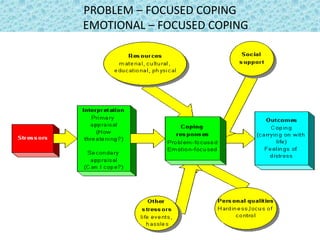
Loss is a universal human experience that can occur throughout life. There are several types of loss, including maturational loss resulting from normal life transitions, situational loss from sudden external events, and personal loss requiring adaptation through grieving. Coping with loss involves both problem-focused strategies aimed at modifying the stressor's source, and emotion-focused strategies aimed at managing the emotional impact, such as meditation, biofeedback, relaxation techniques, spiritual practices, humor, and developing new skills. Effectively coping with loss is important for reducing anxiety, depression, and health problems.