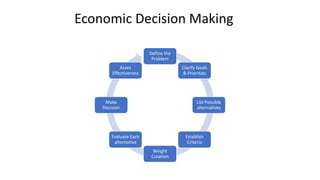
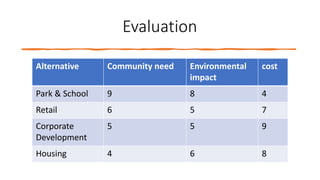
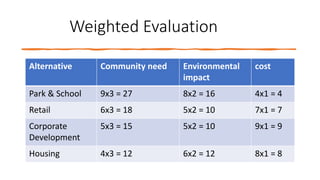
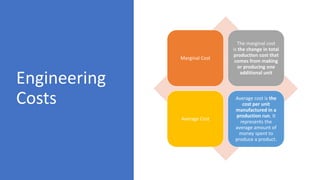
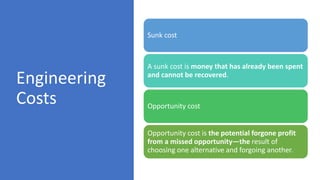
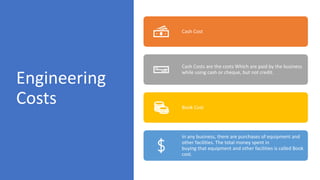
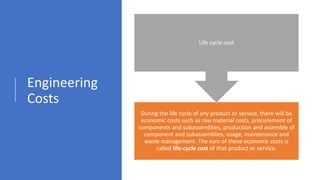
The document provides an overview of economic decision-making within engineering, including various types of engineering costs such as fixed, variable, sunk, and opportunity costs. It outlines a decision-making process using a case study from Dholakpur, evaluating alternatives based on community needs, environmental impact, and costs. Additionally, it details methods for engineering cost estimation, emphasizing accuracy and the importance of models like the segmentation and power sizing models.