The document summarizes the history, manufacturing process, and economic potential of Disprin tablets. It discusses how Bayer patented aspirin in 1899 and how it became the most common drug for pain, fever, and inflammation. It then describes the manufacturing process for hard Disprin tablets, which involves weighing ingredients, mixing, drying, compressing into tablets, testing, and packaging. Finally, it provides an economic analysis of Disprin, listing the chemicals used, their costs per kilogram, and calculating the total cost of production and potential sales price at $111.18 per kilogram of Disprin tablets.



![Manufacturing process
Aspirin tablets are manufactured in different shapes. Their weight, size, thickness, and
hardness may vary depending on the amount of the dosage. The upper and lower surfaces of
the tablets may be flat, round, concave, or convex to various degrees. The tablets may also
have a line scored down the middle of the outer surface, so the tablets can be broken in half, if
desired.
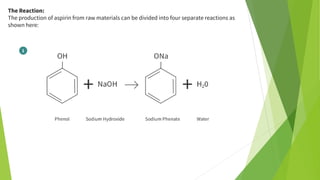
Raw material
❖ Phenol C6H5-OH
❖ Sodium Hydroxide [NaOH]
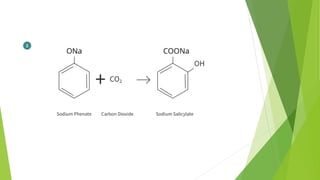
❖ Carbon Dioxide [CO2
❖ Acetic Anhydride [CH3COOCOCH3
❖ Hydrogen
The procedure for manufacturing hard aspirin tablets, is known as dry-granulation or slugging.
It involves following steps.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpdpresentationpdf-220919102529-87a198bf/85/CPD-presentation-pdf-pdf-4-320.jpg)




![Economic potential:
Chemicals [kg/kg] used in Disprin Cost [$/kg ]
Silicyclic acid 0.138 60
Acetic anhydride 0.102 1000
Corban dioxide 0.009 100
Purchase Sales
0.138*60 8.28
0.102*1000 102
0.009*100
Balance
0.9
111.18/kg Disprin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpdpresentationpdf-220919102529-87a198bf/85/CPD-presentation-pdf-pdf-11-320.jpg)

