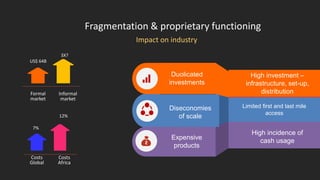
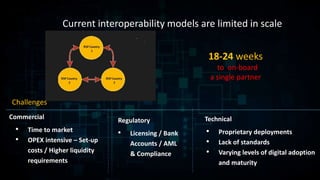
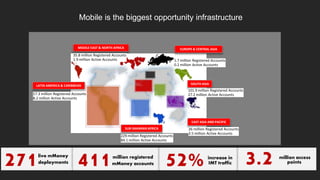
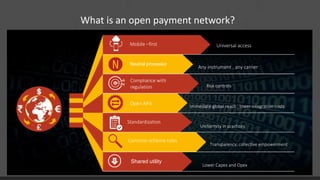
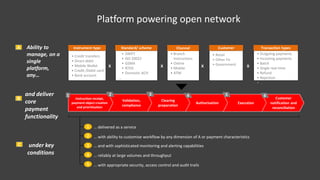
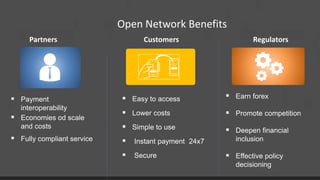
TerraPay proposes an open payment network to address fragmentation across payment platforms and providers. Currently there is a proliferation of providers like banks, mobile operators, and payment companies, but lack of interoperability. This causes high costs, access issues, and duplicated investments. An open network would use common standards and rules to allow any instrument or carrier to process transactions through a single platform. This would provide universal access, lower costs through economies of scale, and benefits for partners, customers, and regulators through increased competition, financial inclusion, and effective policy-making. TerraPay asks for regulatory support to promote market-wide interoperability and an open, collaborative approach.