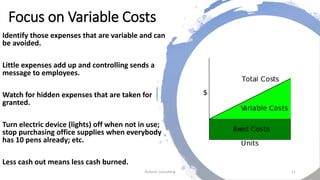
This document provides tips for entrepreneurial companies during an economic slowdown. It recommends preparing detailed short-term forecasts, strengthening the balance sheet by improving financial ratios and having more cash, cutting costs and reducing burn rates, focusing on revenue generation and variable costs, shifting to equity-based compensation, slowing down payables and accelerating receivables, turning inventories, and exploring funding alternatives. Maintaining strong financial management is key to weathering an economic downturn.