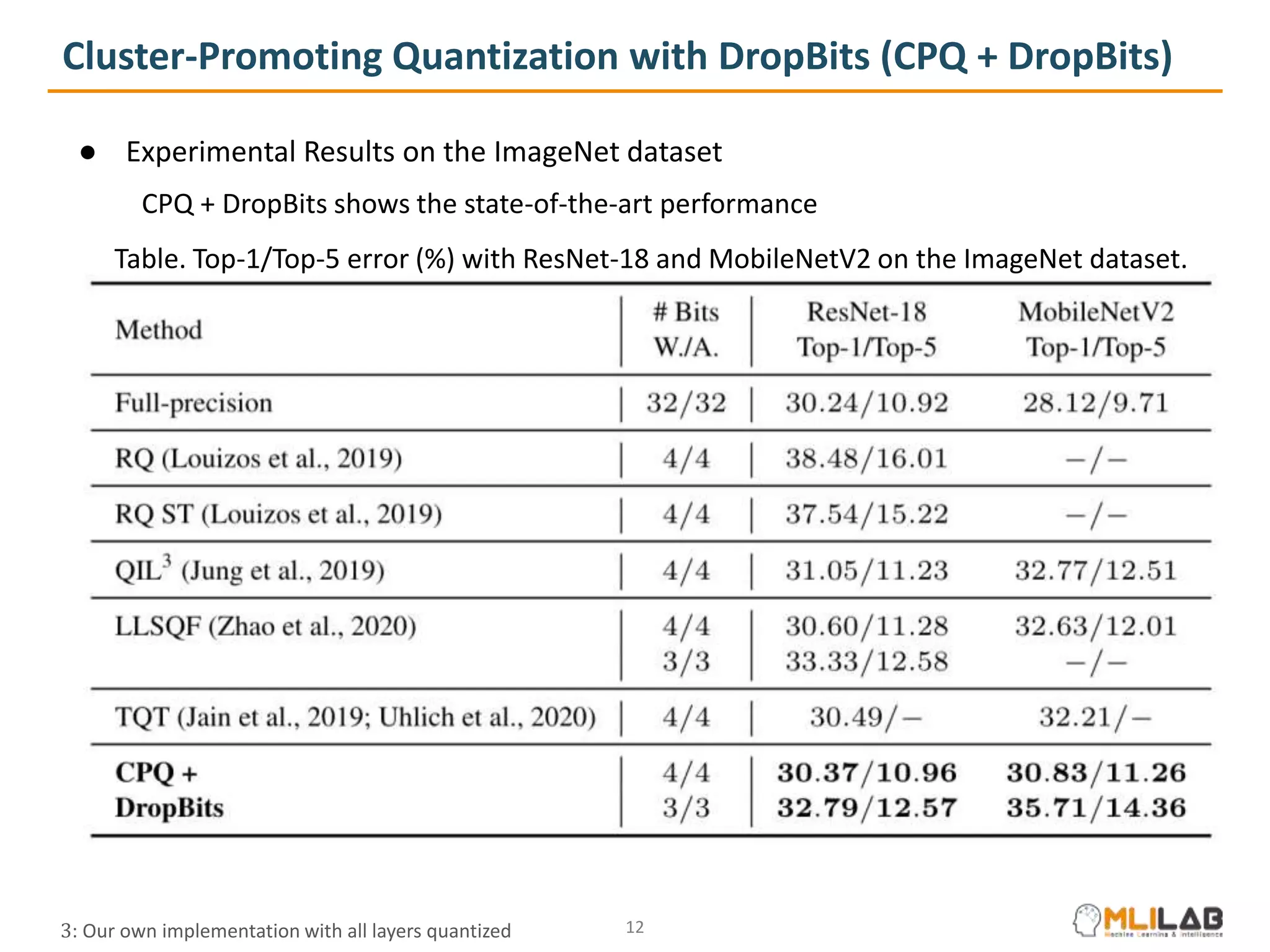
The document presents a novel method called cluster-promoting quantization (CPQ) aimed at reducing quantization loss in neural network models by clustering full-precision weights around optimal quantization grids. It introduces a bit-drop technique, 'dropbits', to mitigate biases in the multi-class straight-through estimator (STE) used in CPQ. Experimental results demonstrate that the combination of CPQ and dropbits achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ImageNet dataset for models like ResNet-18 and MobileNetV2.