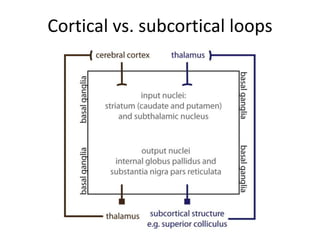
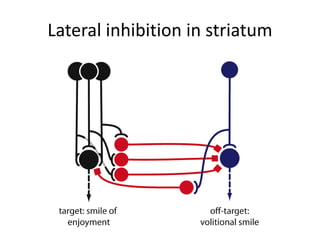
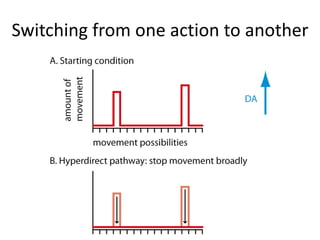
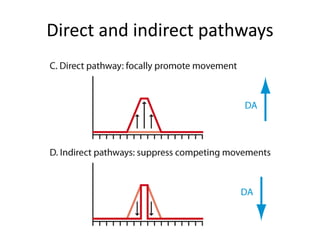
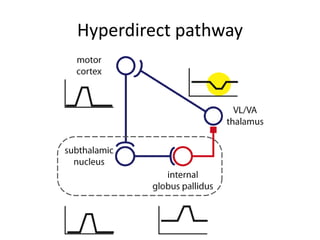
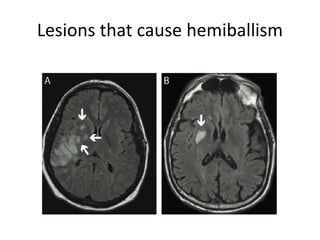
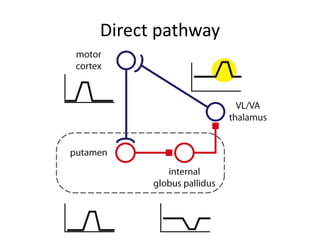
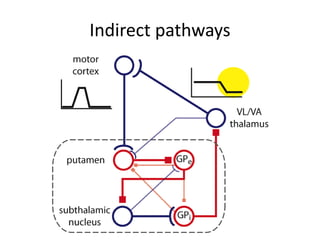
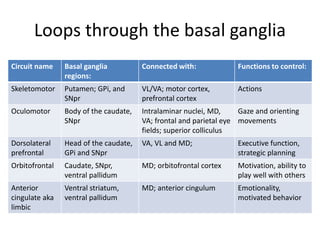
The document discusses the basal ganglia circuitry which controls different functions through connections between basal ganglia regions and other areas of the brain. It specifically mentions cortical vs subcortical loops, direct and indirect pathways within the basal ganglia, and lesions that can cause hemiballism. The basal ganglia circuits connect motor, oculomotor, dorsolateral prefrontal, orbitofrontal, and anterior cingulate regions to control actions, gaze, executive function, motivation, and emotionality.