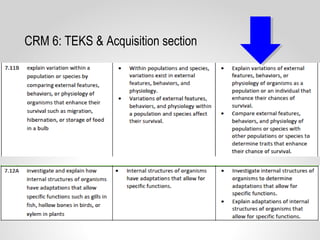
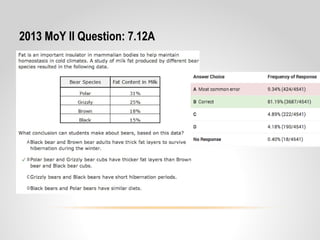
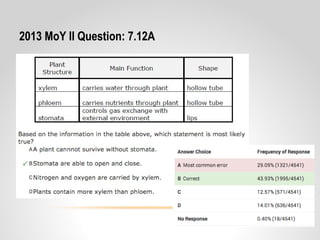
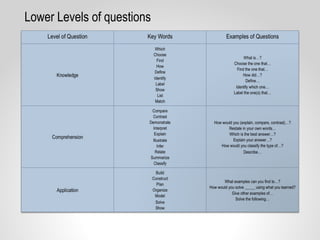
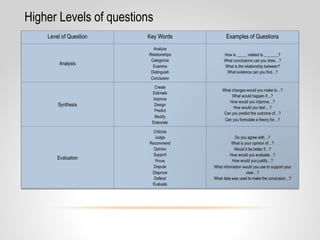
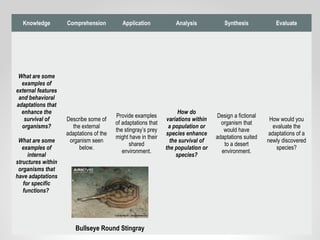
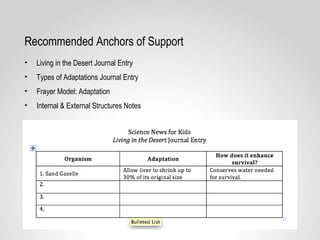
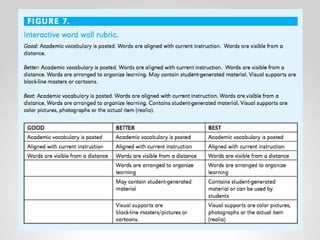
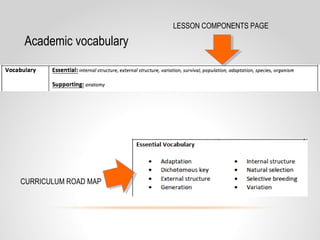
This document provides resources and guidance for teaching a unit on internal and external structures in 7th grade science. It includes the relevant state standards, a pacing guide, lesson plan components, activities, and strategies for differentiation and assessment. The key objectives are for students to explain how variations within populations enhance survival, and to investigate and explain how internal structures allow specific functions in organisms.